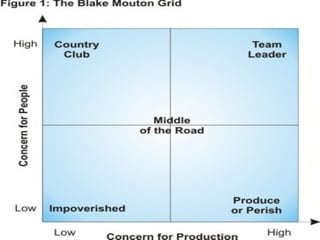
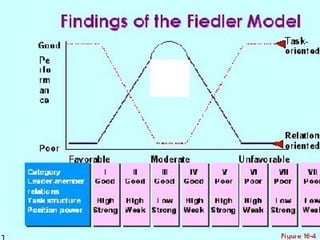
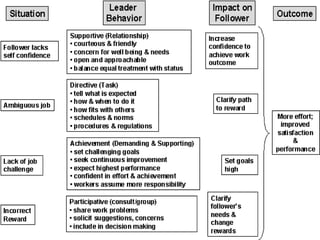
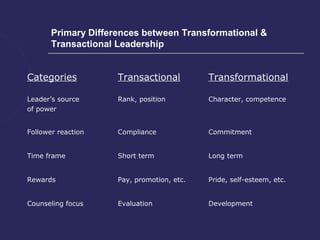
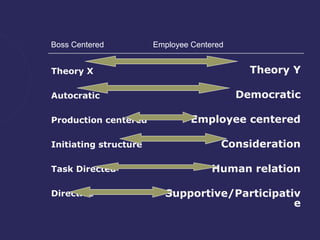
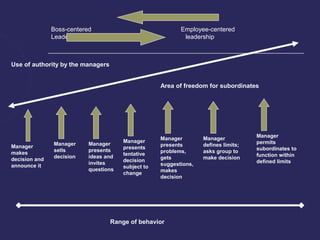
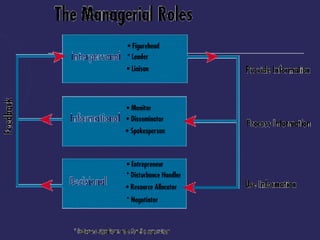
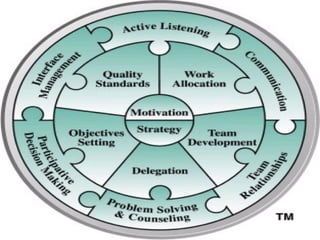
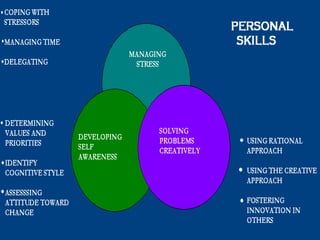
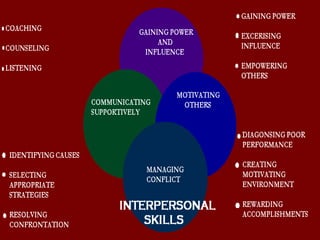
The document discusses various theories of leadership that have developed over time. It begins with trait theories from the 1940s-1960s that focused on identifying innate qualities of leaders. Then it shifts to behavioral theories from the 1960s that examined specific leader behaviors. More recently, contingency and modern theories take into account situational factors and how leaders adapt their style based on the environment. The document provides an overview of several prominent leadership theories such as Fiedler's contingency model, path-goal theory, transformational leadership, and discusses differences between leadership styles like autocratic versus democratic approaches.