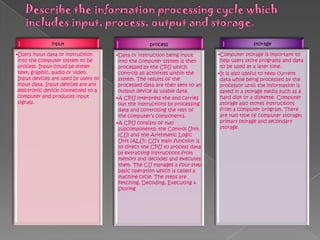
A computer system consists of four main hardware components: input devices that allow users to enter data, a processor that processes the data, storage devices that hold data and files for future use, and output devices that display processed data for users. A computer requires both hardware components like input/output devices and storage as well as software programs and an operating system to manage the processing and storage of data. An operating system controls basic computer operations like launching programs, allocating memory and storage, and providing a user interface between the computer and applications.