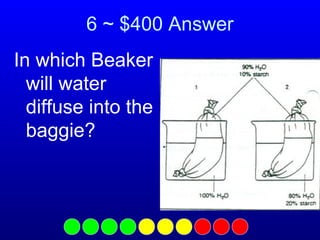
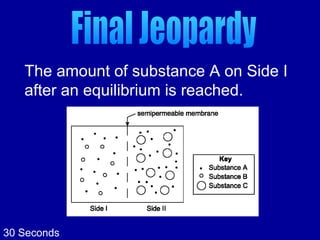
The document contains questions and answers about cell transport mechanisms. It covers topics like osmosis, diffusion, passive transport, active transport, and the role of the cell membrane. The questions progress from simpler concepts to more complex topics involving transport directionality and cellular responses to different solution concentrations.