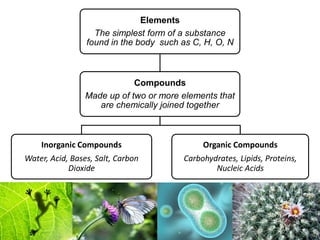
This document discusses biological molecules, including their classification, structure, and functions. It covers the main types of biological molecules:
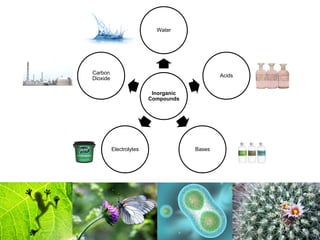
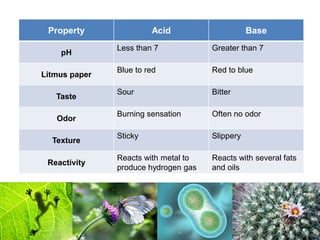
1) Inorganic molecules like water, acids, bases, electrolytes, and carbon dioxide which are essential for life processes. Water acts as a solvent and is crucial for chemical reactions in the body.
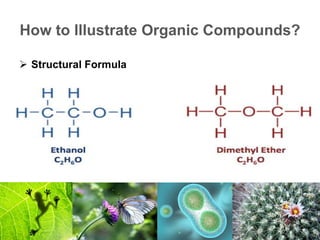
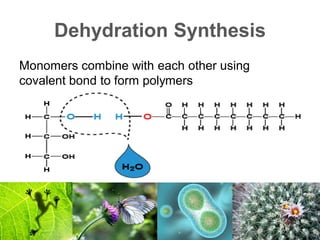
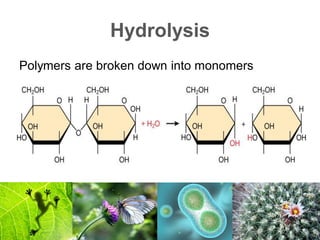
2) Organic macromolecules including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids which are polymers formed from smaller organic subunits. Carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are synthesized through dehydration reactions between monomers.
3) The four main classes of biological macromolecules each have distinct monomeric subunits and play critical structural or functional