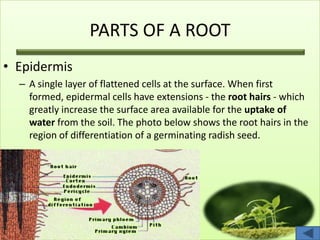
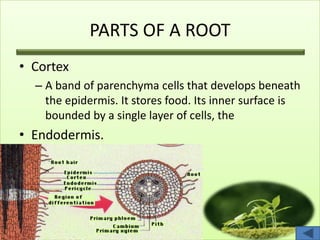
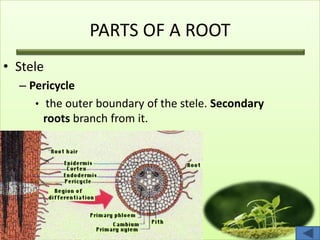
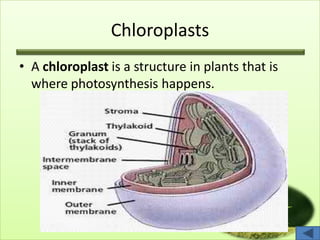
The document summarizes the main plant organs systems. It discusses that the plant body consists of shoot and root systems. The shoot system includes leaves, stems, flowers and fruits and develops above ground, carrying out photosynthesis, reproduction, storage and transport. The root system includes roots and develops underground, providing anchorage, absorption, storage and transport. It then proceeds to describe the main parts and functions of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits in detail.