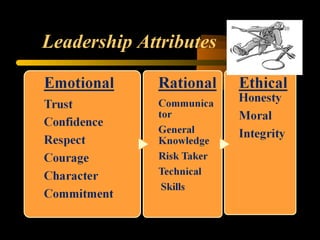
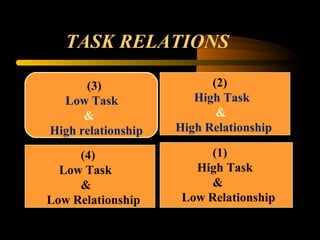
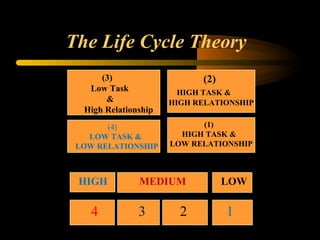
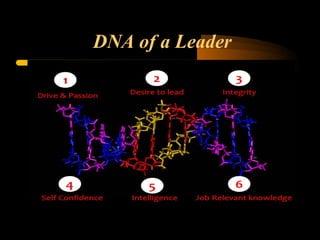
The document explores the concept of leadership, defining it as the ability to achieve exceptional results through ordinary individuals, and outlines the qualities and traits of effective leaders. It emphasizes the importance of communication, interpersonal skills, and adaptability in leadership styles according to situational needs. Additionally, it contrasts management and leadership, highlighting that successful leadership is crucial for overall organizational performance.