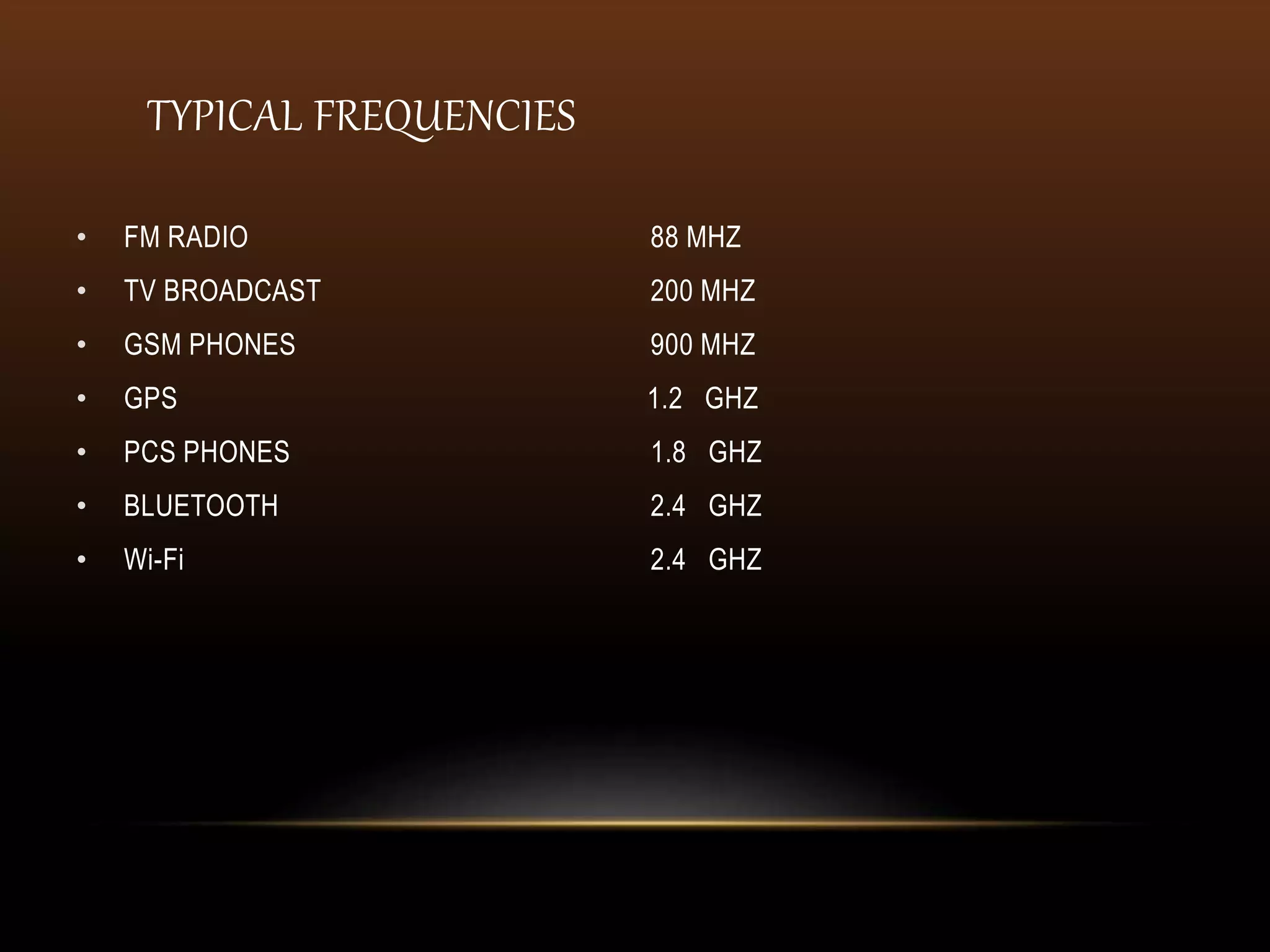
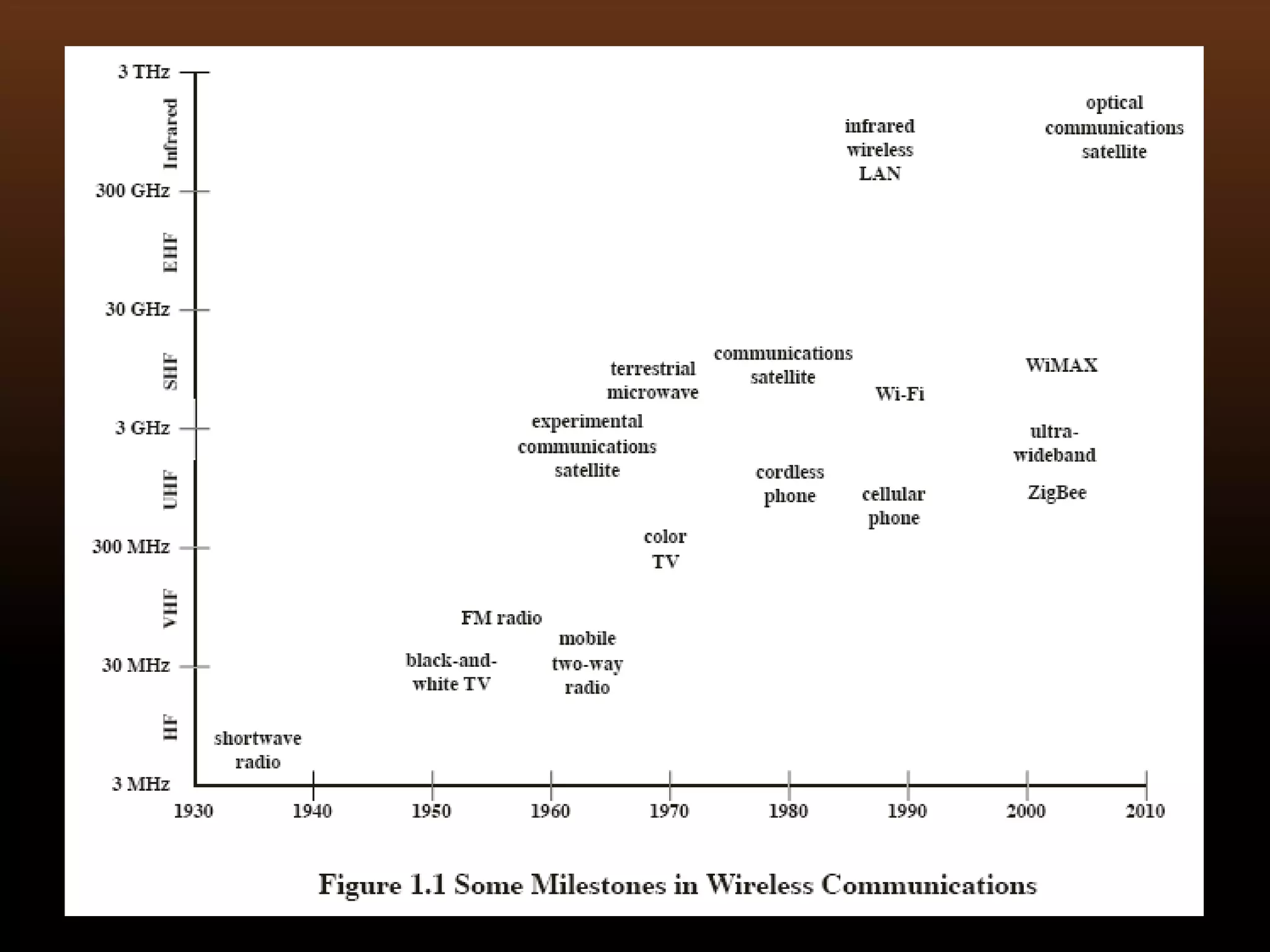
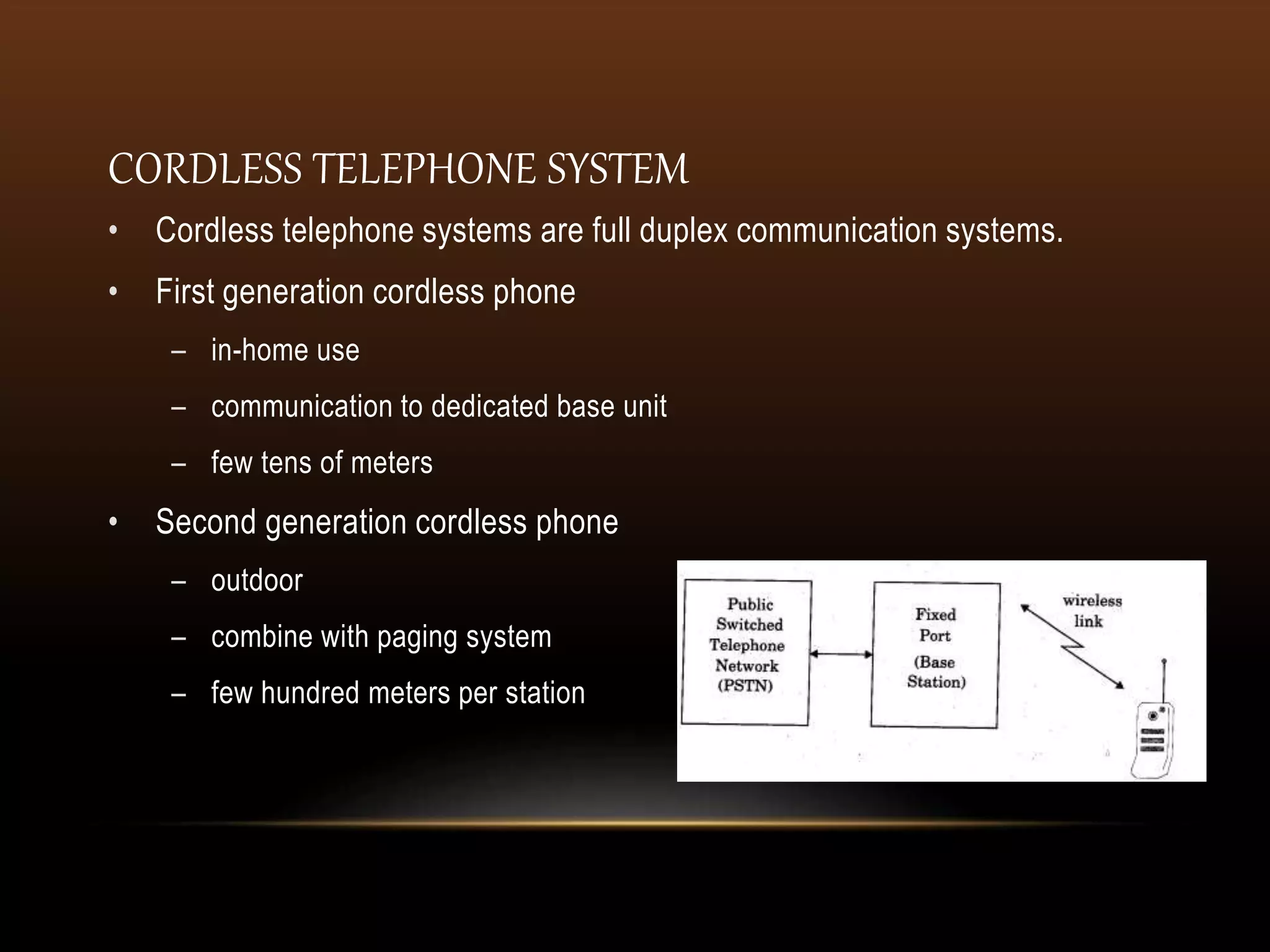
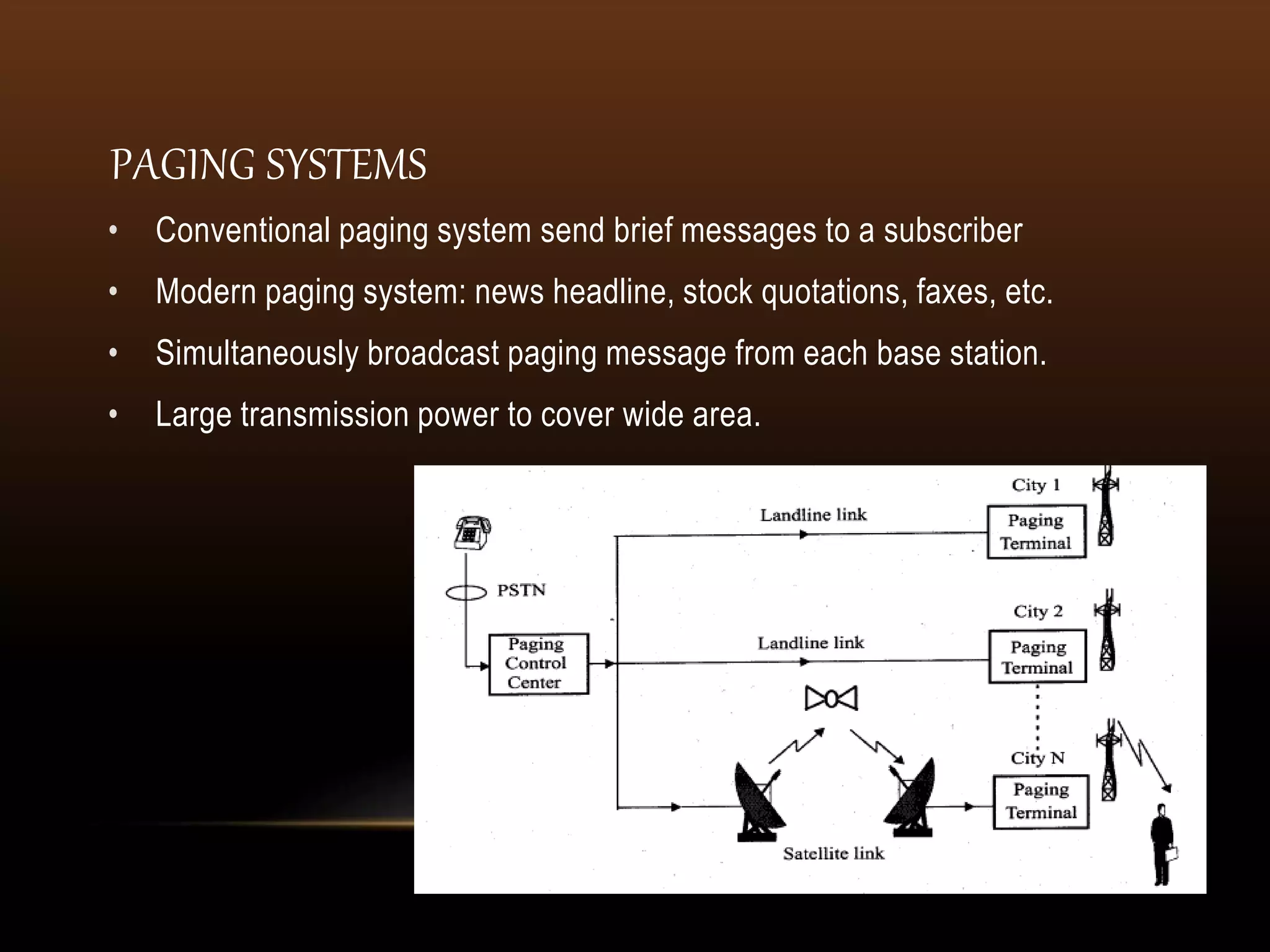
Wireless communication transmits voice and data using electromagnetic waves without physical connections like wires. It provides freedom of movement and flexibility to connect multiple devices. Common wireless technologies include radio, TV, Bluetooth, WiFi, and cellular networks. Wireless communication faces challenges like security issues, infrastructure costs, and signal interference, but enables connectivity anywhere through standards like LTE and 5G.