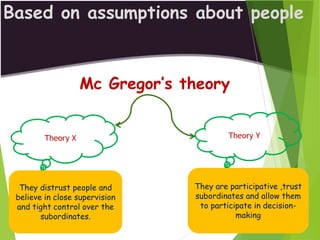
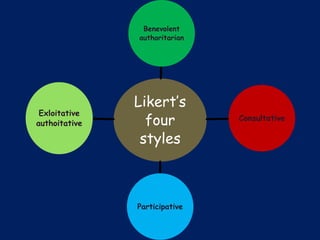
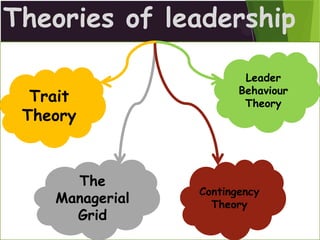
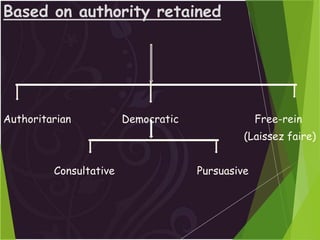
The document discusses leadership as the art of motivating groups towards common goals, emphasizing the distinction between leadership and management. It outlines different leadership styles—such as autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire—along with their impacts on decision-making and group dynamics. Additionally, it covers various leadership theories, including trait theory and contingency theory, highlighting the importance of traits and situational factors in effective leadership.







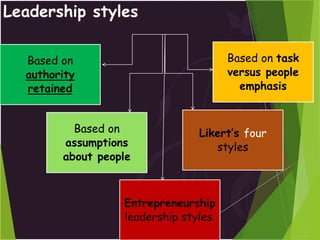



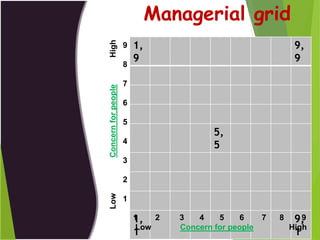
![Based on task versus people Emphasis
High relationship and low-
task
[ supporting style ]
High task and high relationship
[ participative style]
Low-task and low relationship
[ free rein style ]
High task and low relationship
[ autocratic style ]
Low High
LowHigh
Task Emphasis
PeopleEmphasis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leadershipfinal-120114122346-phpapp01-190929141312/85/Leadership-13-320.jpg)