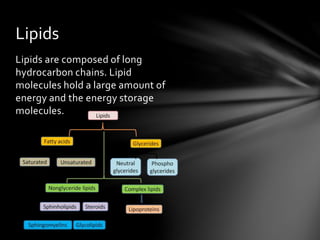
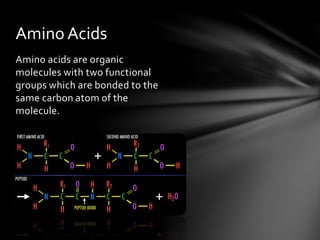
Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. There are four main classes of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids all have different structures and functions within the body. Carbohydrates provide energy and support various systems, proteins have a variety of roles including structure and defense, and lipids store energy and are composed of hydrocarbon chains.