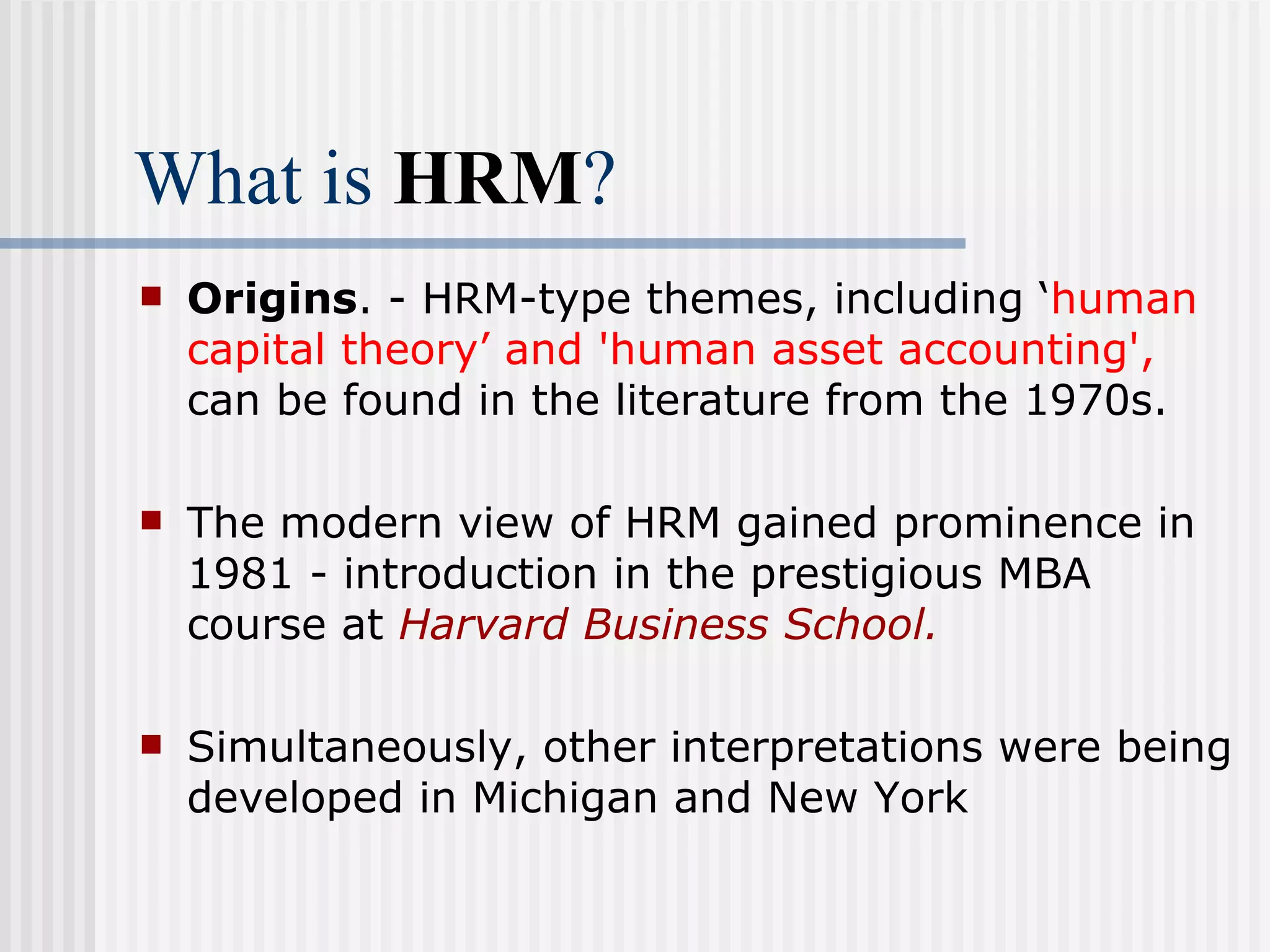
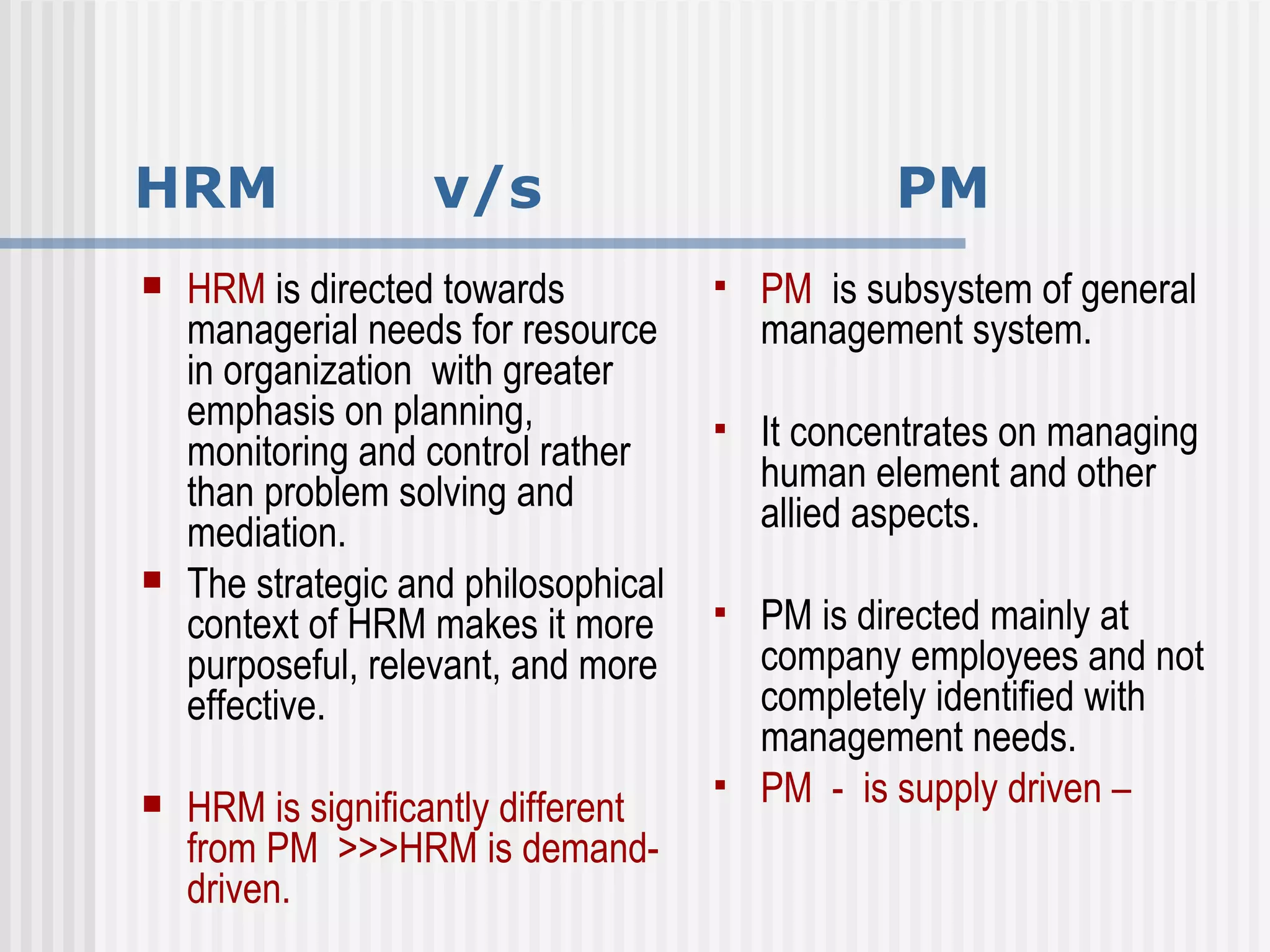
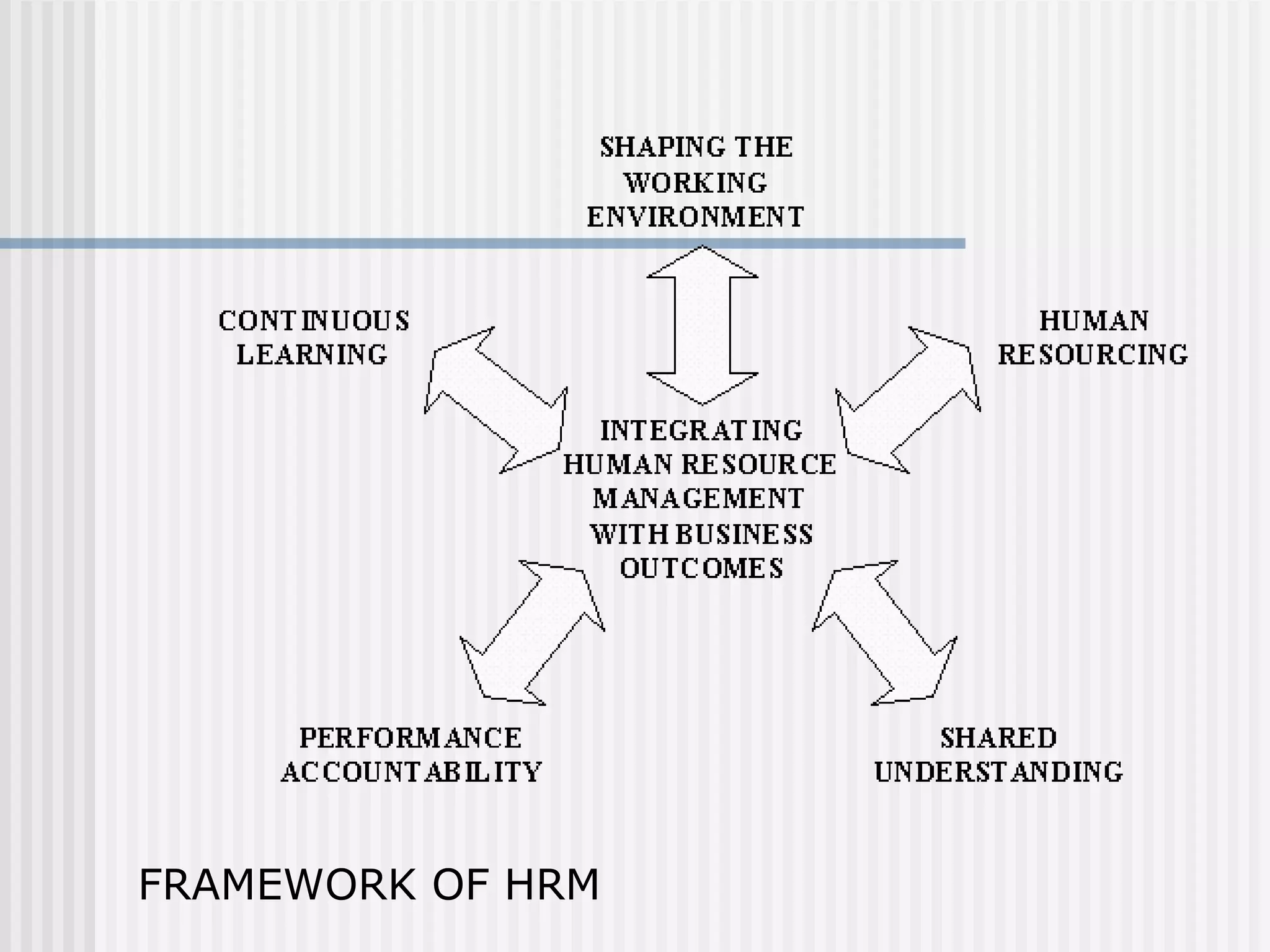
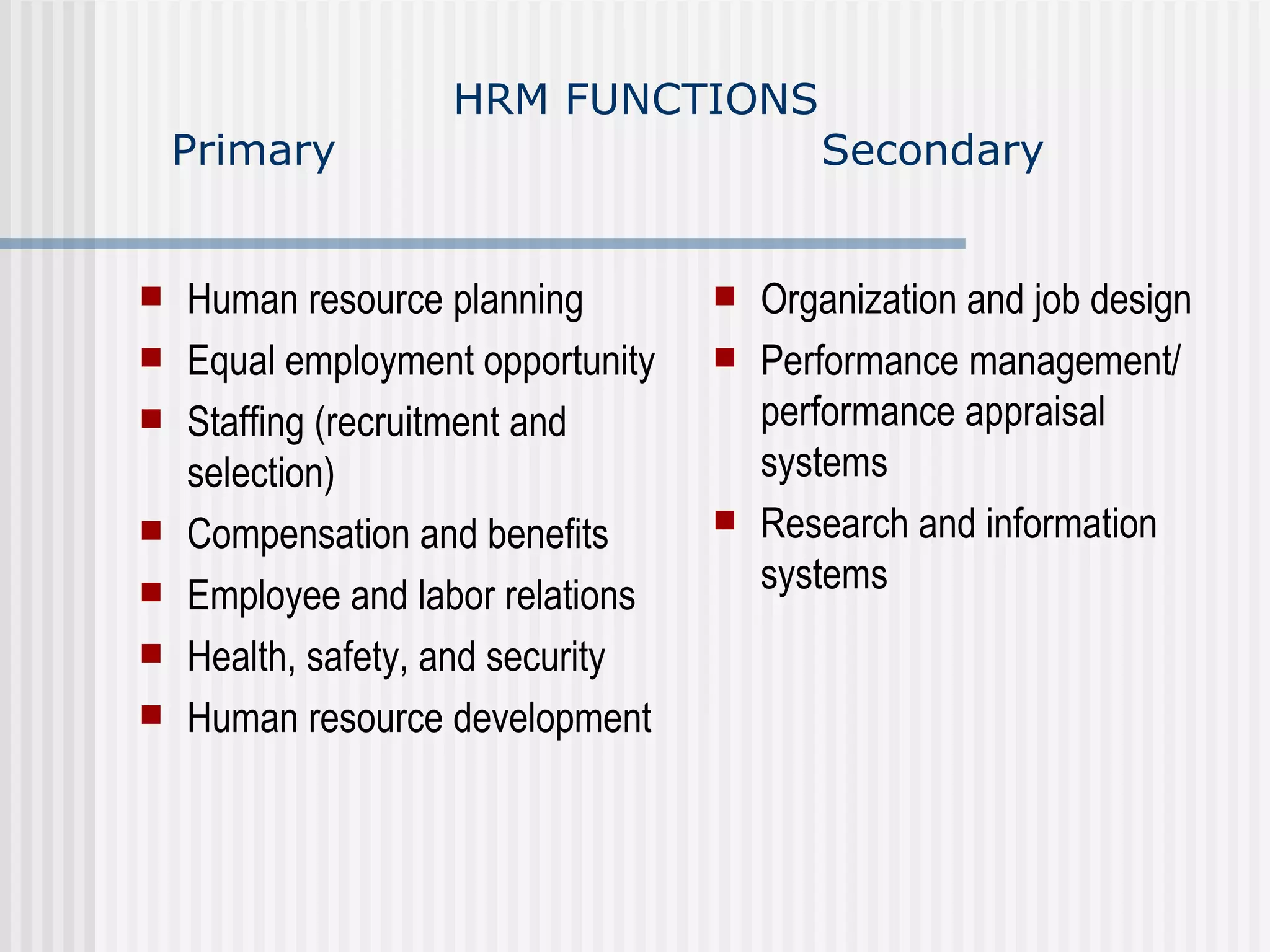
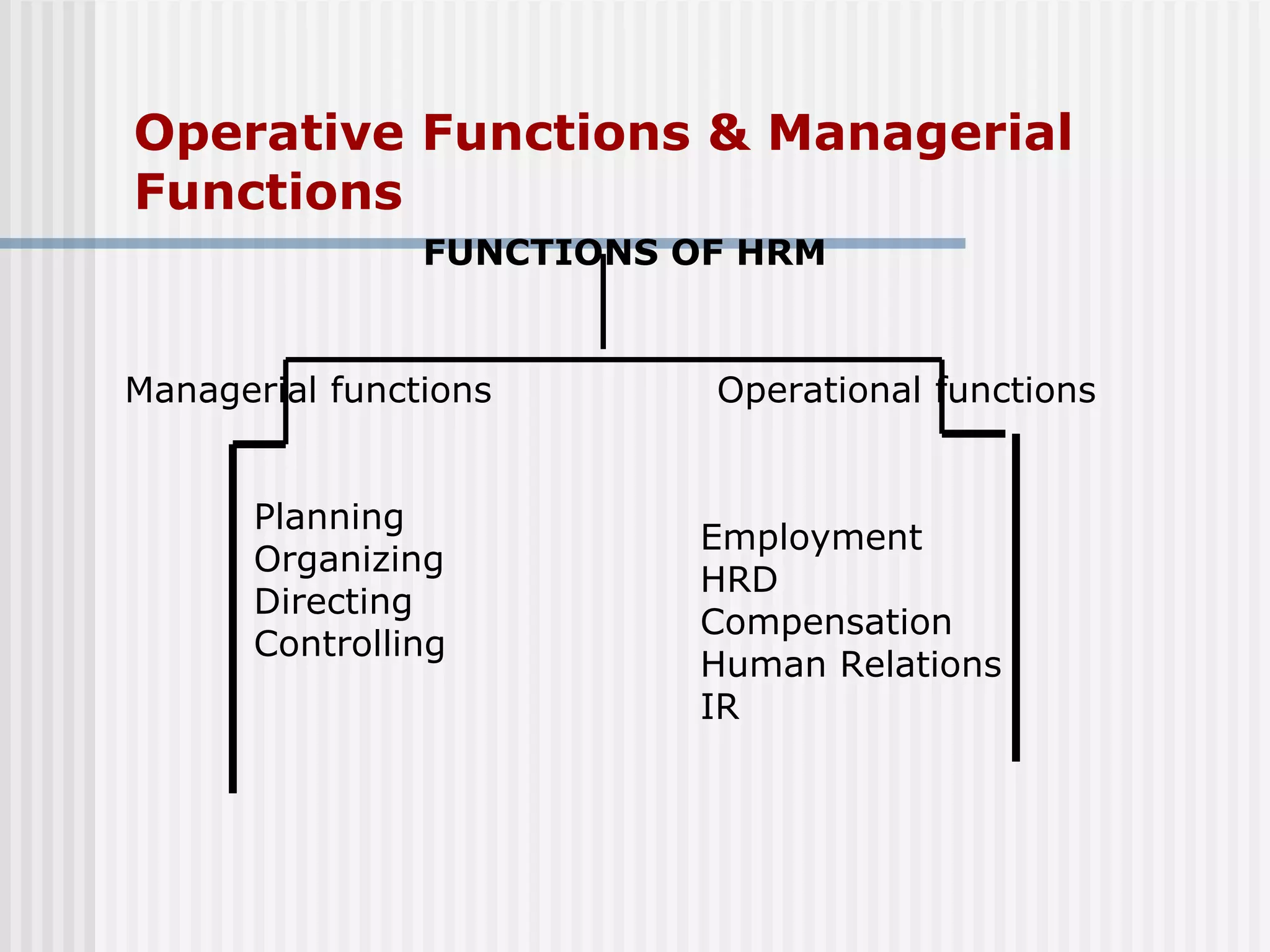
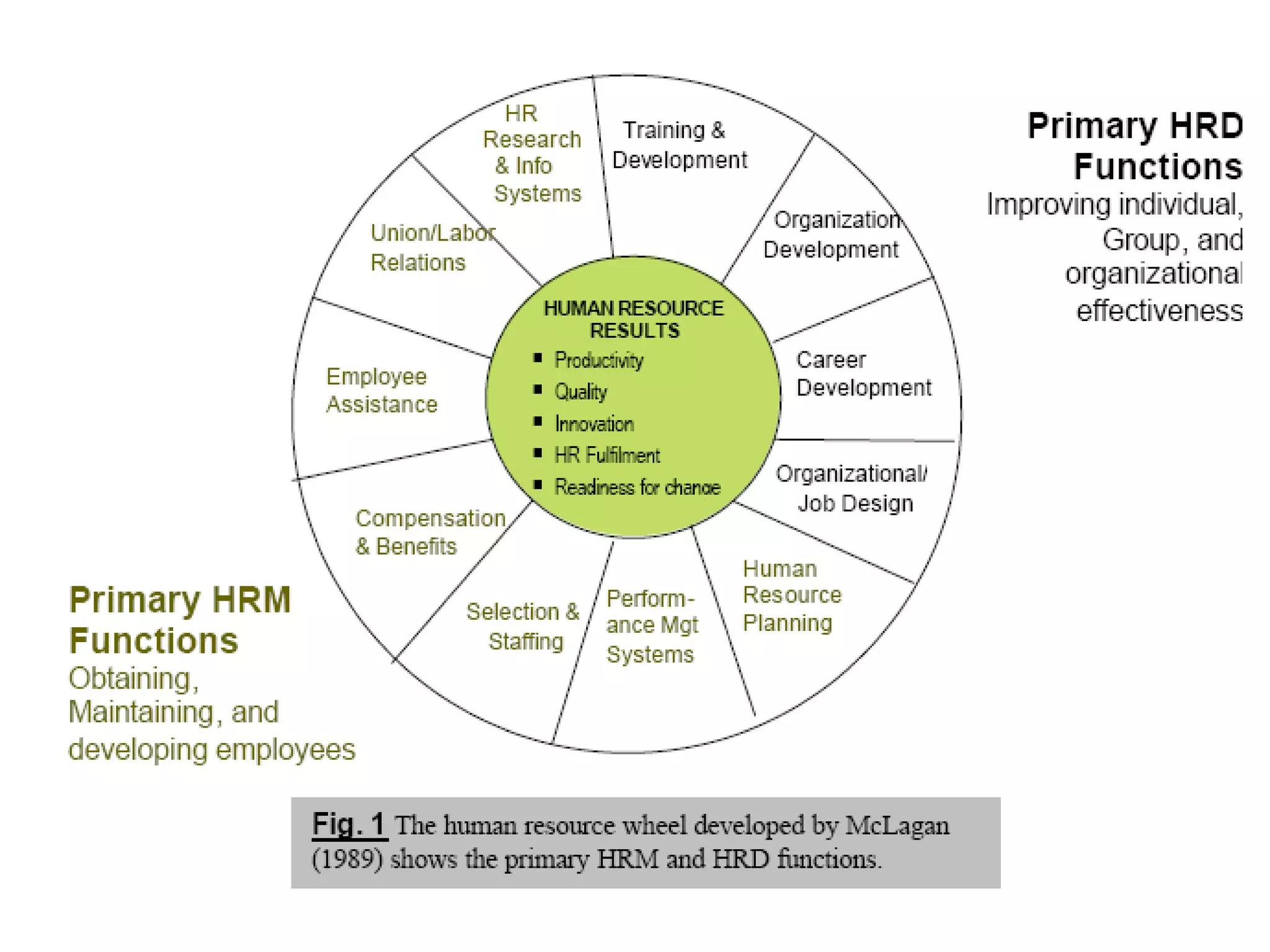
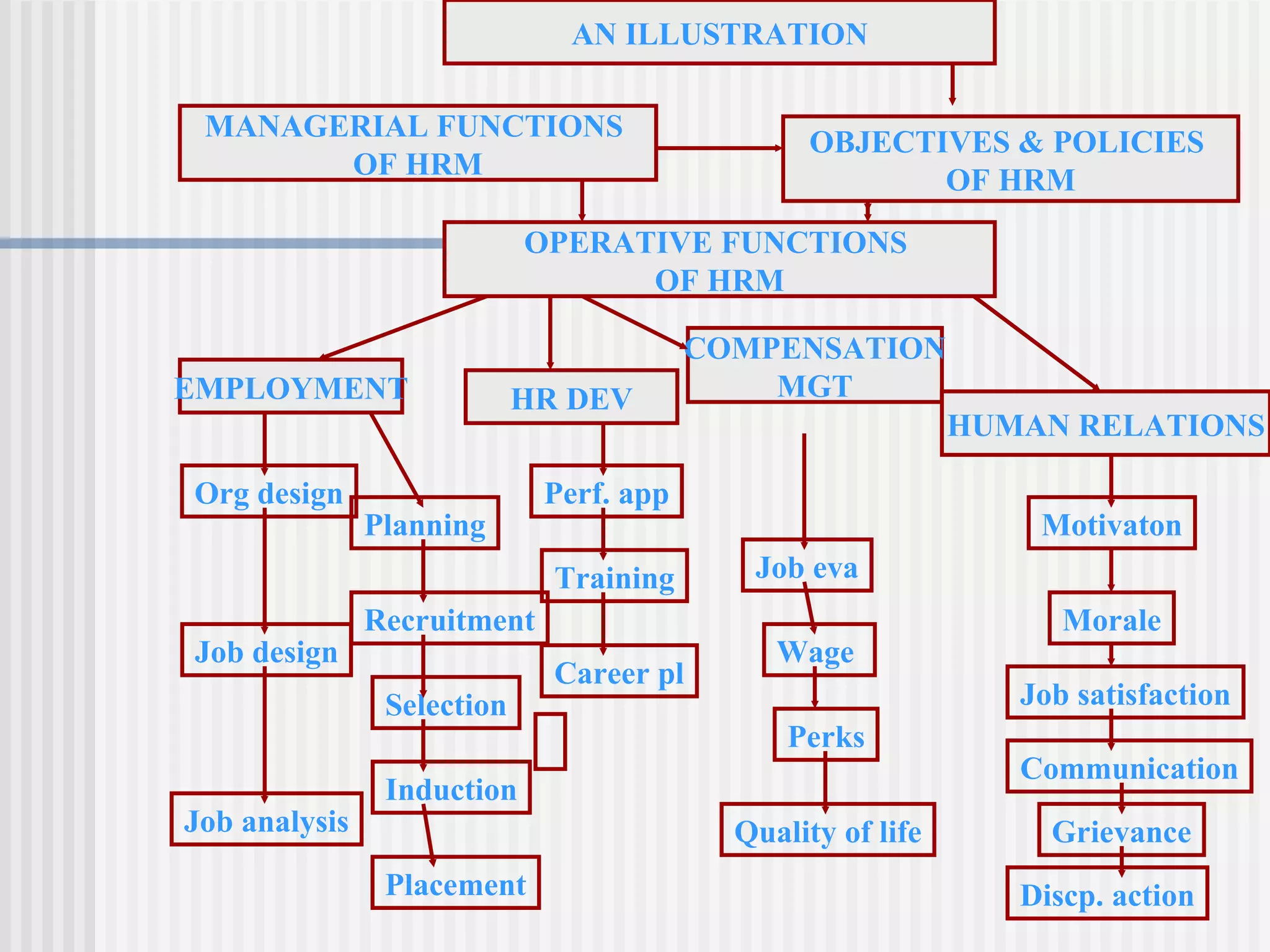
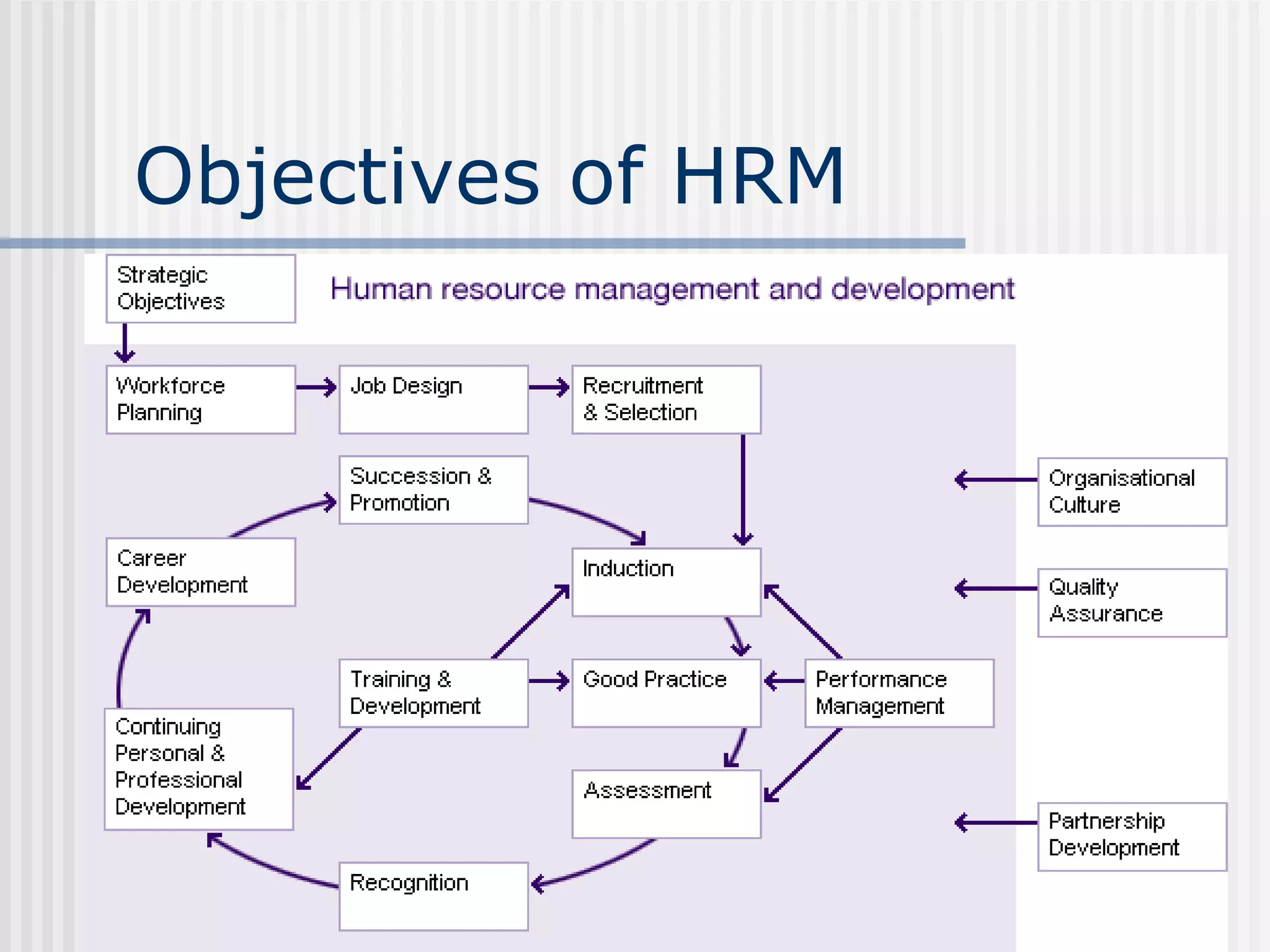
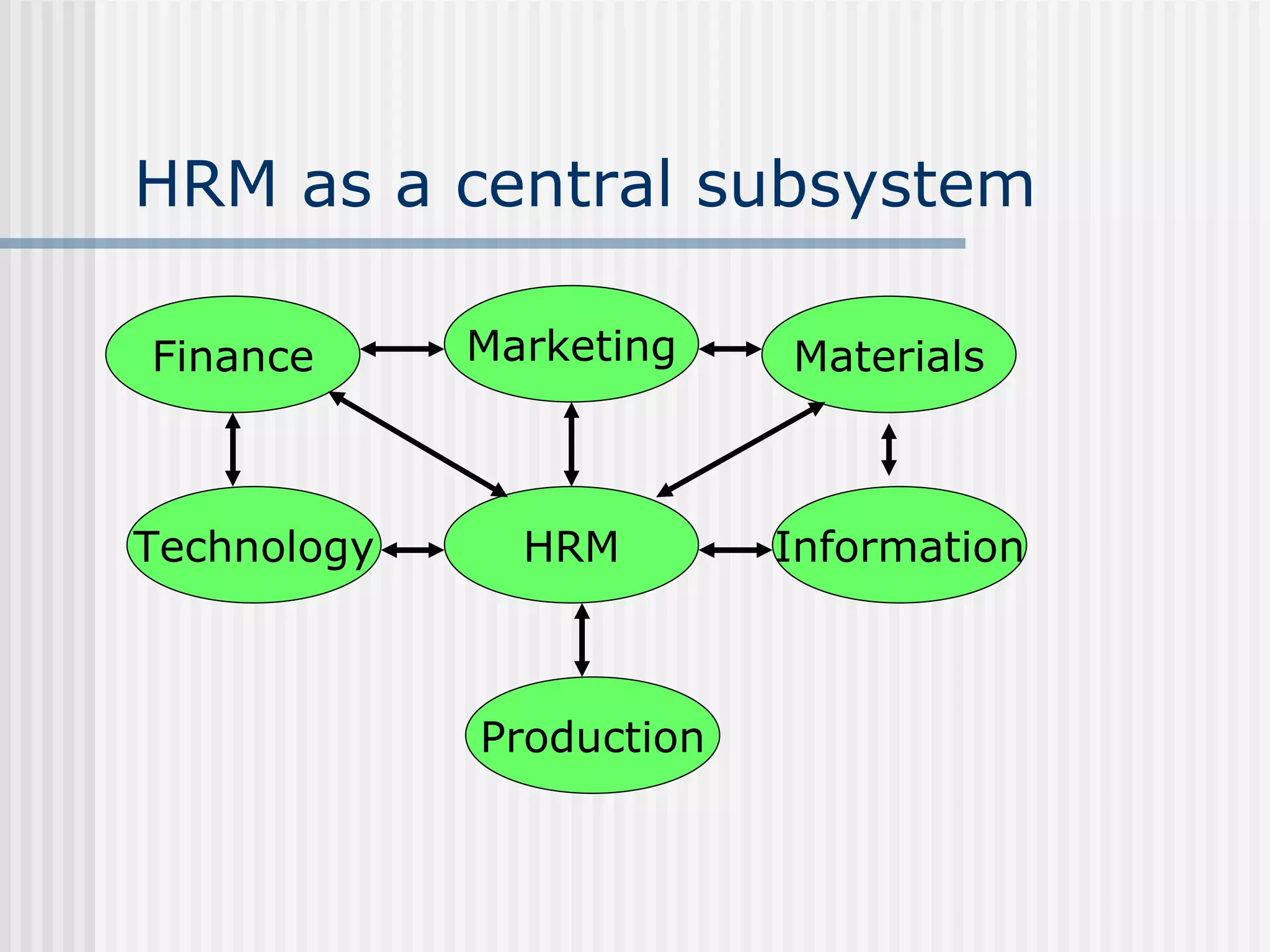
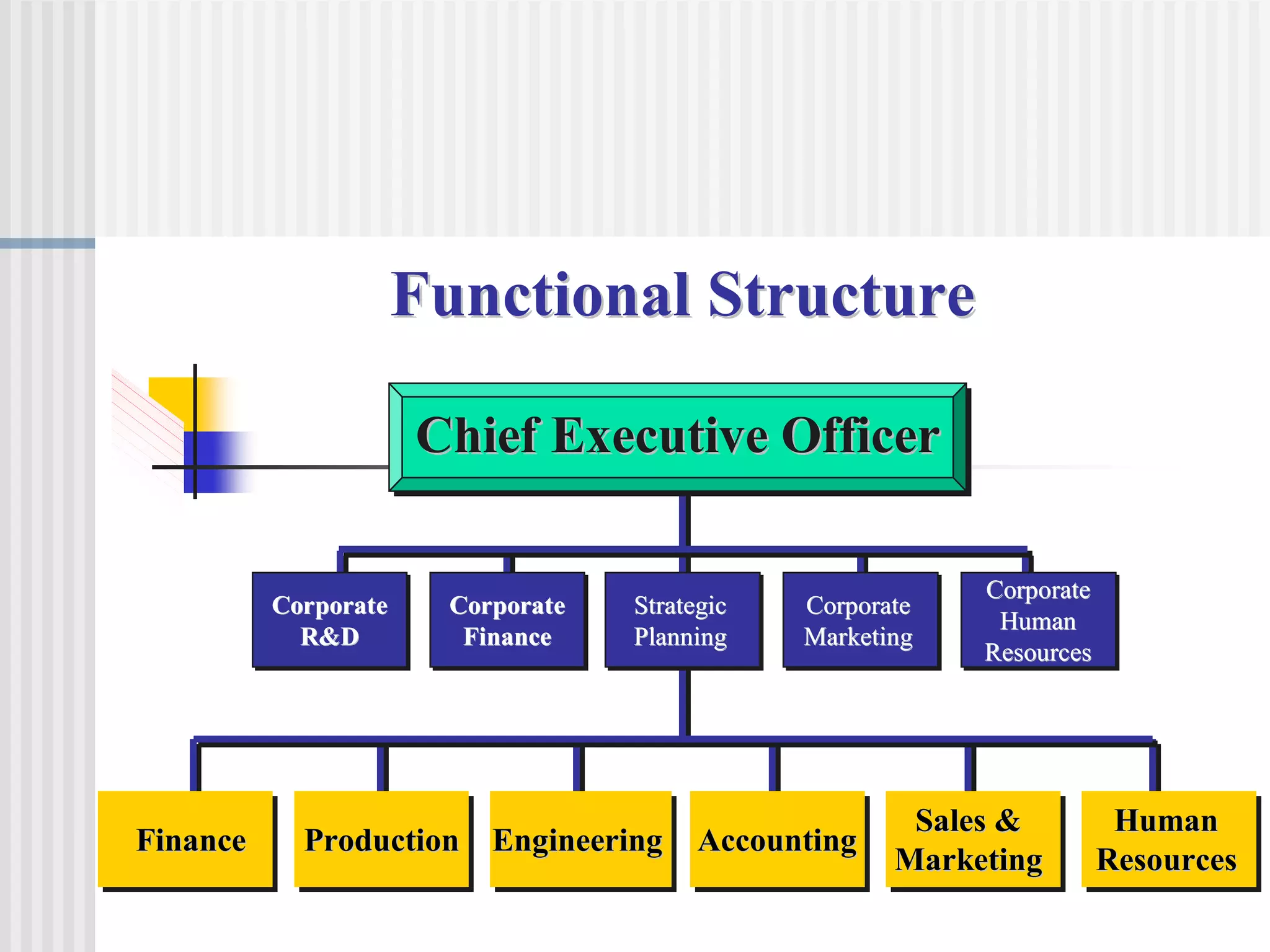
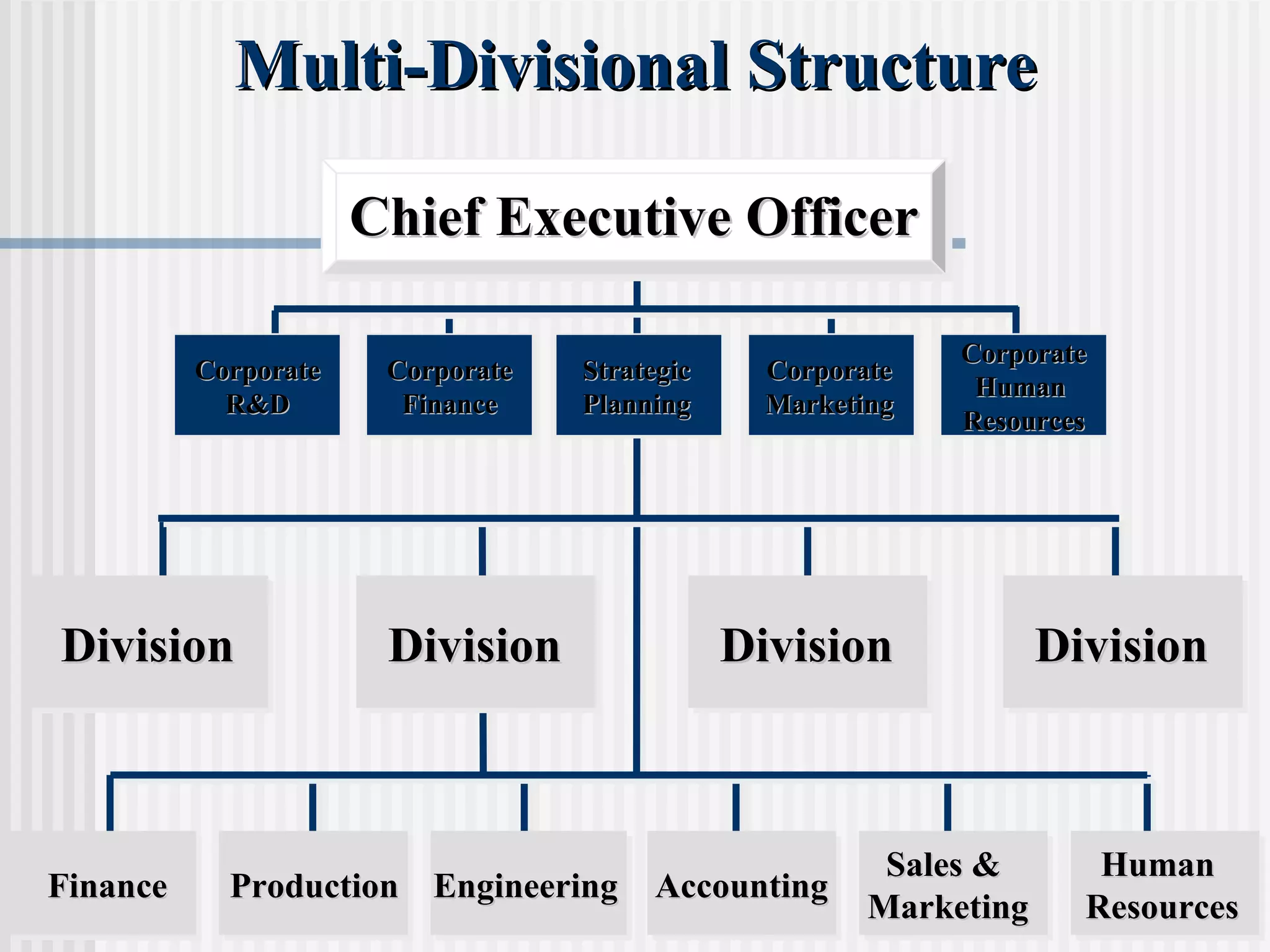
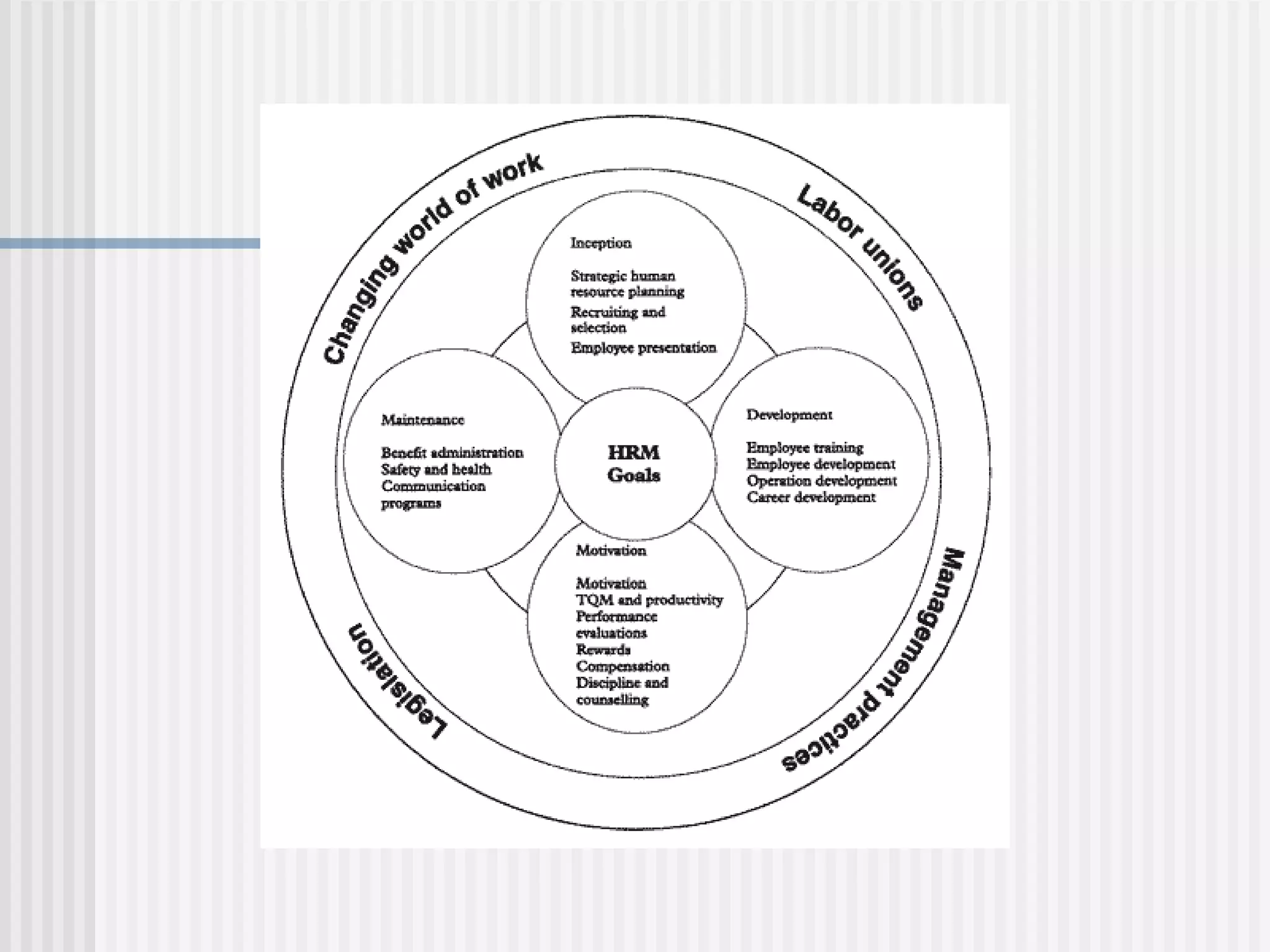
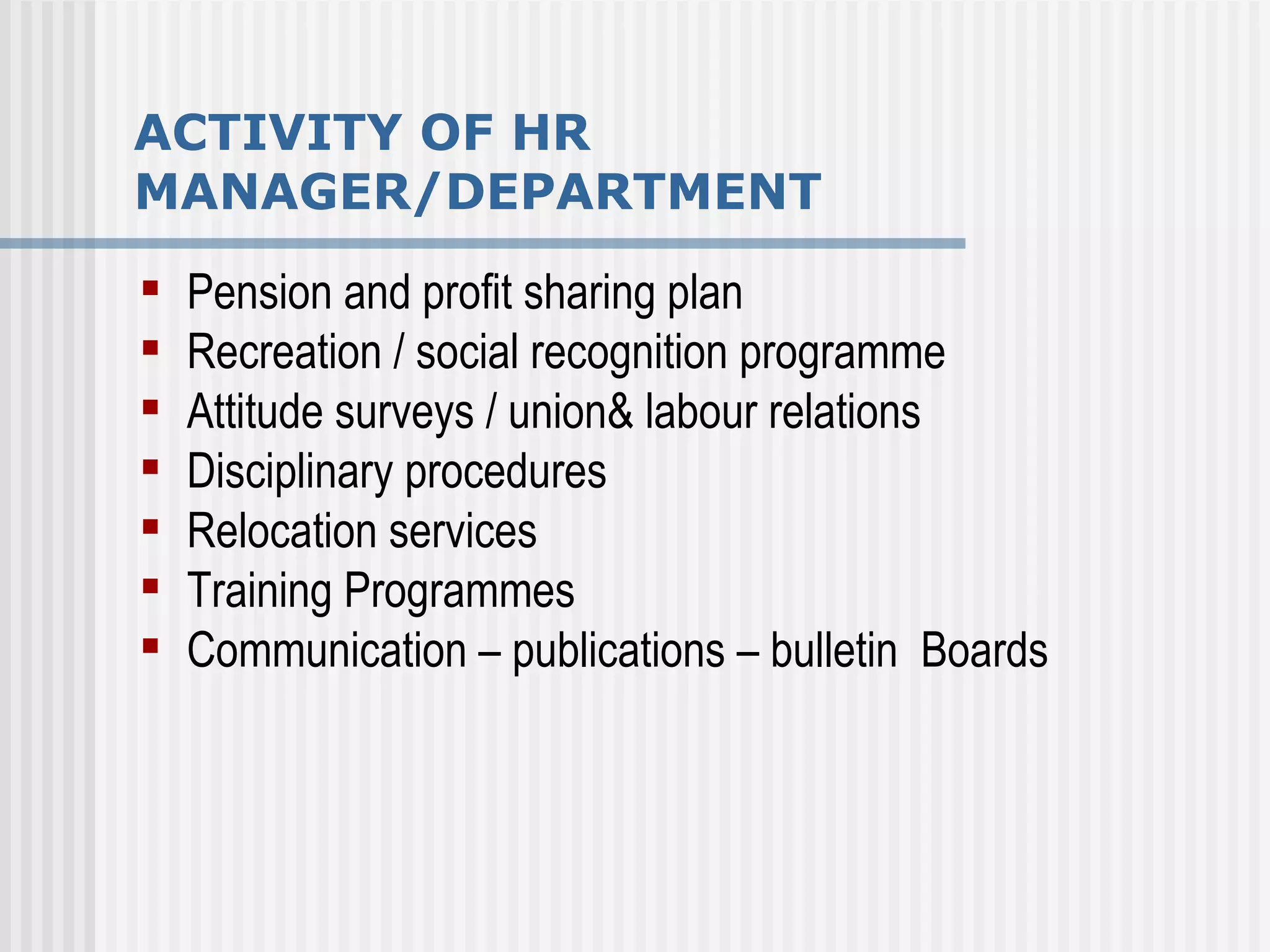
The document discusses the key concepts of human resource management (HRM) and personnel management (PM). It defines HRM as the effective use of human resources to achieve organizational goals and enhance performance. The history and evolution of HRM is outlined, moving from craft systems to scientific management to a human relations approach. The functions of HRM include recruitment, training, compensation and benefits administration, employee relations, and more. HRM is presented as strategic and goal-oriented while PM is more operational and problem-solving focused. The objectives of HRM policies, procedures and programs are to achieve organizational and individual goals through the effective management of human resources.