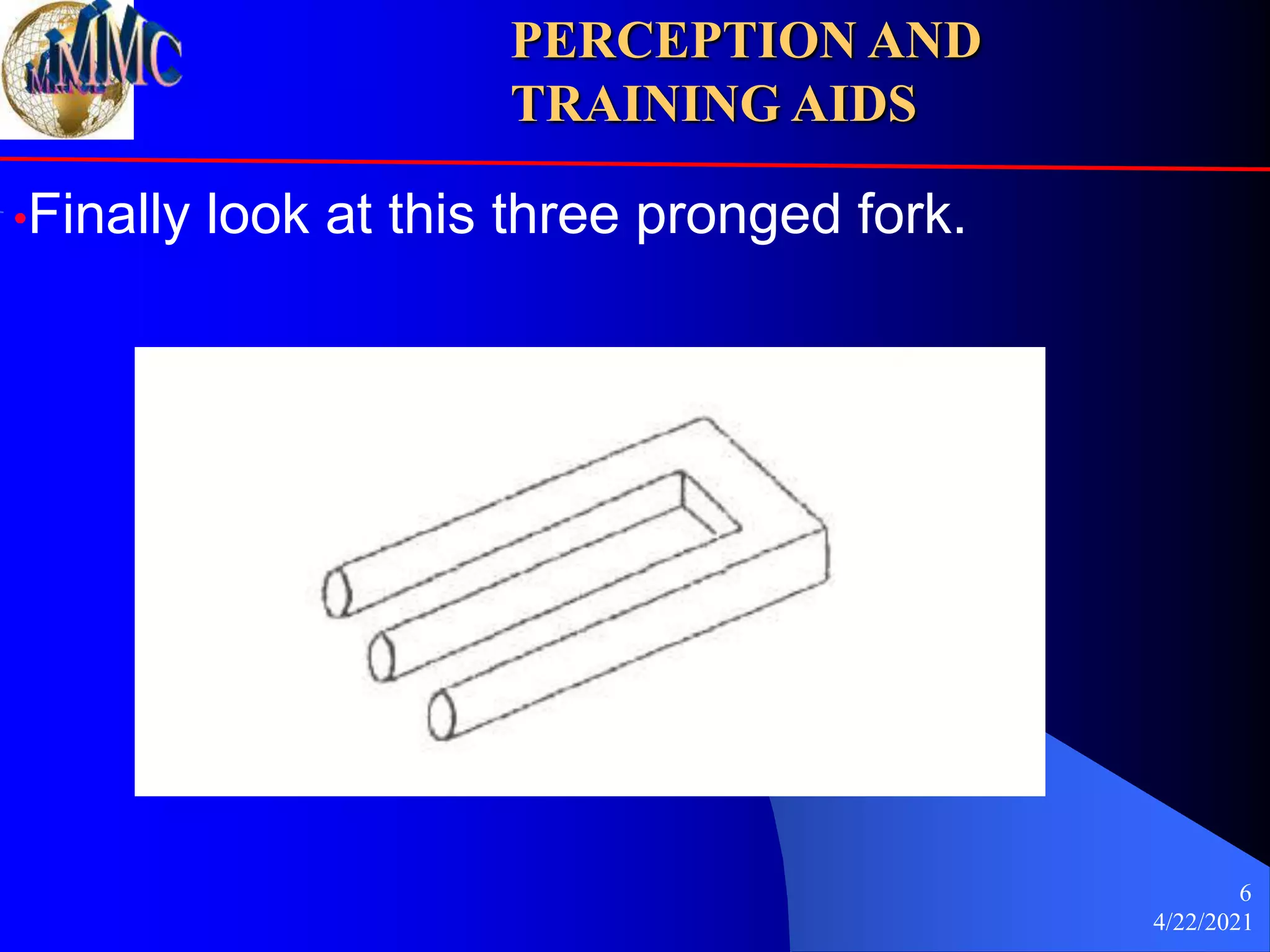
This document discusses the importance of perception in training and the effective use of training aids. It emphasizes that trainers must carefully select visual aids and ensure they align with trainees' perceptions, while also outlining best practices for various types of training materials, including real materials, charts, flip charts, and overhead projectors. The document concludes with guidelines to optimize learning environments and enhance trainee engagement.