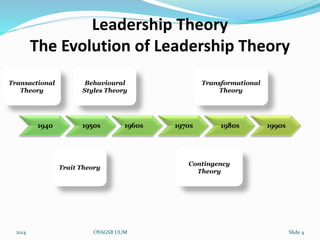
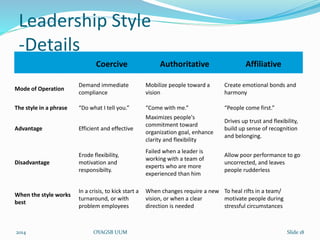
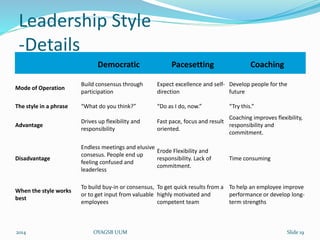
This document discusses leadership styles and organizational effectiveness within Sony-Ericsson. It begins with definitions of leadership and an overview of different leadership theories. It then provides background on Sony and Ericsson's structures and cultures prior to forming a joint venture. The partnership combined Sony's consumer electronics expertise with Ericsson's telecom experience. The document evaluates the leadership decisions at the time and how they would affect current situations. It stresses the importance of addressing cultural gaps upfront and having clear, supported goals and strategies for organizational effectiveness and sustainability.