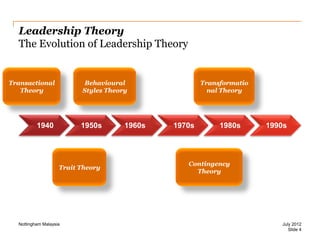
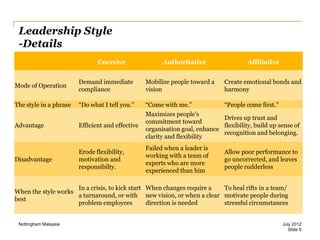
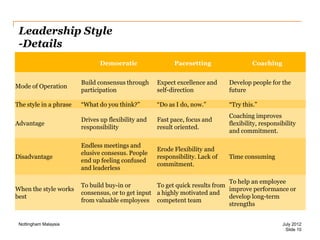
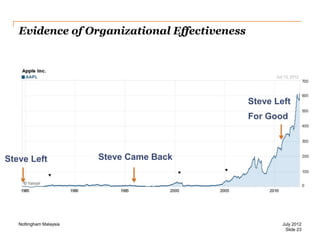
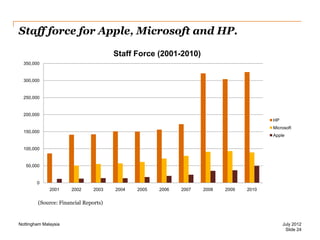
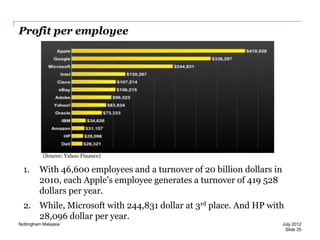
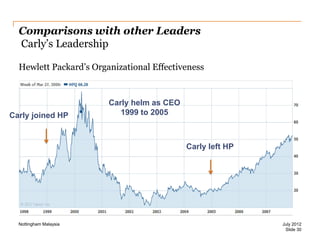
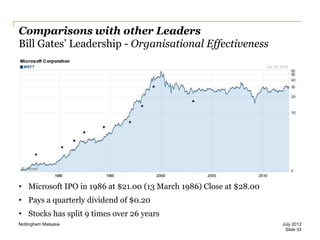
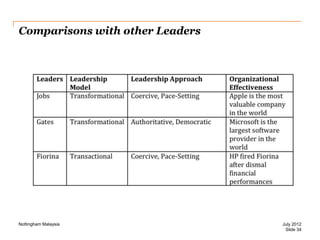
The document discusses leadership style and organizational effectiveness. It begins with an introduction on leadership and provides definitions of leadership. It then covers various leadership theories such as transformational, transactional, and contingency leadership theories. It also discusses six different leadership styles identified by research. The document uses Apple Inc. as a case study, providing a timeline of key events and analyzing Steve Jobs' transformational leadership style. It discusses the impact of Jobs' style on organizational behavior at the individual and group level. Finally, it explores the relationship between leadership, organizational climate, and organizational effectiveness.