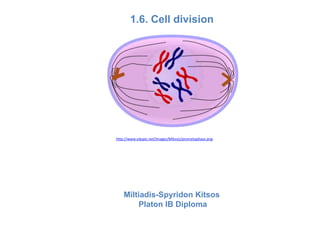
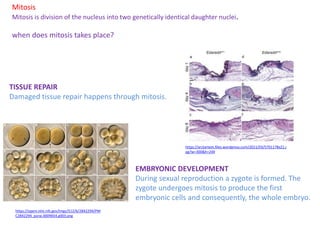
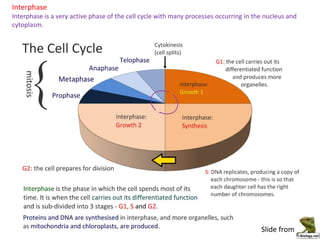
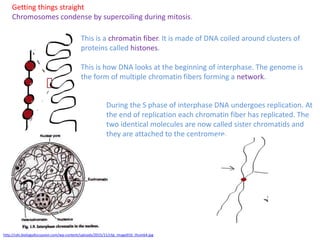
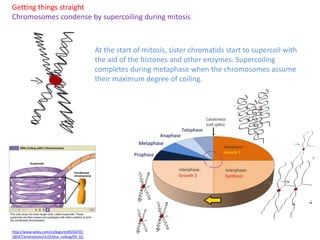
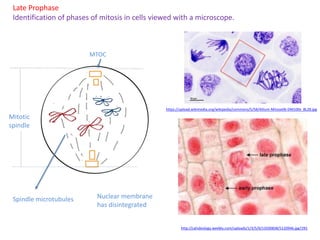
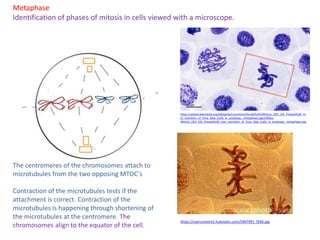
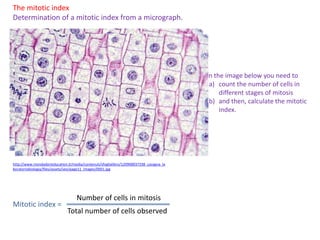
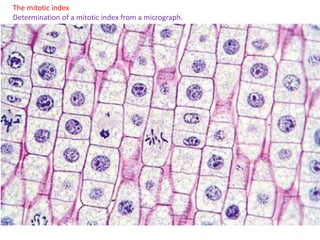
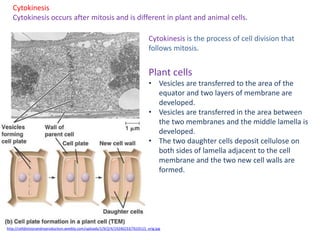
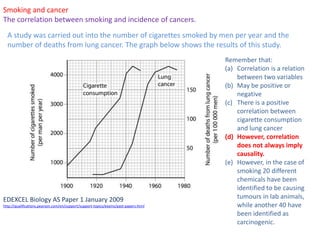
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells with identical genetic material to the original parent cell. It occurs in eukaryotic cells and involves several phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then separates the daughter cells. Mitosis is important for tissue growth, repair and regeneration, asexual reproduction and embryonic development. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases control the progression of cells through the cell cycle phases. Disruptions can lead to uncontrolled cell division and cancer. Smoking is strongly correlated with increased lung cancer rates due to carcinogens in tobacco smoke.