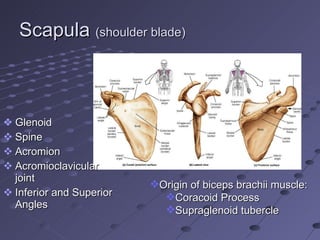
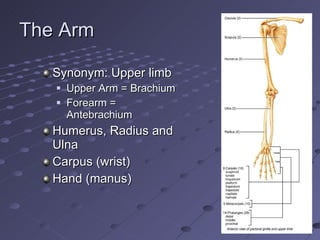
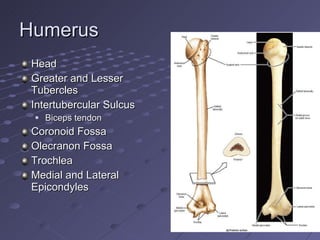
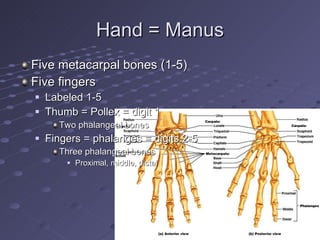
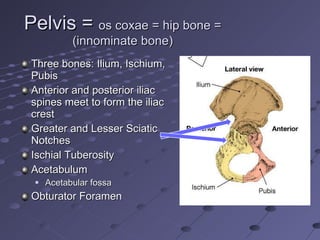
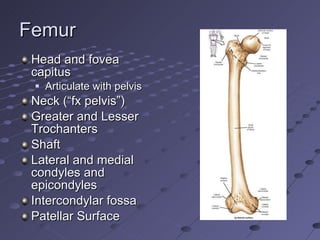
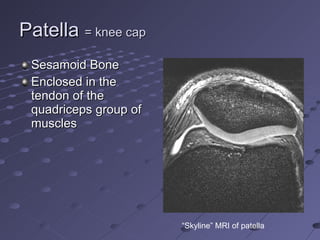
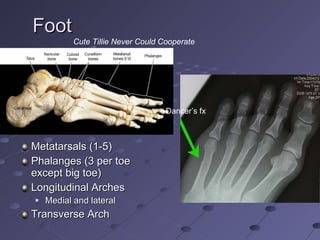
The document summarizes the bones that make up the appendicular skeleton, which includes the pelvis and limbs. It describes the bones that make up the pectoral girdle (shoulder), pelvic girdle, upper limb (arm), lower limb (leg), wrist, hand, and foot. Key bones discussed include the clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula, and bones of the feet. It also briefly discusses common fractures.