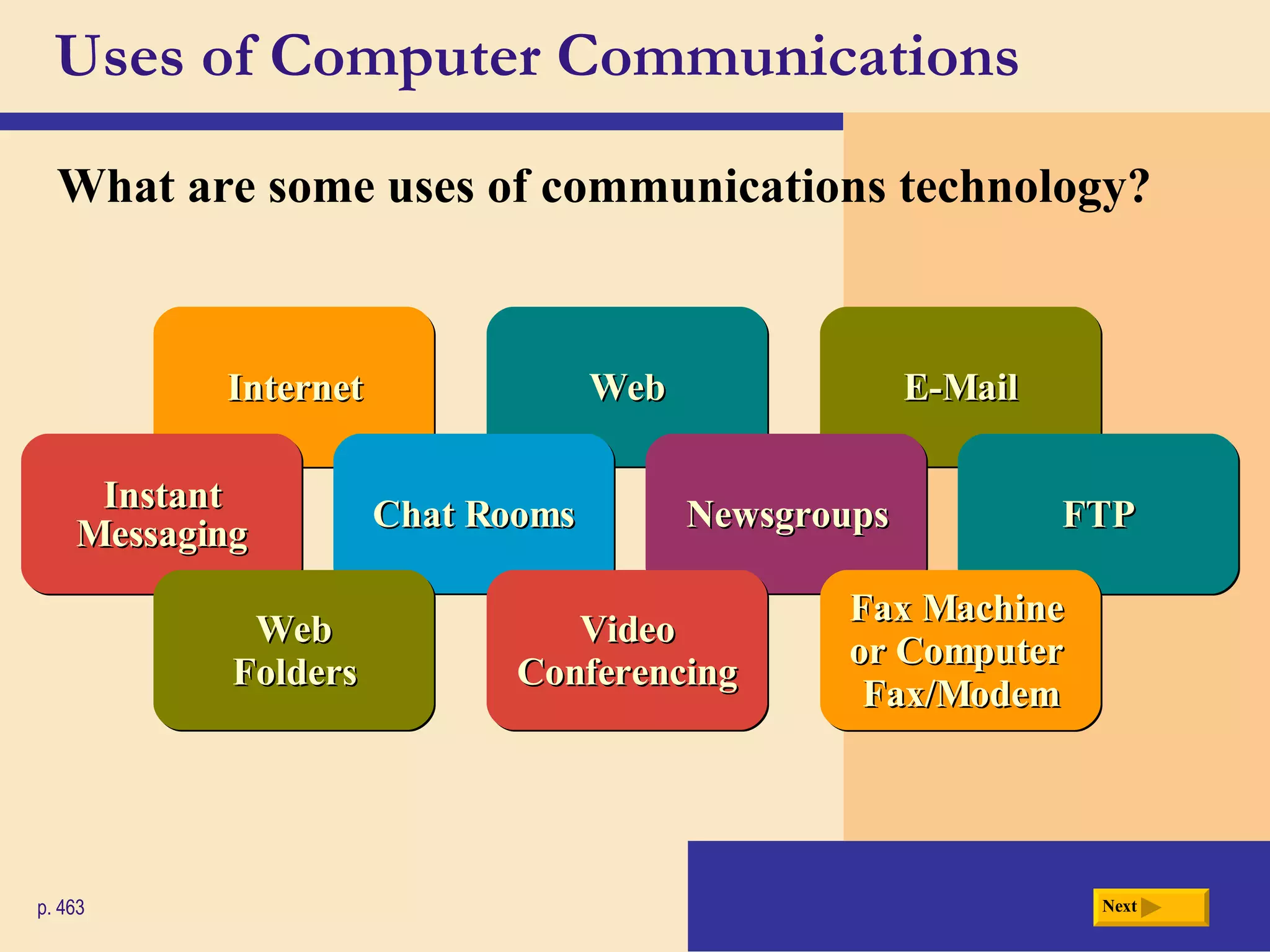
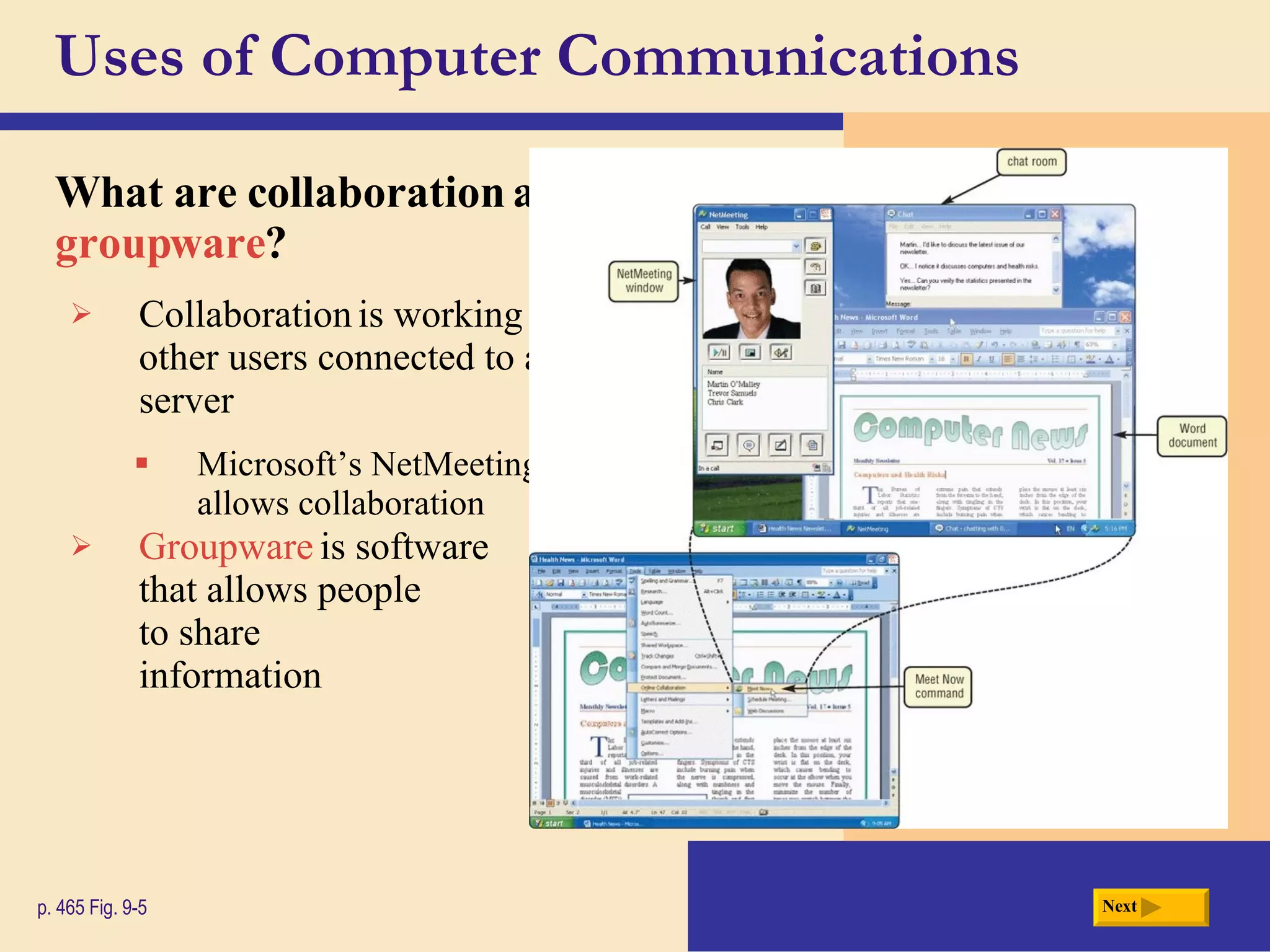
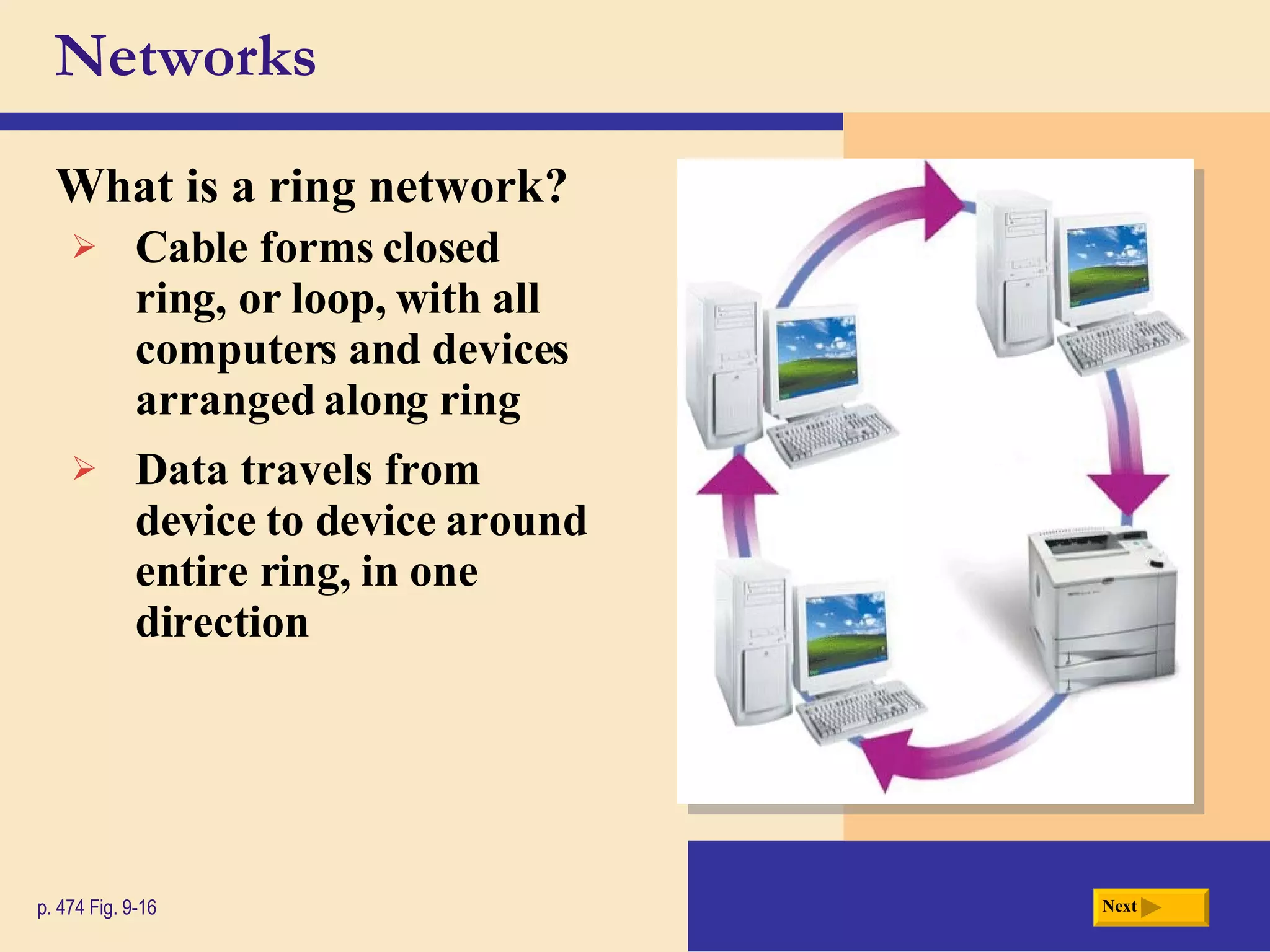
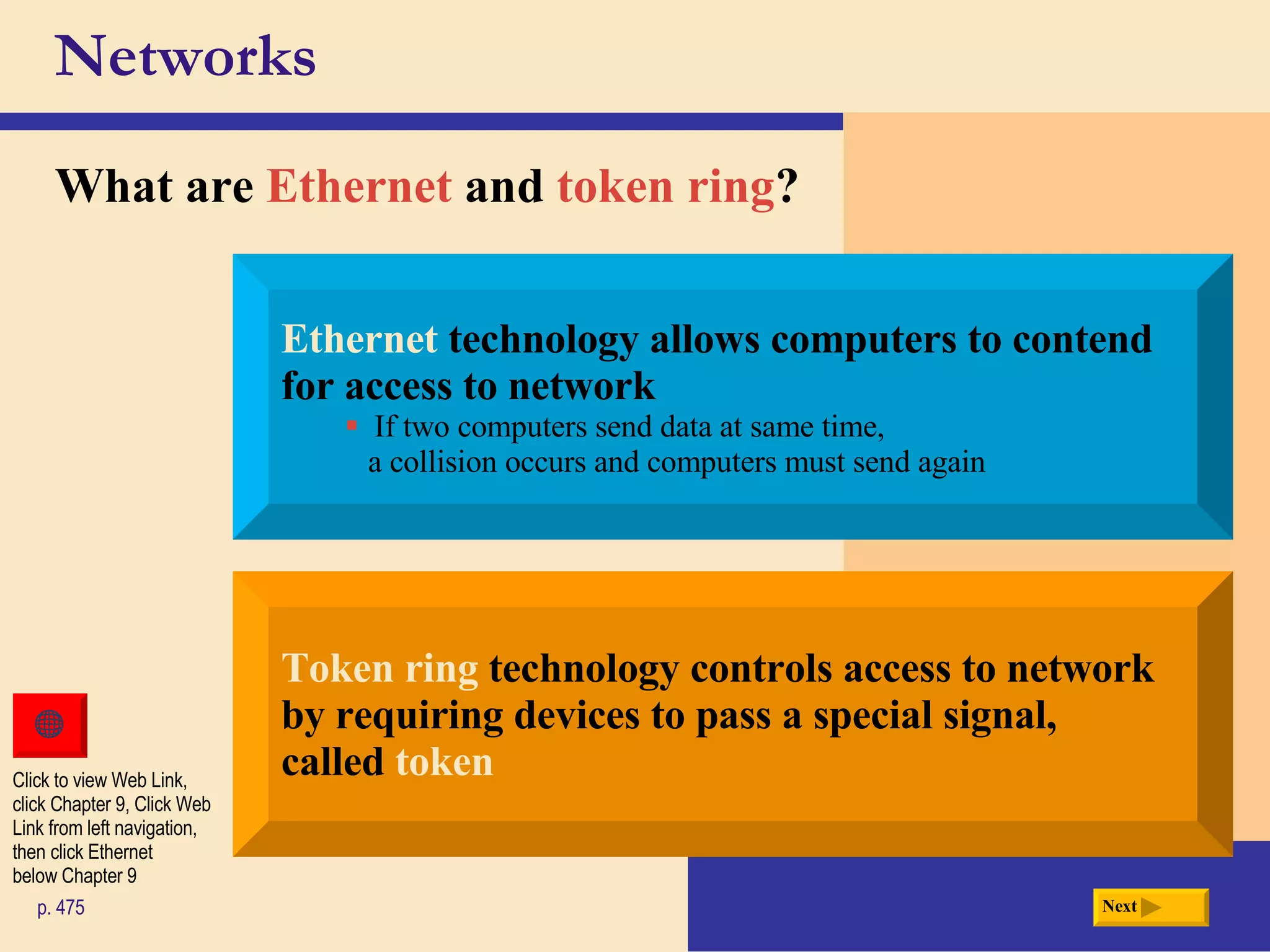
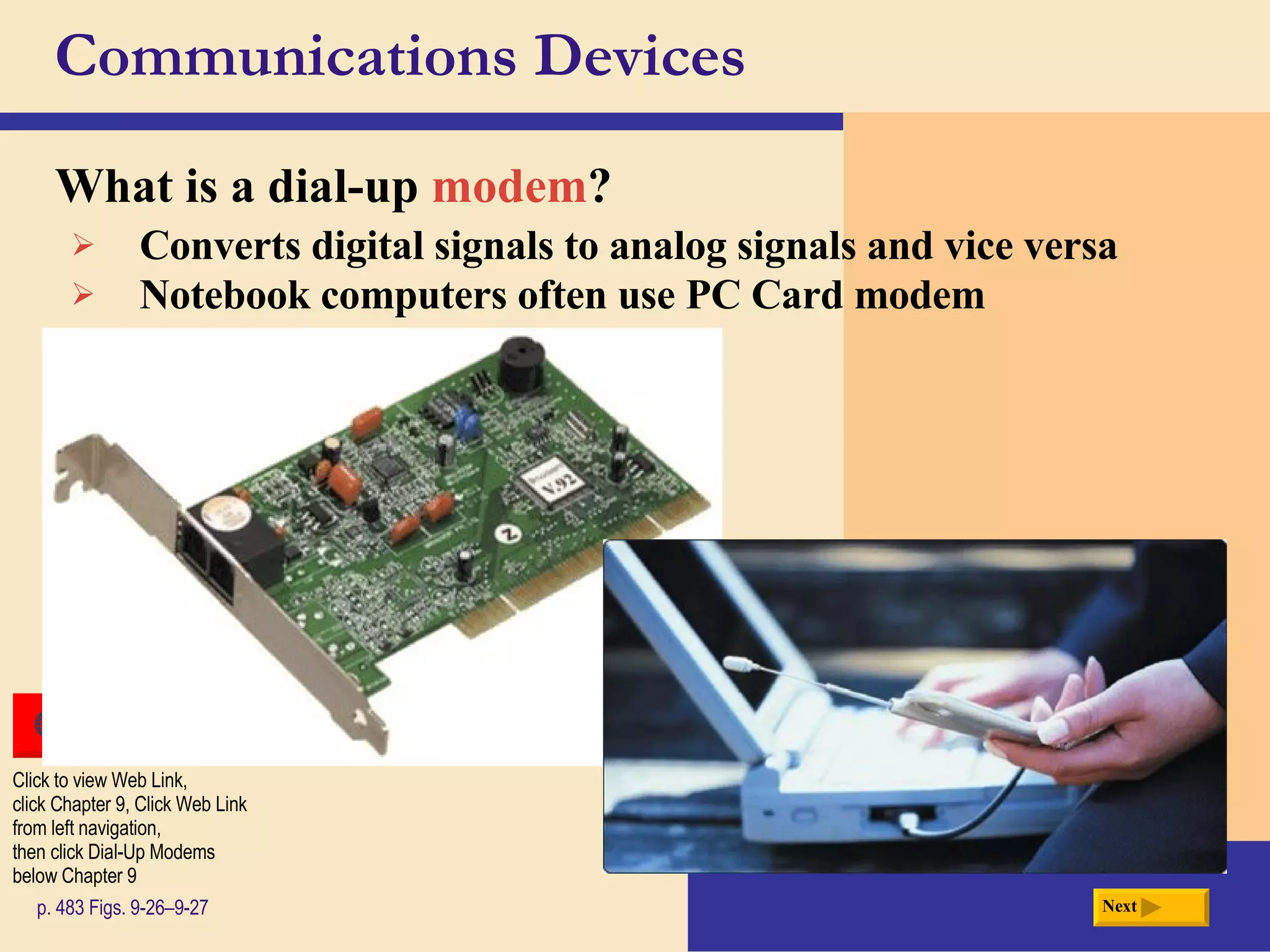
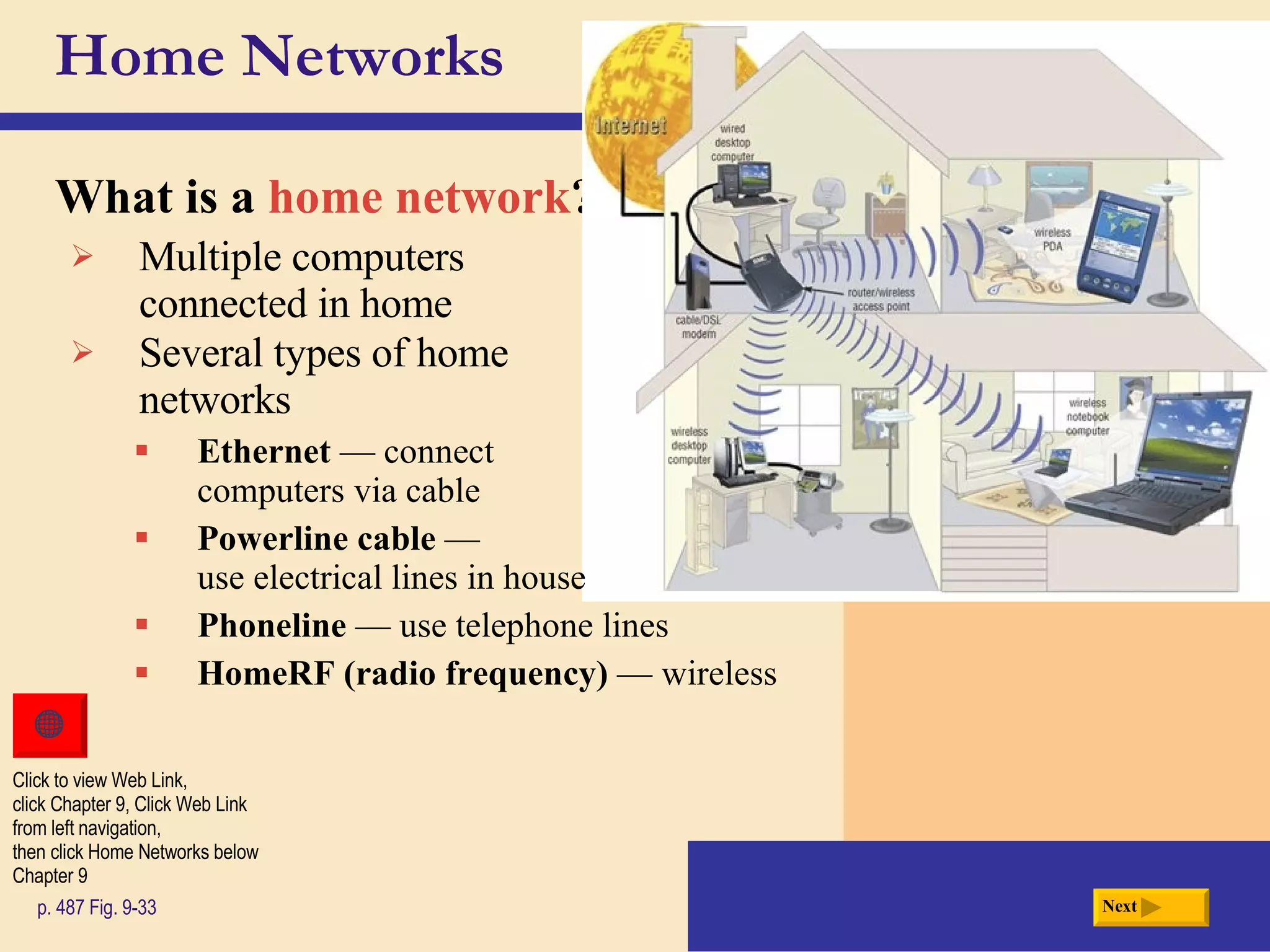
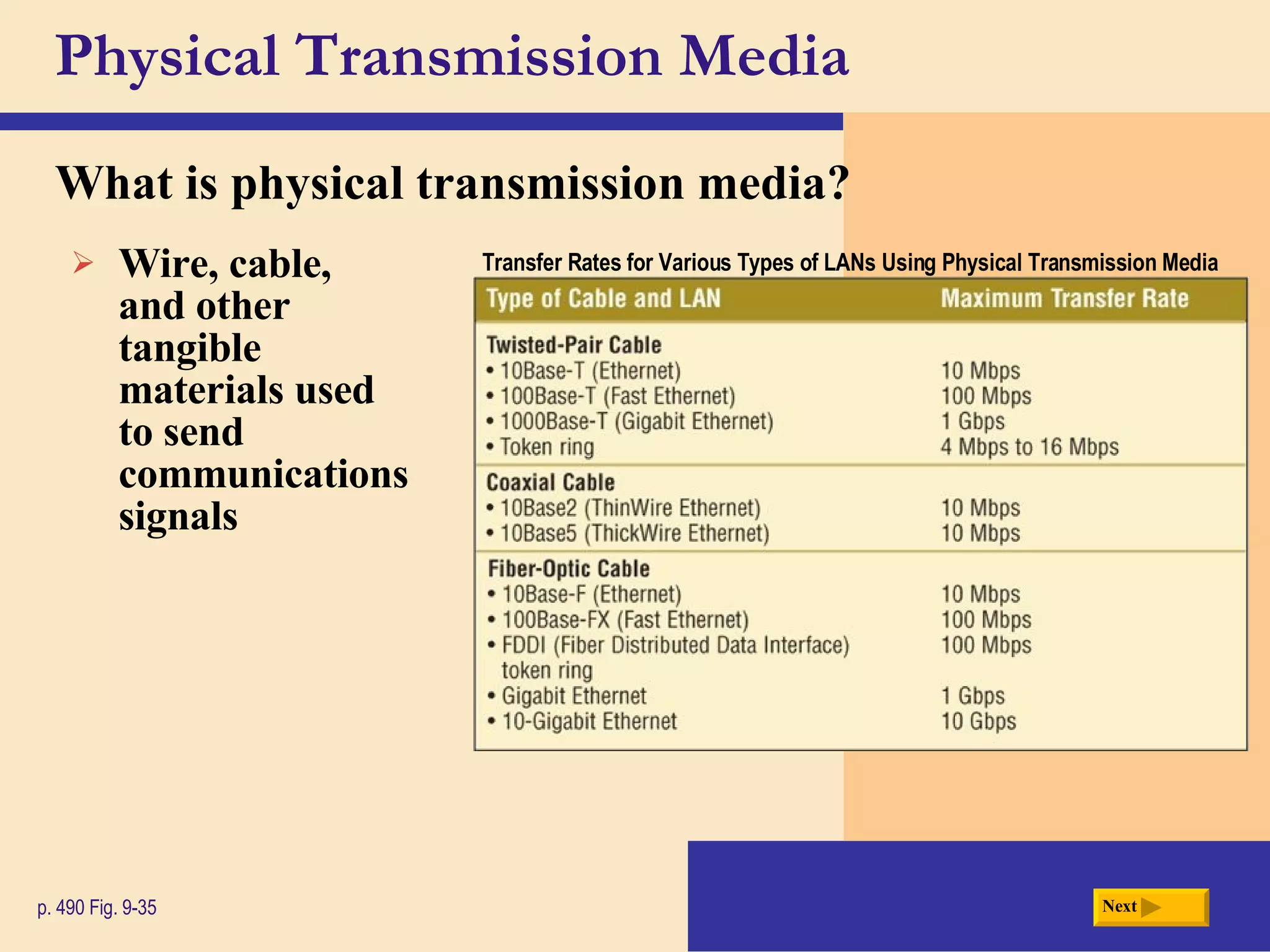
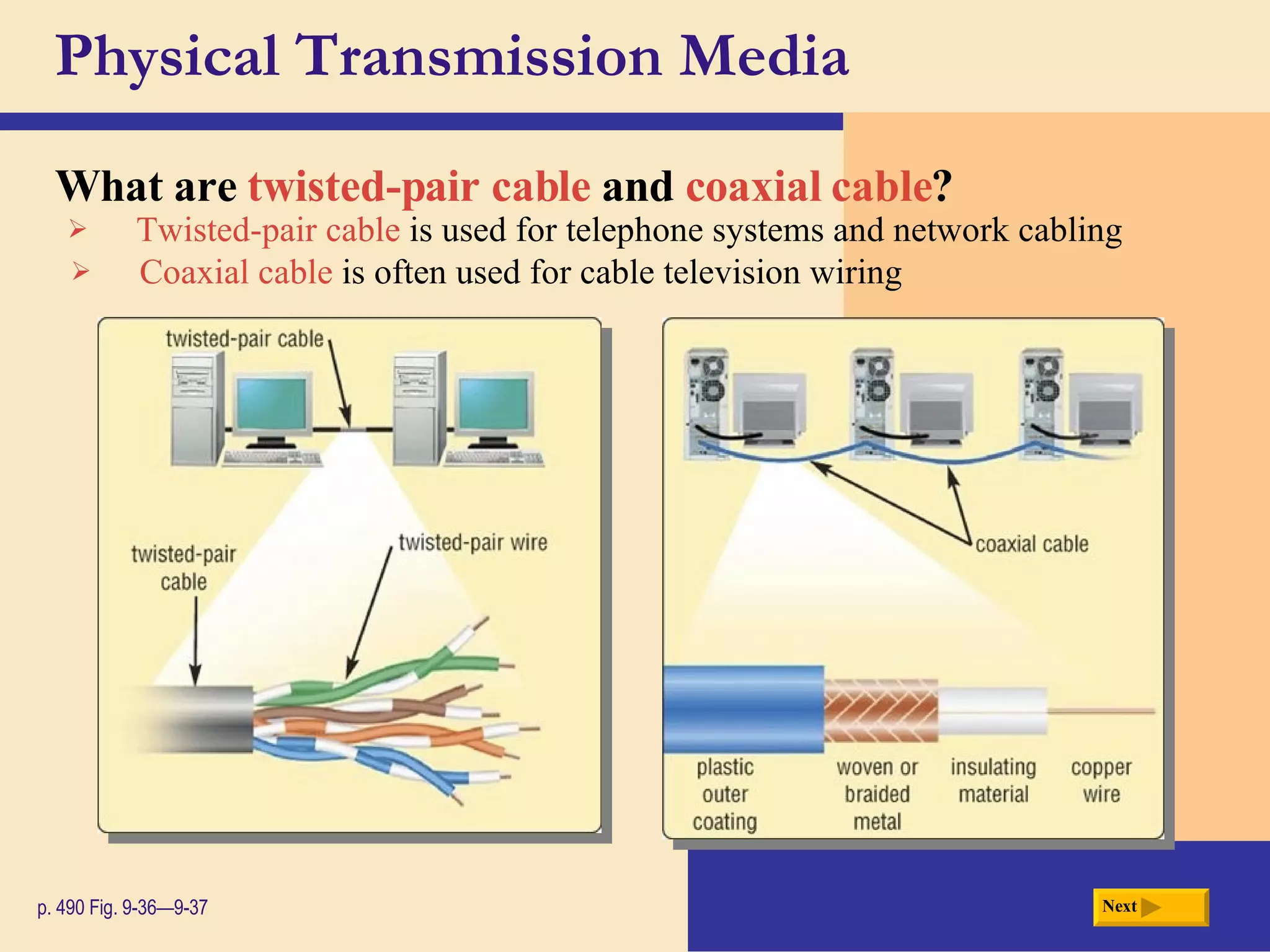
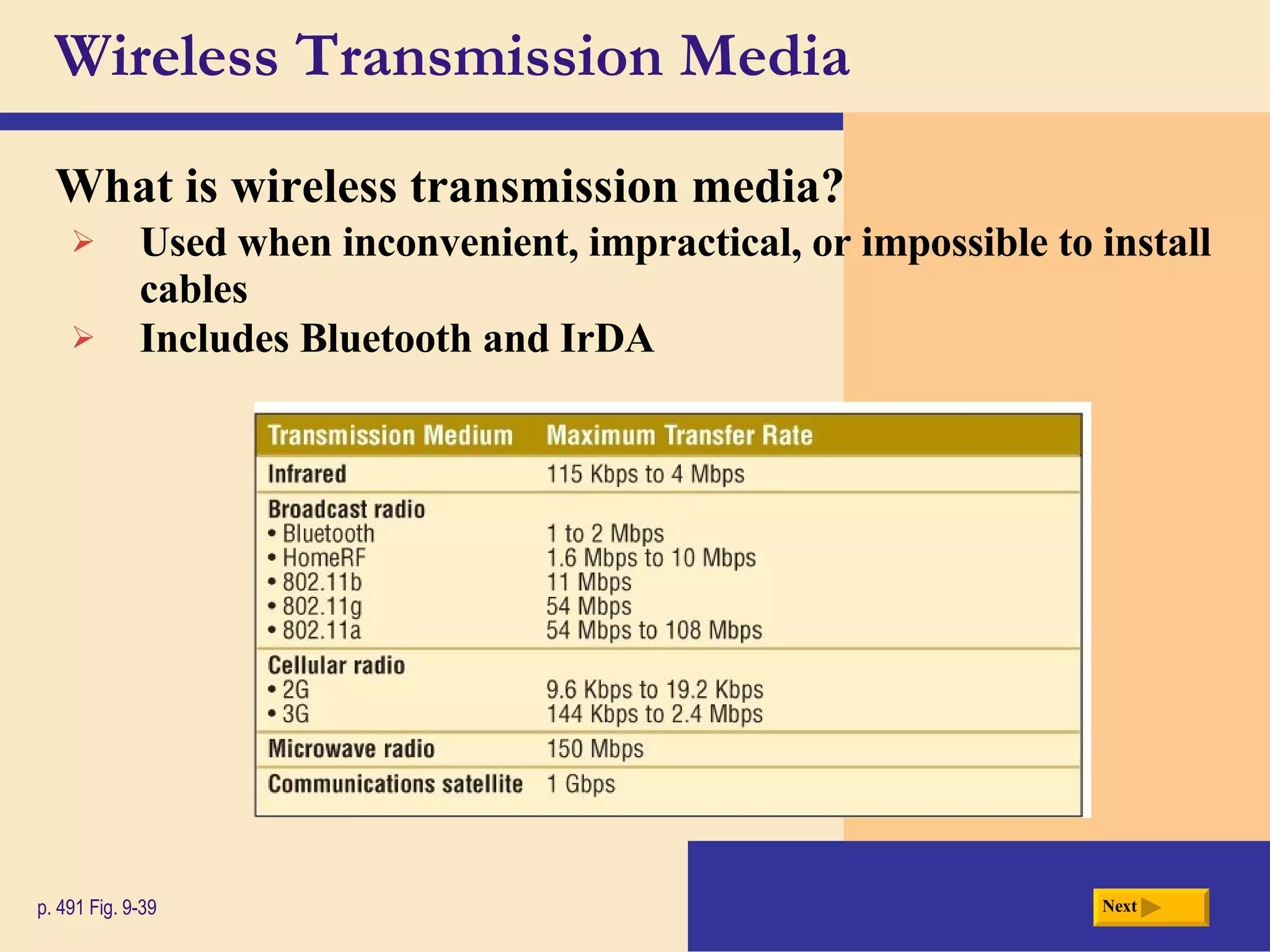
Chapter 9 discusses computer communications and networks. It describes the key components needed for successful communications, including sending and receiving devices, and communications channels. Various network types are defined, such as client/server, peer-to-peer, and P2P networks. Common communications technologies, devices, media, and software are also explained, along with different methods for setting up wired and wireless home and business networks.