1. The document discusses different types of computers including desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and others.
2. It describes the uses of computers for tasks like education, business, entertainment, and more.
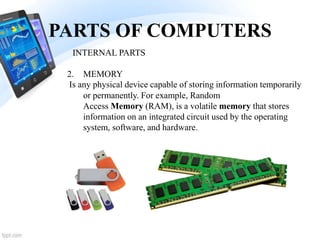
3. The key parts of a computer are discussed as the central processing unit, memory, hard drive, input devices like keyboards and mice, and output devices like monitors.