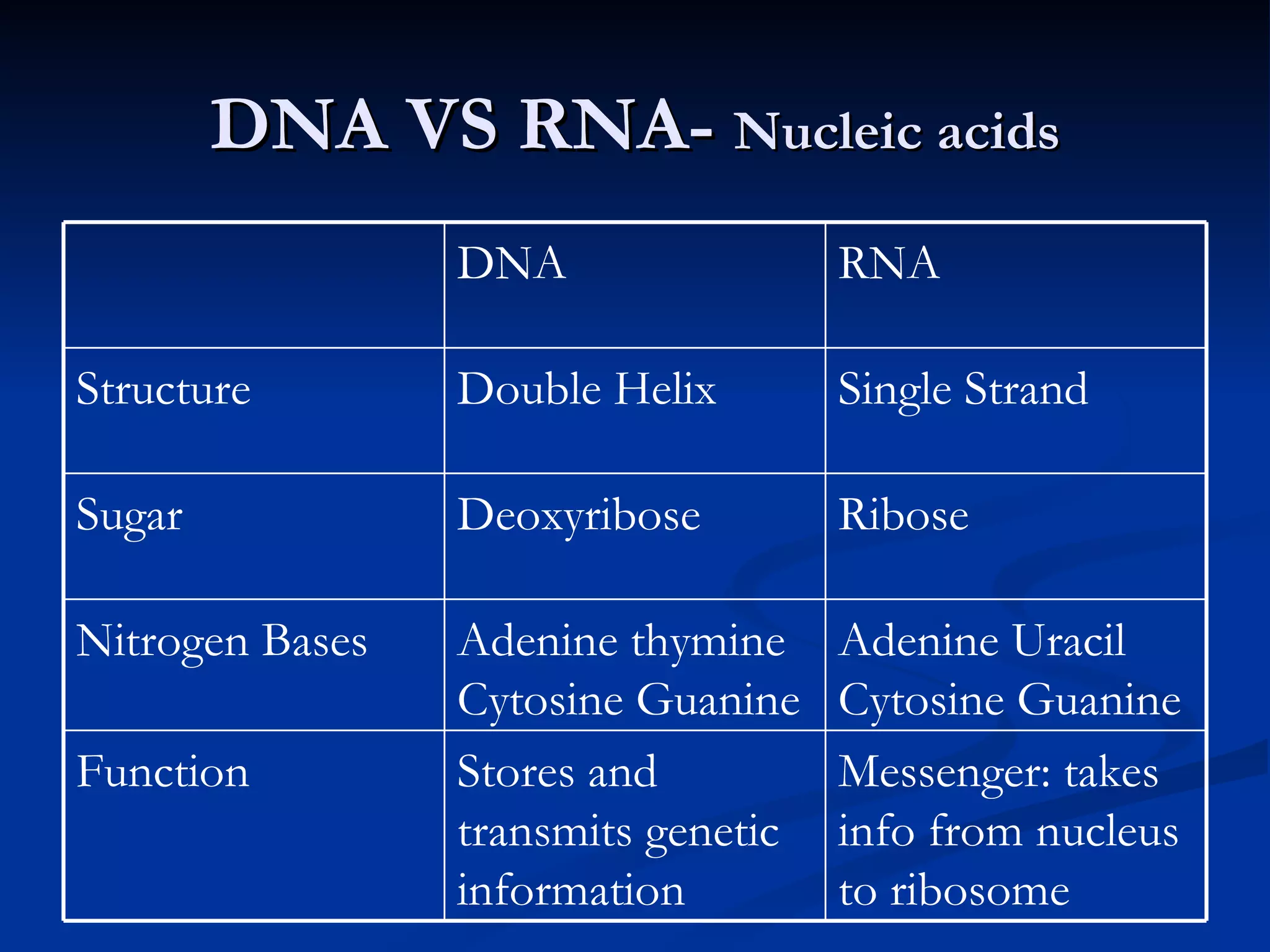
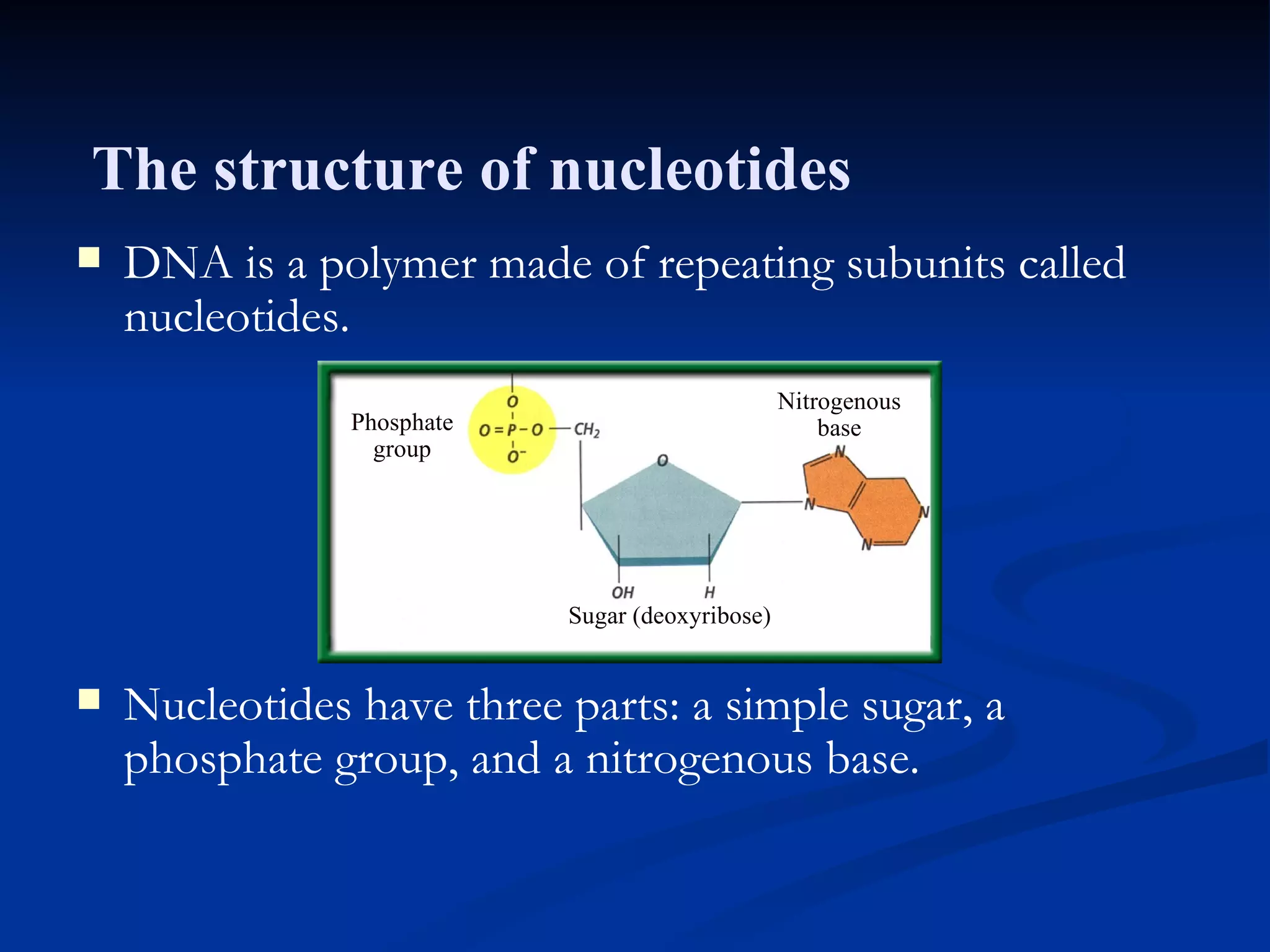
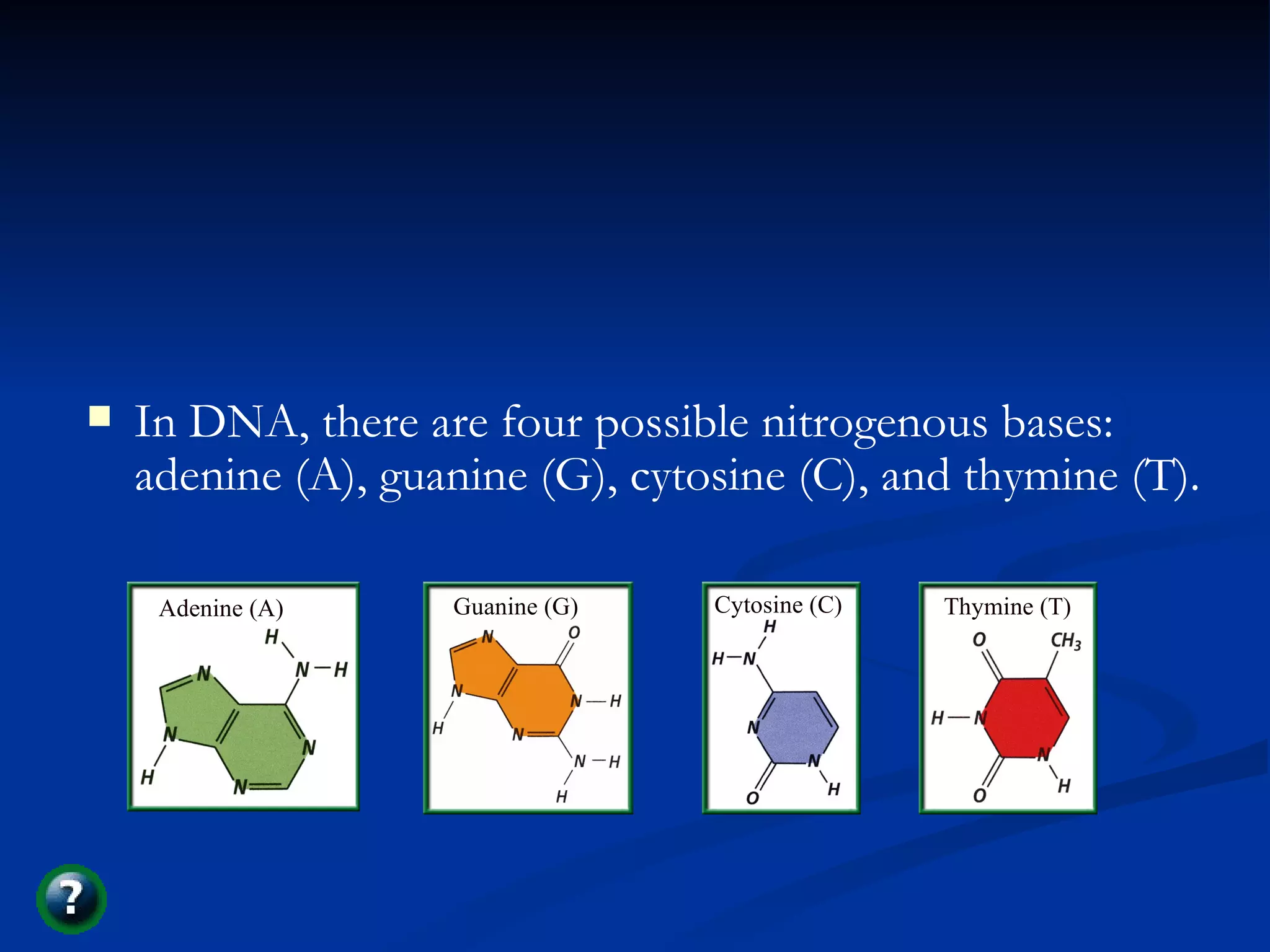
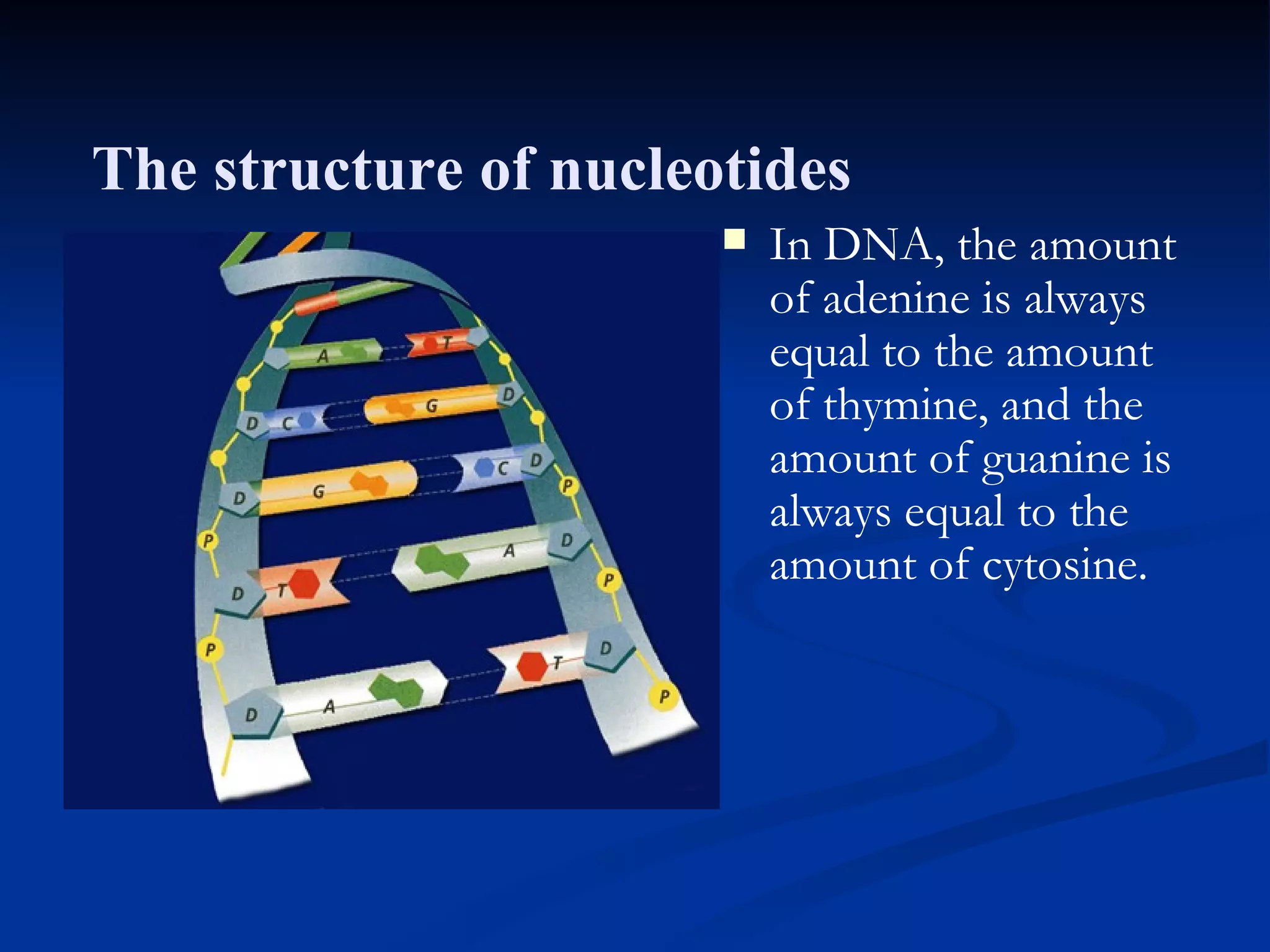
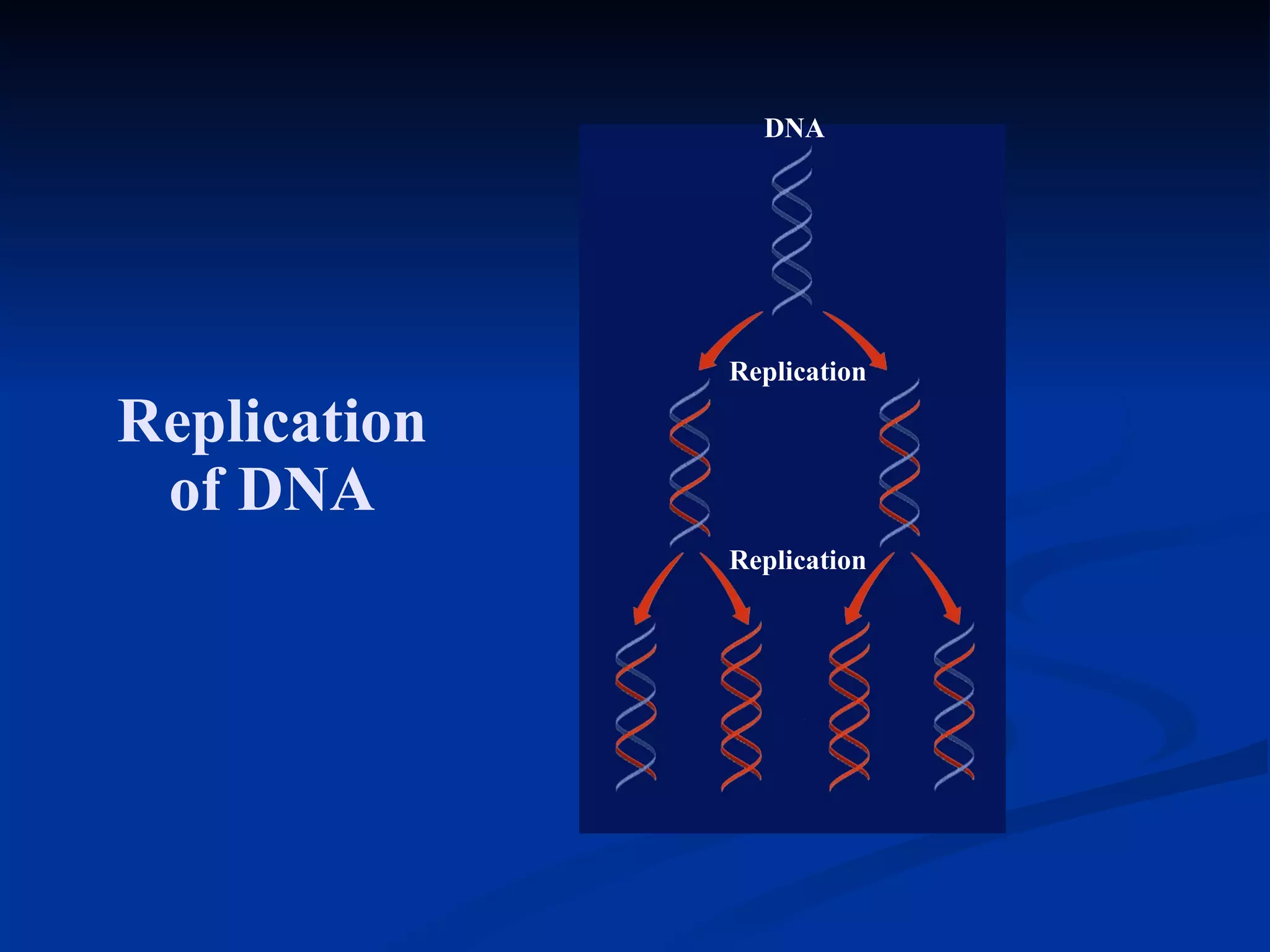
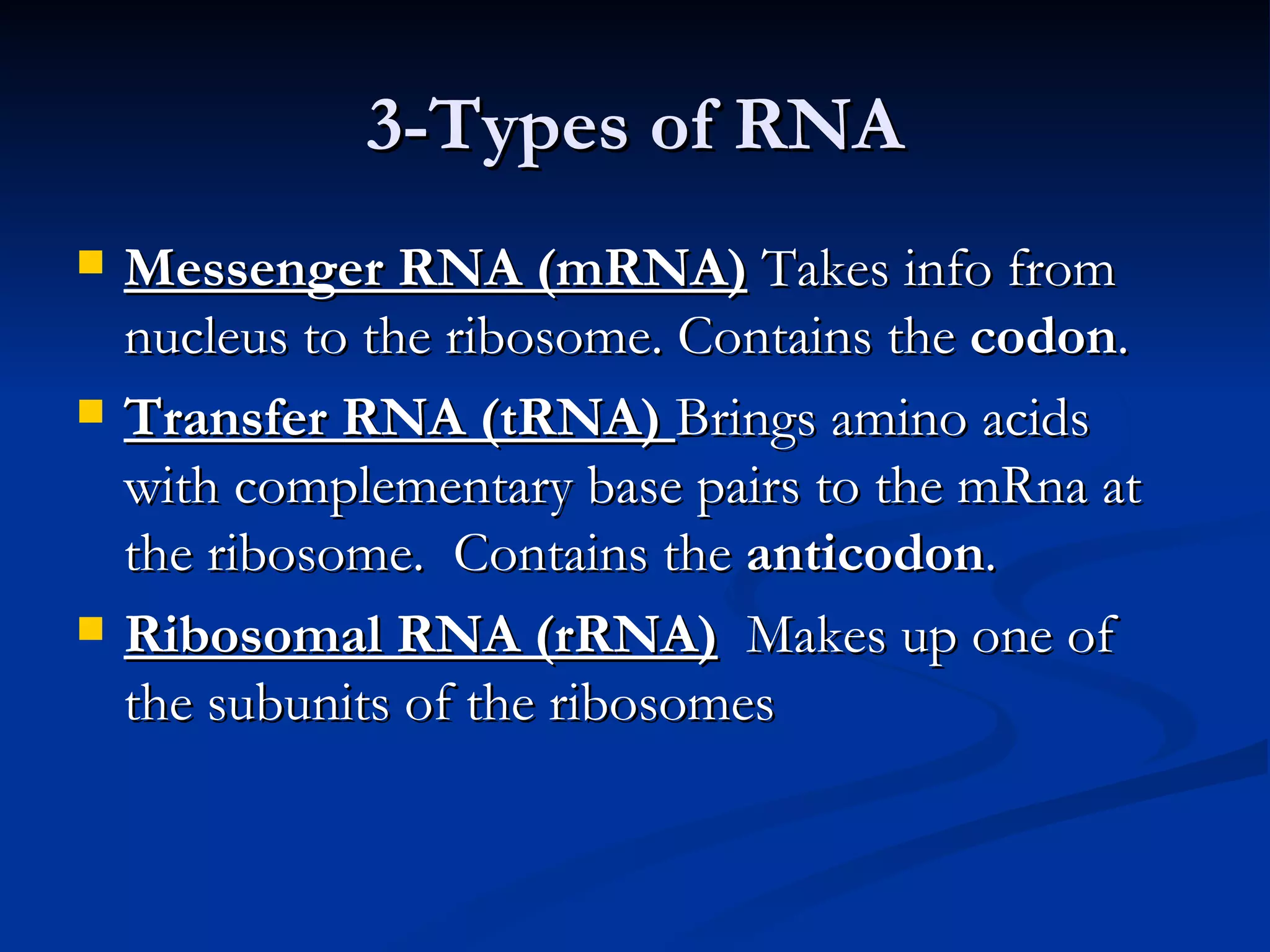
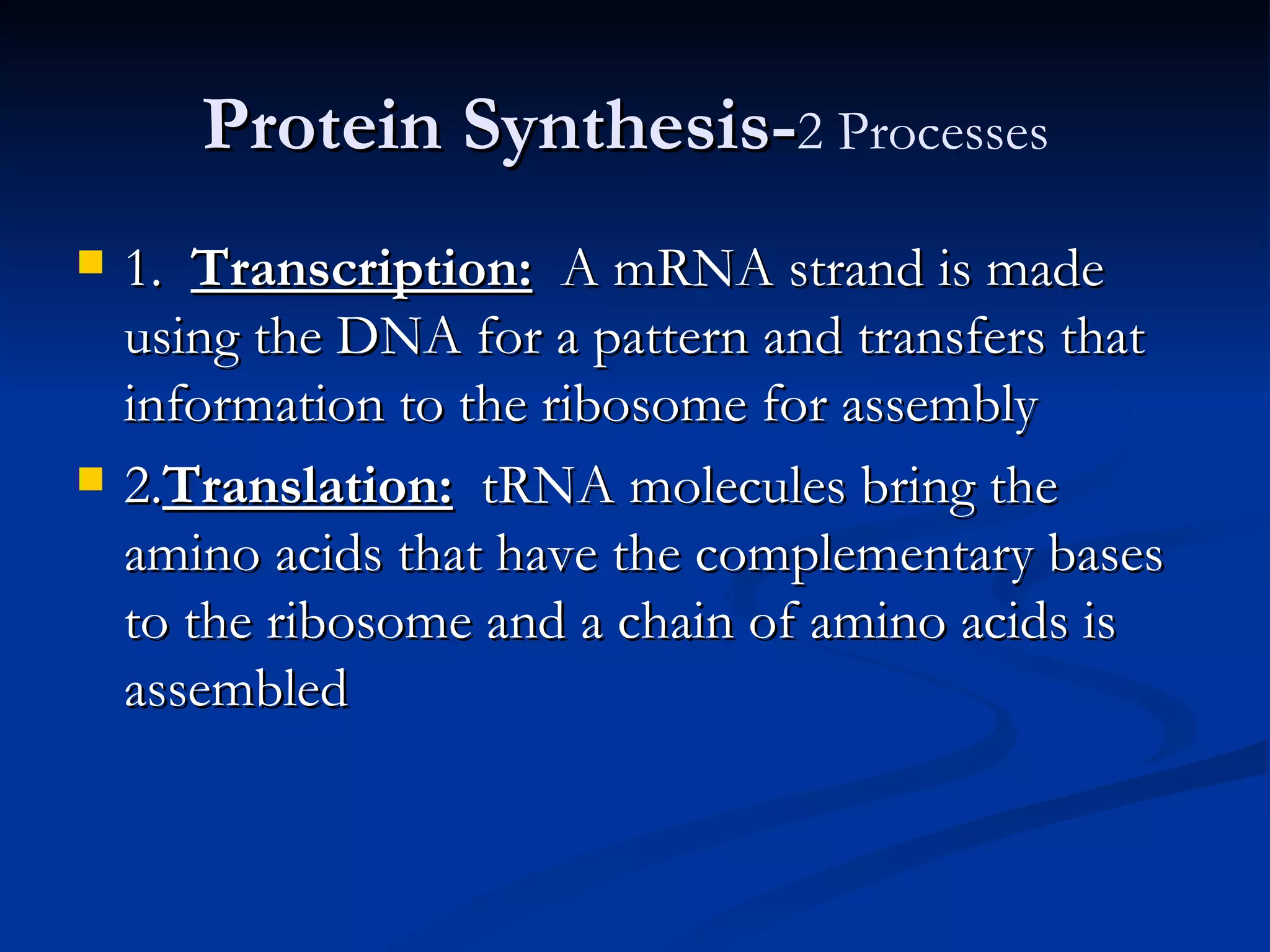
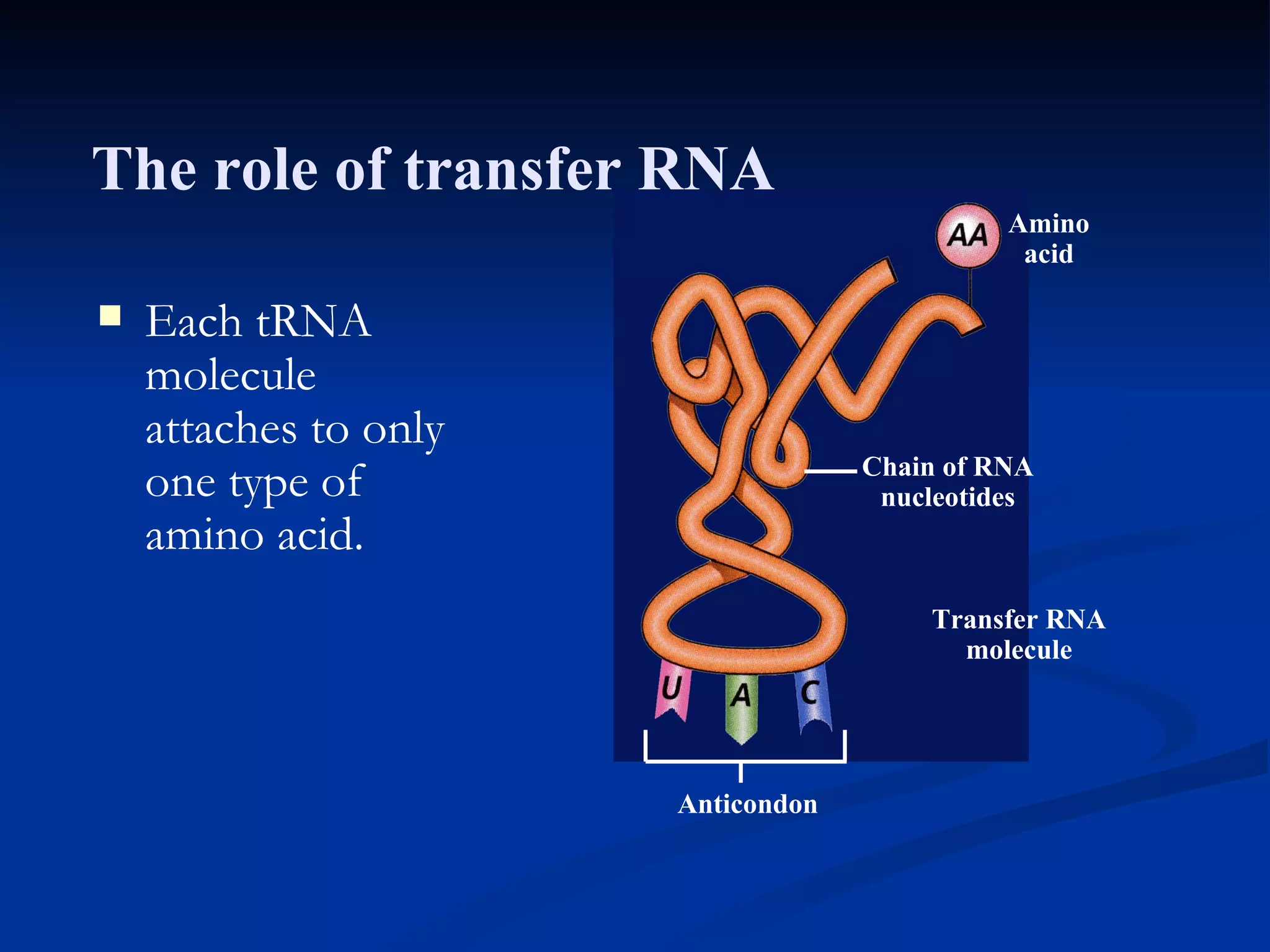
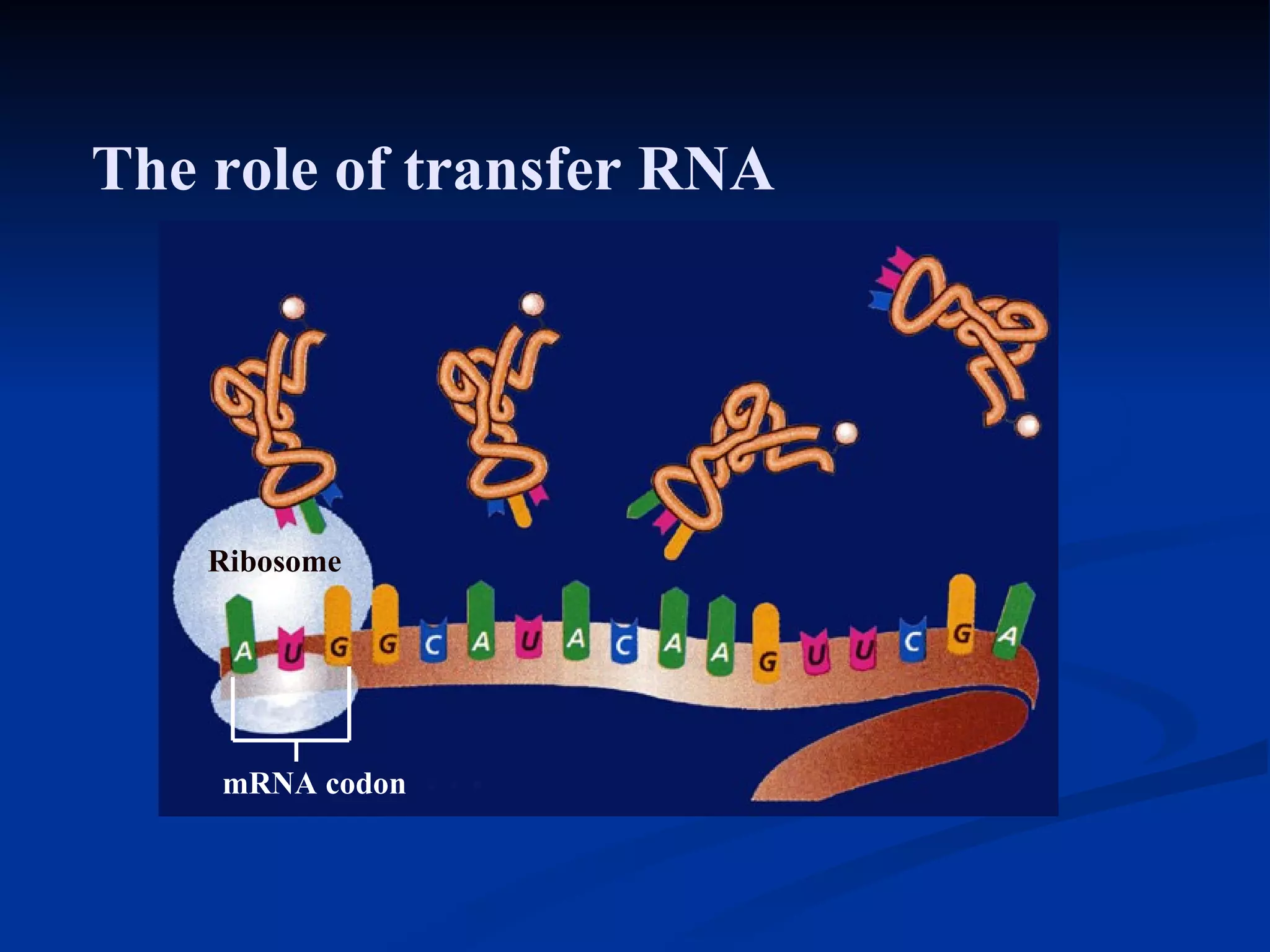
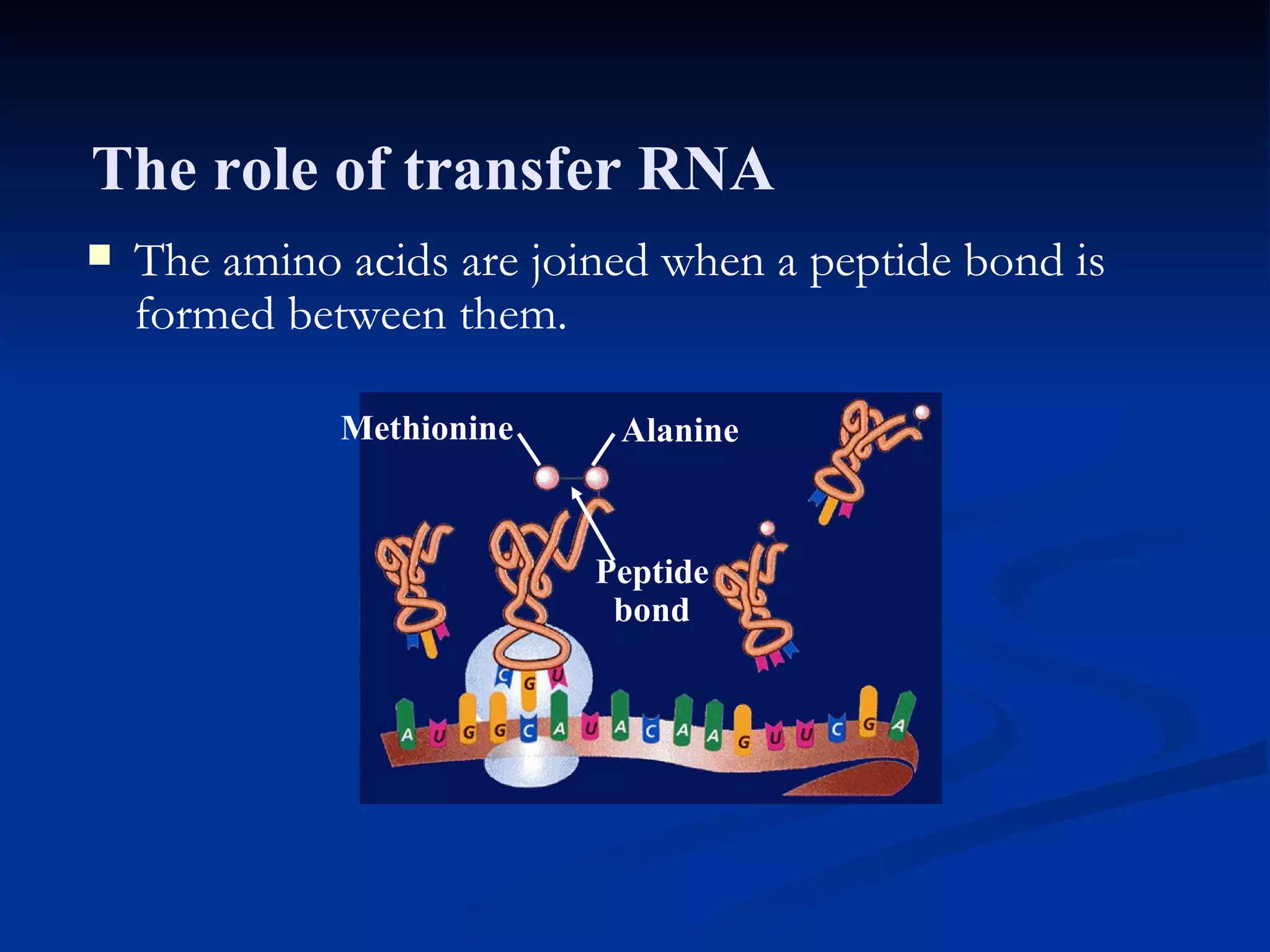
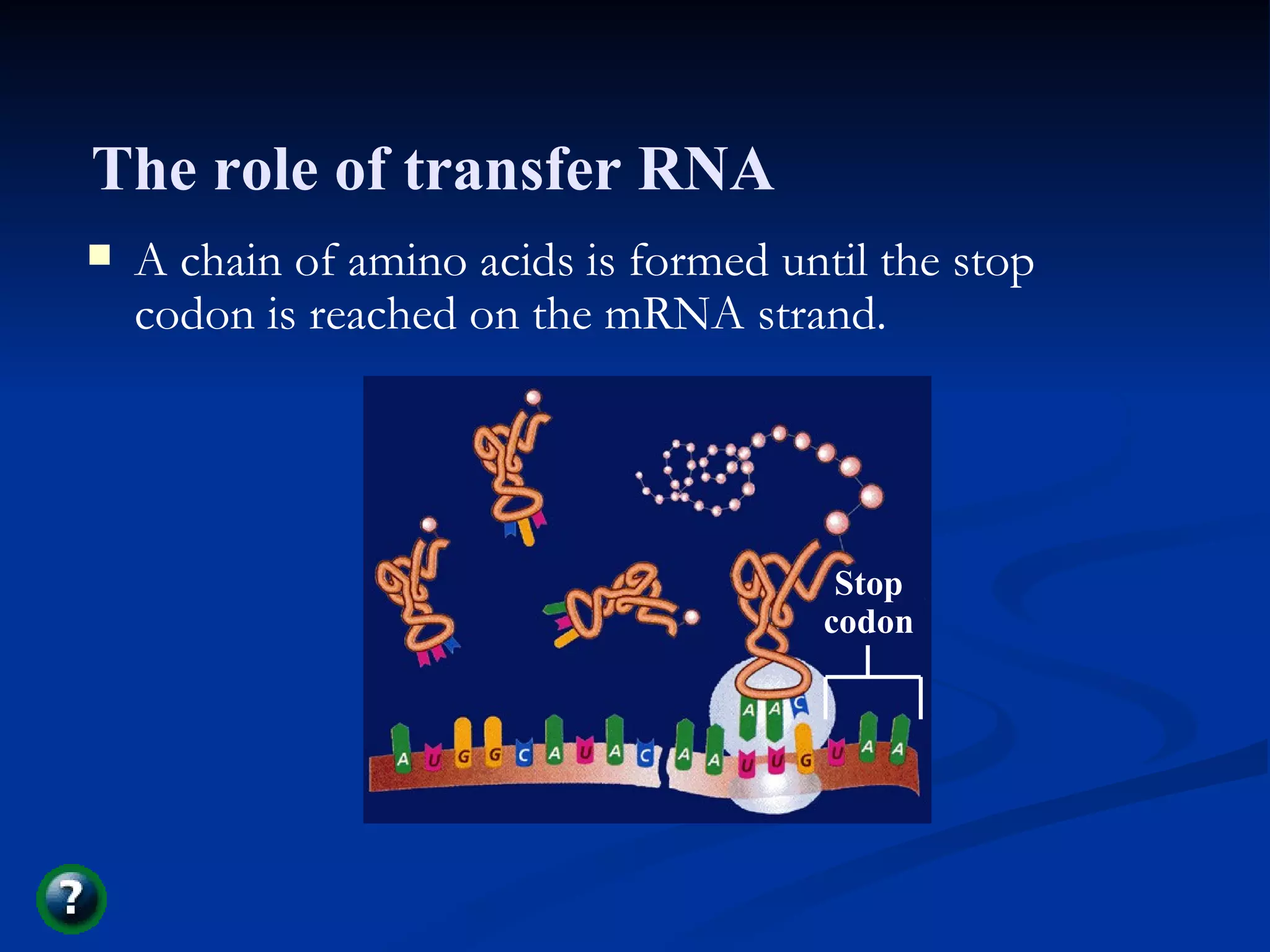
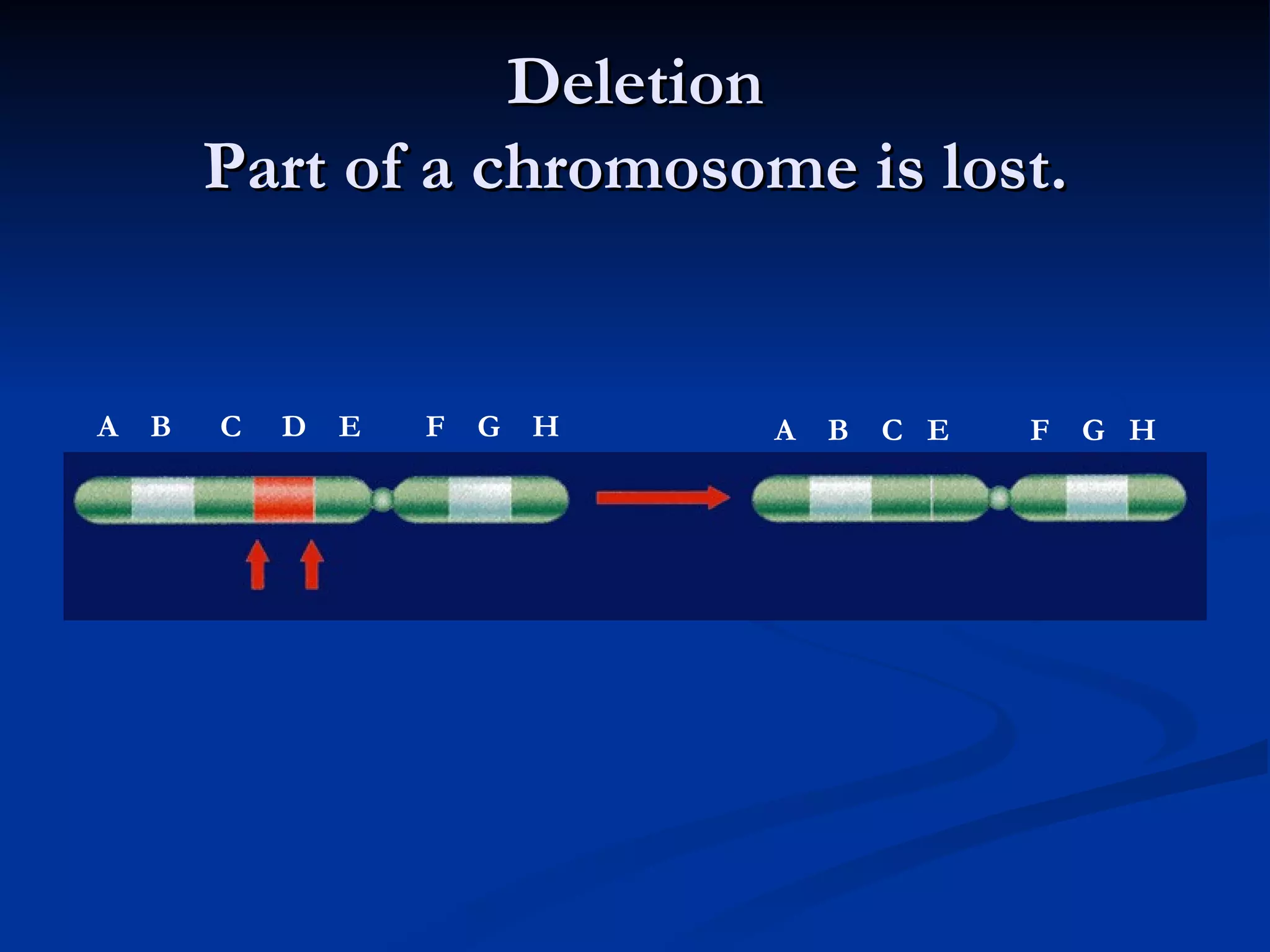
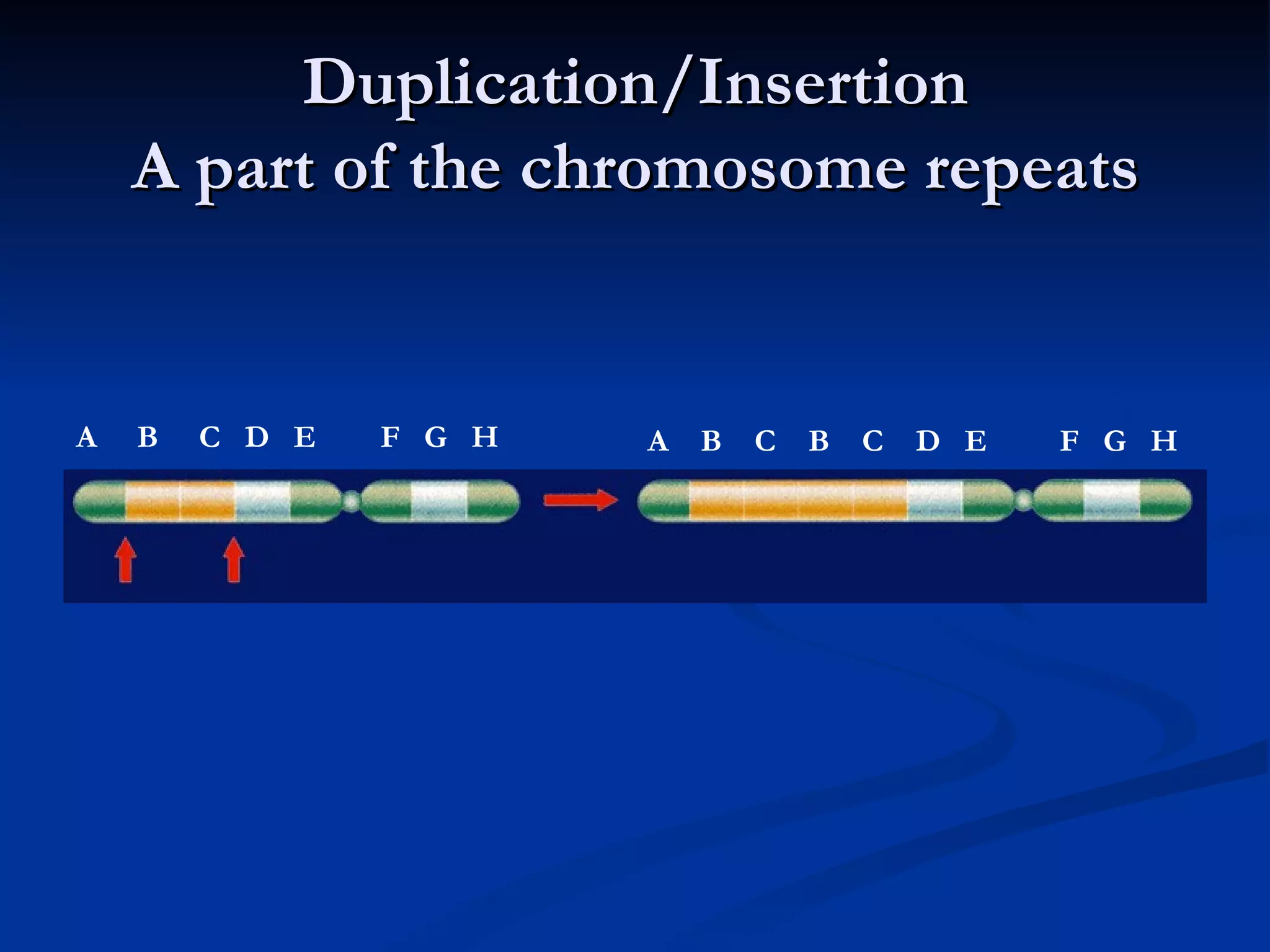
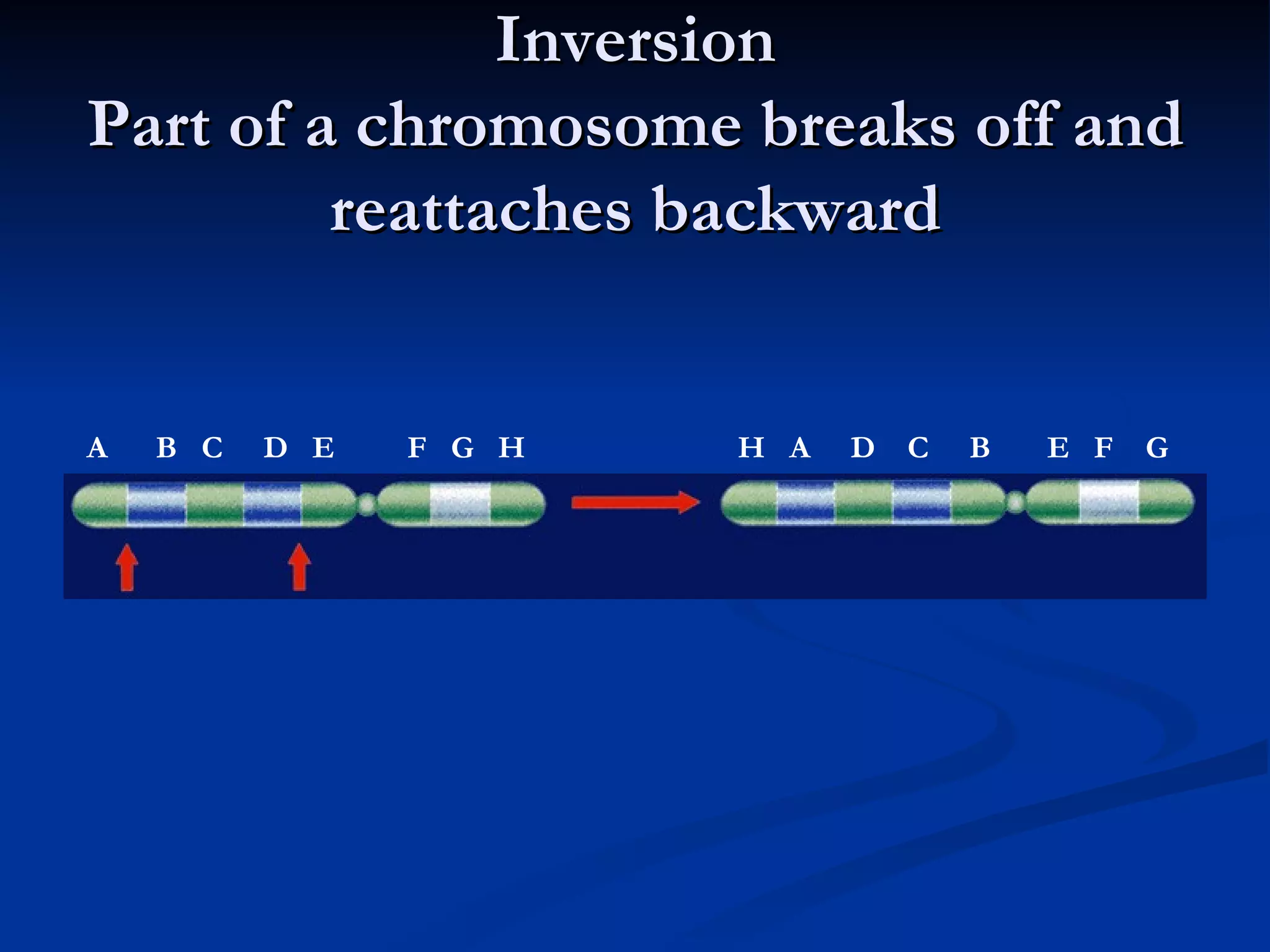
DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms. It is made up of nucleotides with a phosphate group, sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases. DNA replicates through the process of DNA replication in which the double helix unwinds and enzymes add complementary bases to each strand. During protein production, information from DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) which is then translated by ribosomes to produce proteins made of amino acid chains. Mutations can occur through changes in single base pairs or the structure of chromosomes and can be caused by mutagens like radiation, chemicals, or heat.