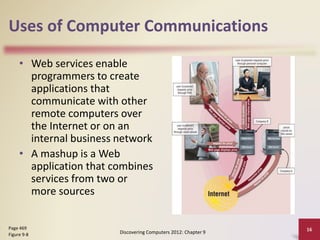
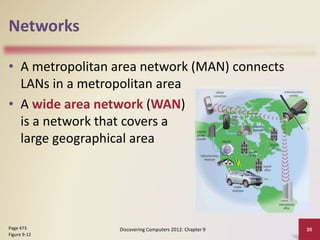
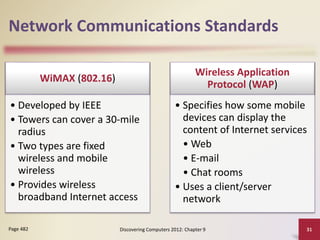
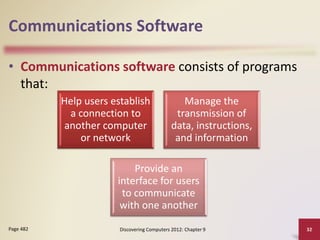
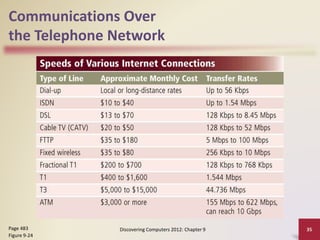
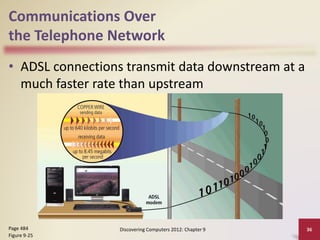
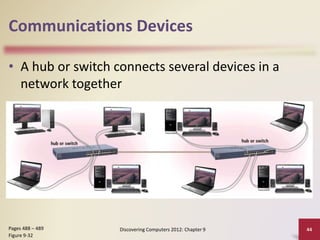
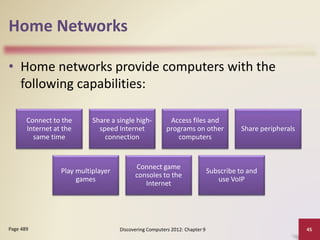
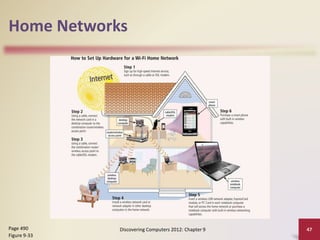
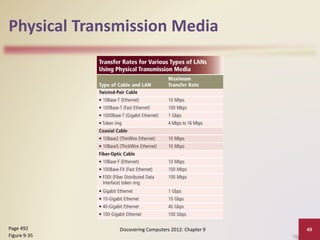
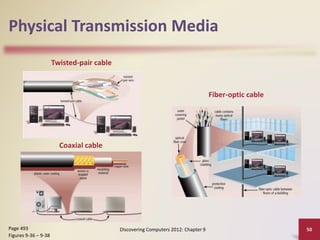
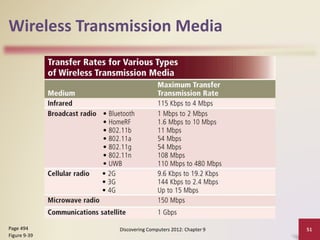
This document provides an overview of objectives and content covered in Chapter 9 of the textbook "Discovering Computers 2012". It discusses computer communications, uses of computer communications such as email and web browsing, advantages of networks, types of networks including LANs and WANs, network topologies, communication standards, setting up communications over telephone networks, communications devices, and setting up home networks. The chapter also covers topics like client/server networks, peer-to-peer networks, intranets and extranets. Diagrams and figures are included to illustrate key concepts.