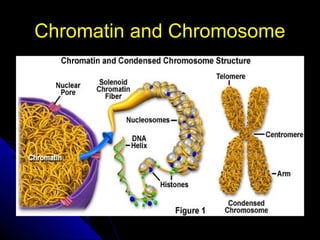
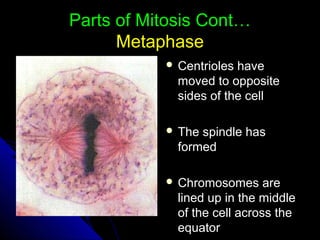
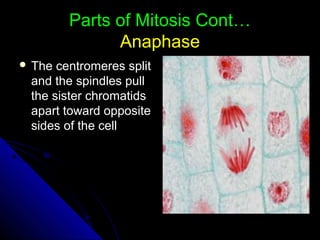
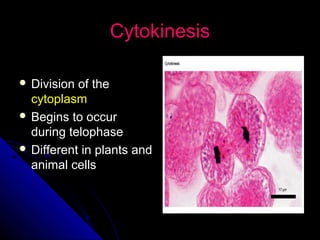
Cellular transport includes passive transport which does not require energy, and active transport which uses energy. There are three types of passive transport - simple diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion. Active transport includes exocytosis and endocytosis. The cell cycle involves interphase where the cell grows and prepares for division, mitosis where the nucleus divides, and cytokinesis where the cell divides. Cancer occurs when cell growth is uncontrolled resulting in tumors that can metastasize throughout the body.