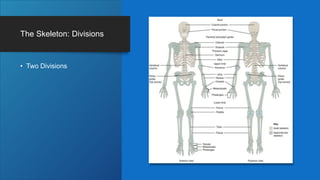
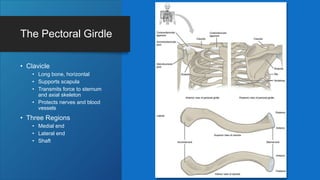
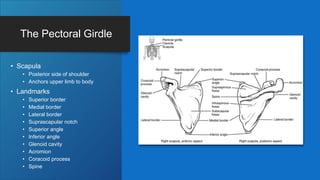
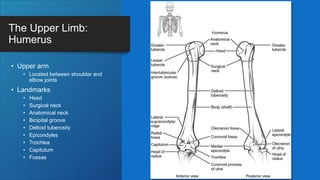
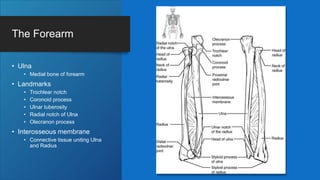
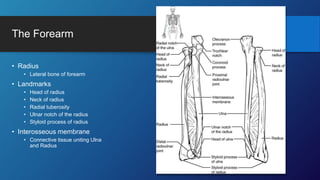
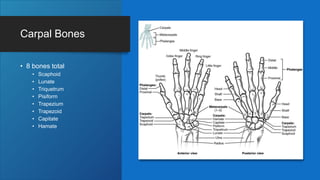
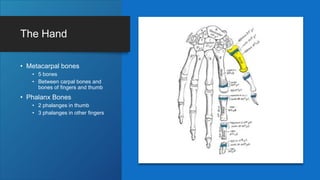
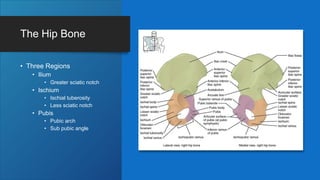
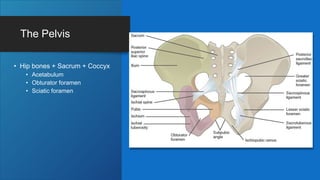
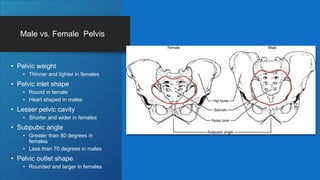
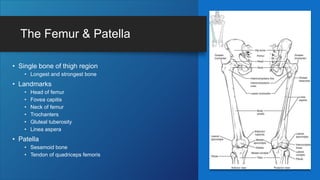
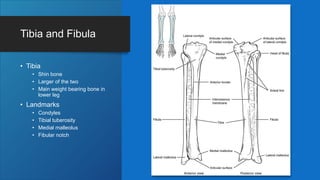
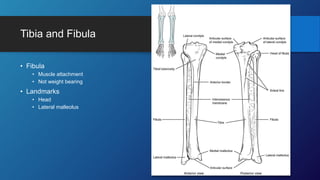
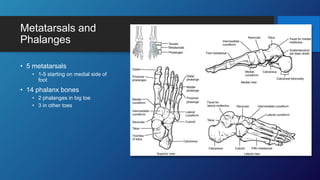
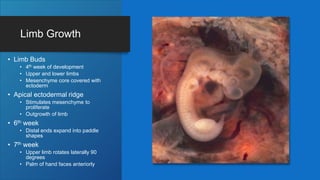
The document describes the bones that make up the appendicular skeleton. It discusses the pectoral girdle including the clavicle and scapula, and their functions. It then describes the bones of the upper limb including the humerus, ulna, radius, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. Next it covers the pelvic girdle and pelvis bones. It then discusses the bones of the lower limb including the femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges. Finally, it summarizes the development of the limb buds and ossification of bones.