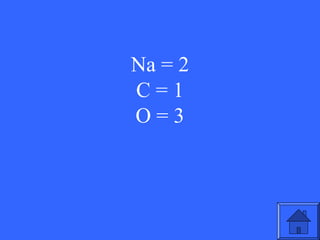This document contains a quiz over various topics in general chemistry, atomic chemistry, and water chemistry. It includes 50 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of subatomic particles, chemical bonding, acids and bases, isotopes, and other foundational chemistry concepts. For each question, the correct answer is provided.