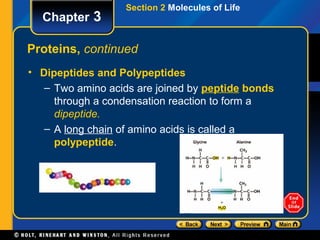
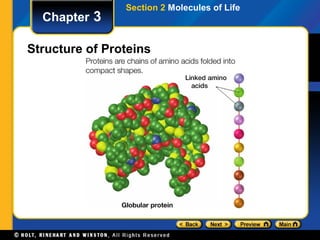
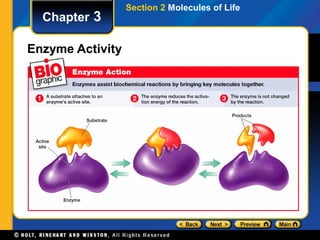
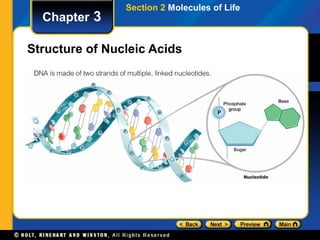
This document provides an overview of the key biomolecules including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. It describes how carbohydrates are made of monosaccharides that join to form disaccharides and polysaccharides. Proteins are made of amino acids that join in chains, and lipids include fatty acids, triglycerides, and phospholipids. The document also compares DNA and RNA as the two main types of nucleic acids.