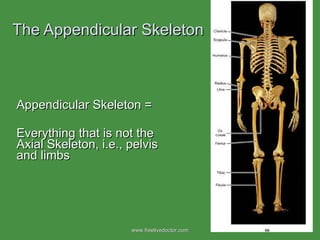
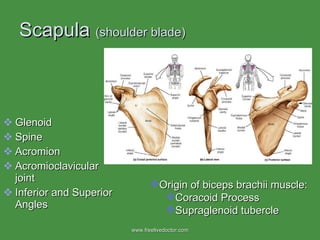
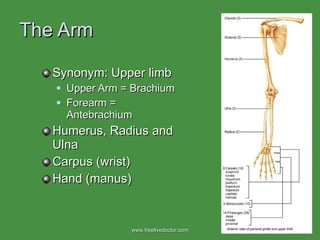
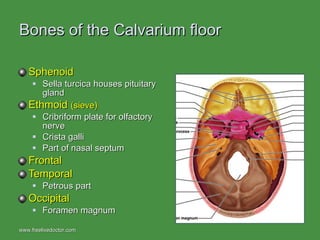
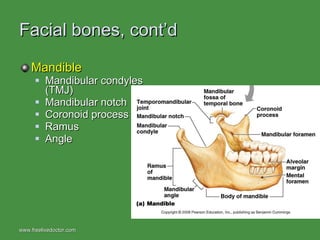
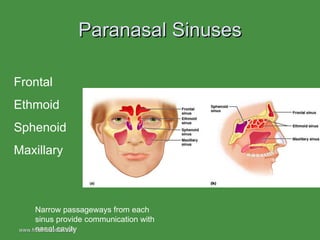
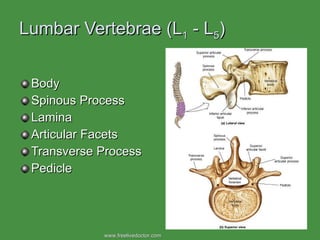
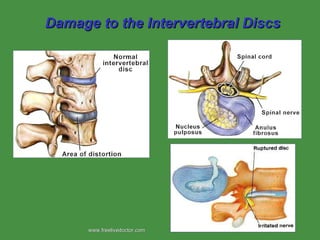
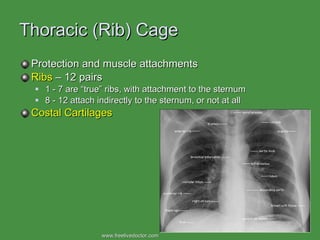
The document summarizes the major bones that make up the appendicular and axial skeleton. It describes the bones of the upper limb (shoulder blade, arm bones, wrist, hand), lower limb (thigh bone, shin bones, ankle, foot), pelvis, skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage. It provides details on the structures and landmarks of each bone.