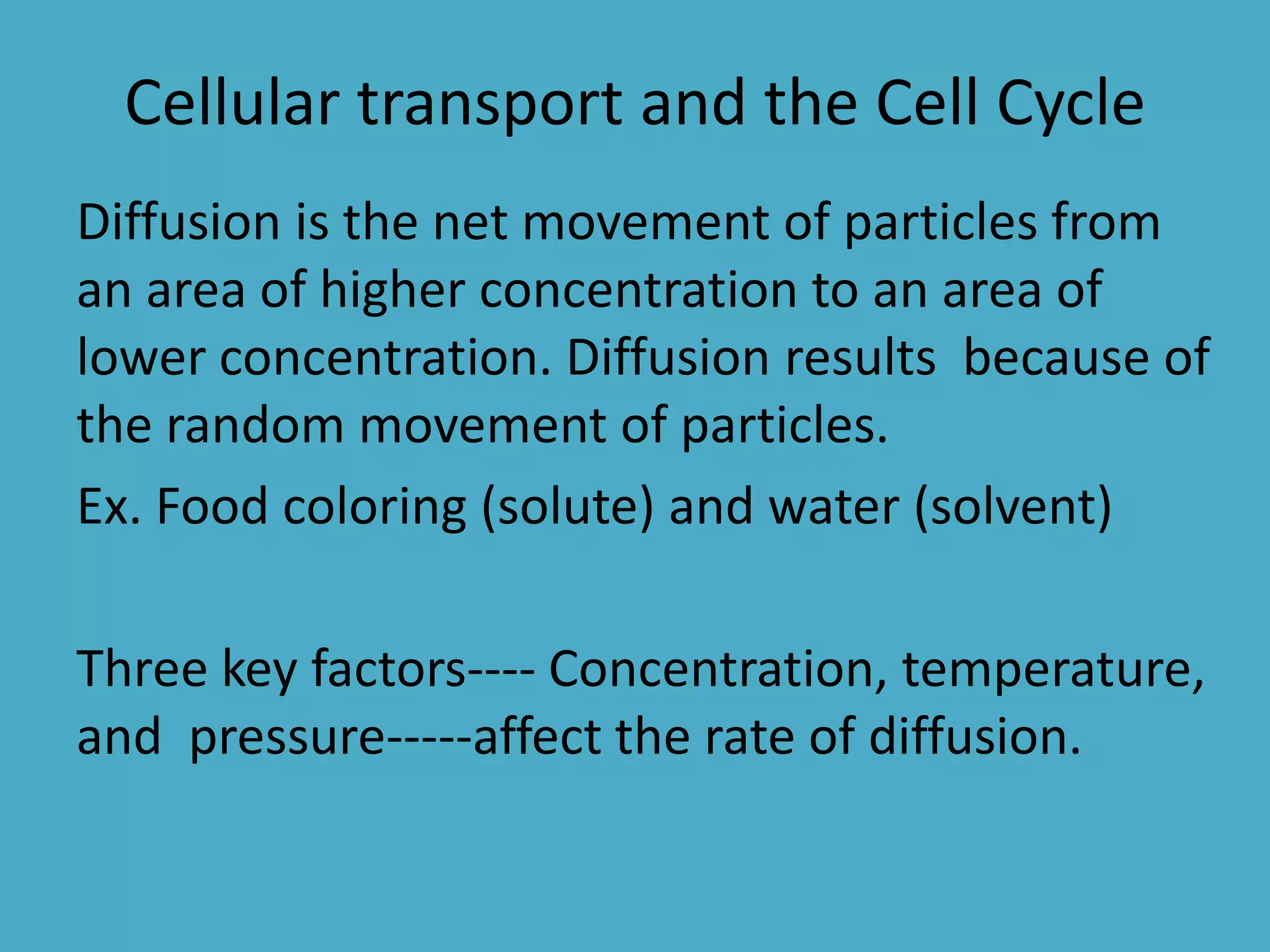
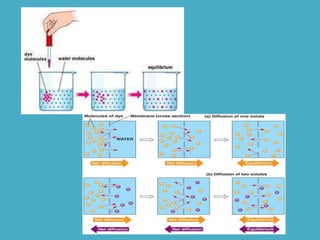
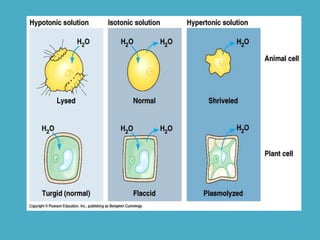
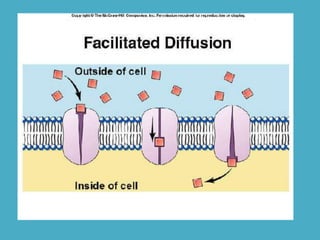
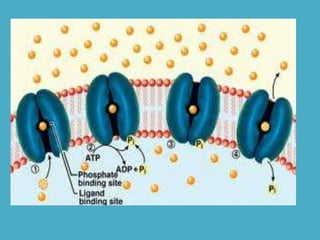
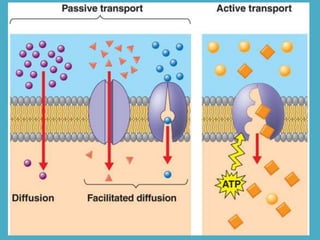
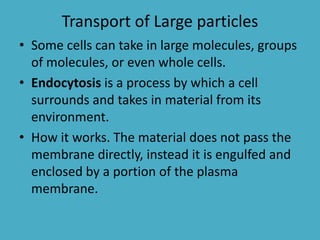
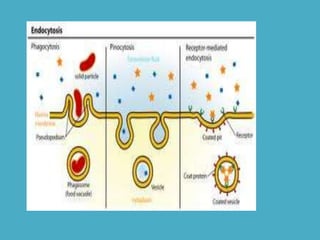
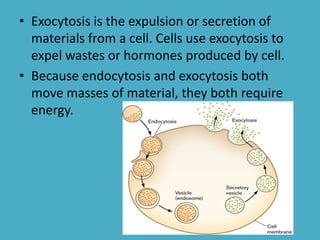
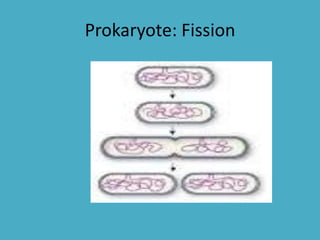
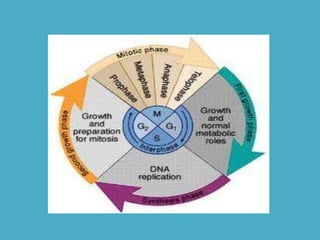
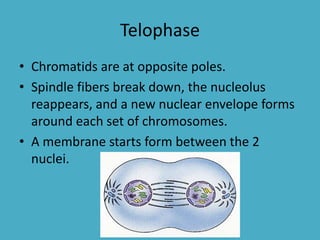
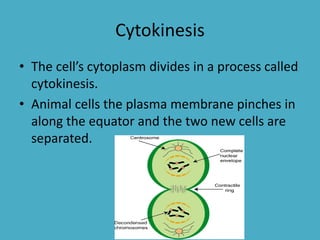
Three key factors - concentration, temperature, and pressure - affect the rate of diffusion, which is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, and regulates water flow to maintain homeostasis. Cells in hypotonic solutions swell as water enters, hypertonic solutions cause water to leave and cells to shrink. Passive transport uses channel or carrier proteins and requires no energy, while active transport moves substances against gradients using energy. Endocytosis and exocytosis transport large particles in and out of cells. The eukaryotic cell cycle includes interphase and the phases of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase