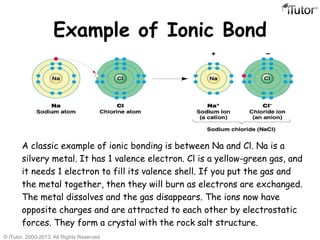
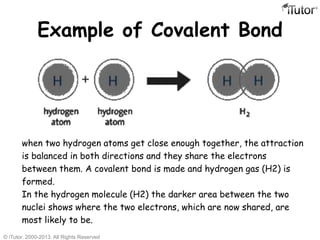
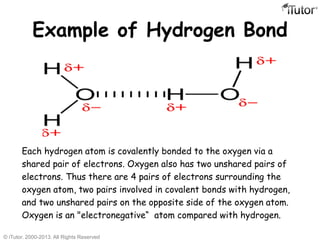
There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals, resulting in oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two atoms. Hydrogen bonds are attractive forces between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, like oxygen or nitrogen, and another electronegative atom.