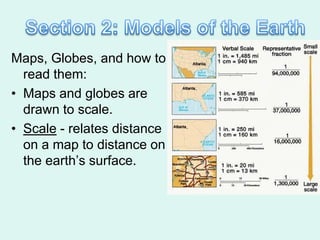
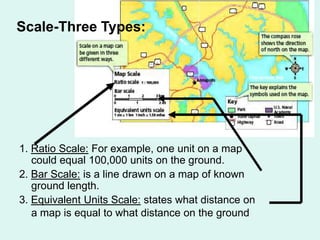
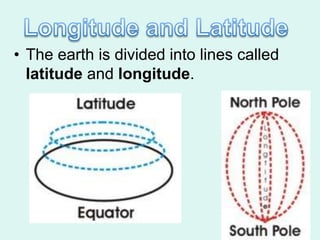
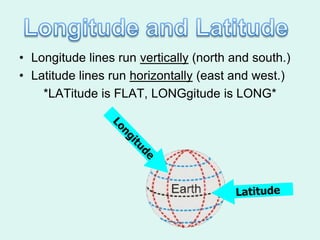
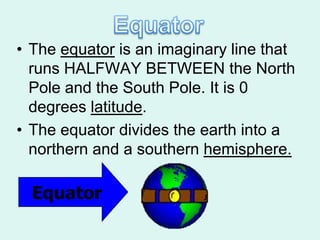
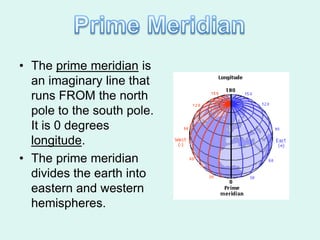
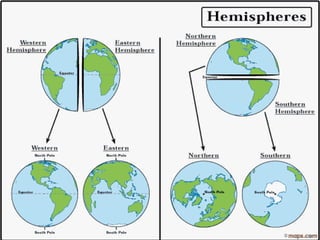
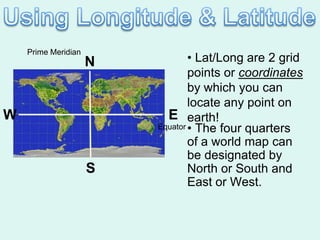
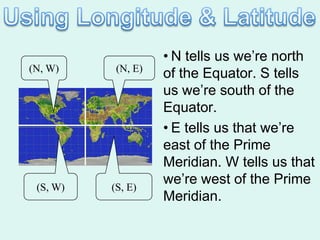
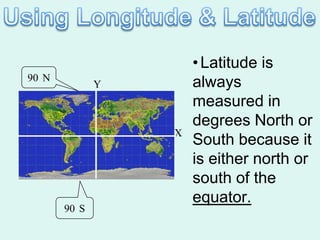
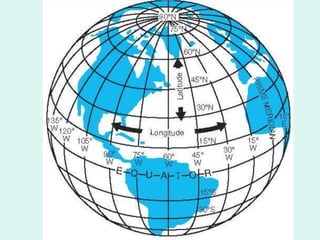
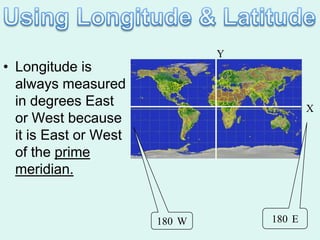
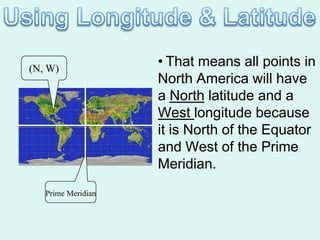
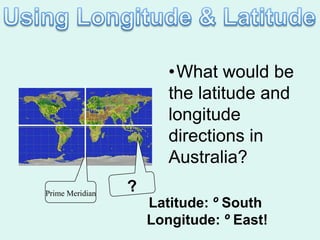
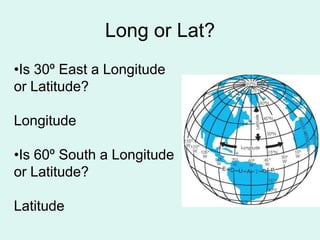
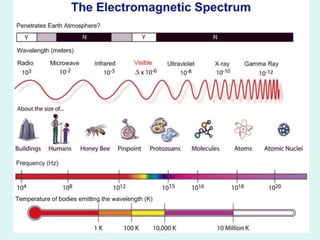
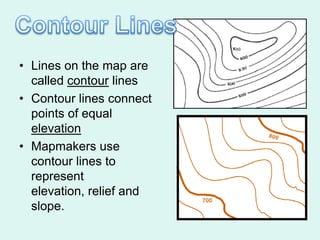
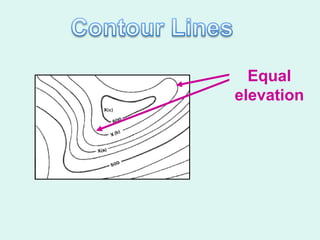
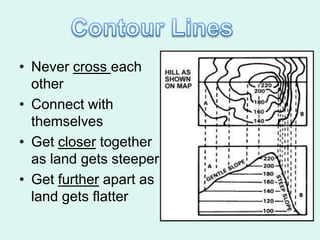
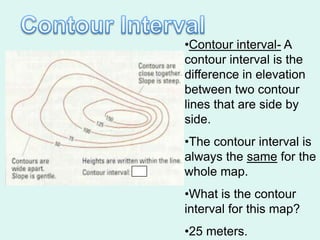
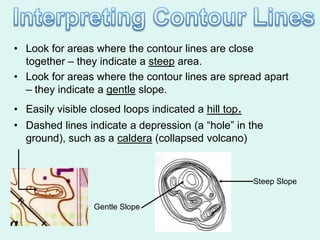
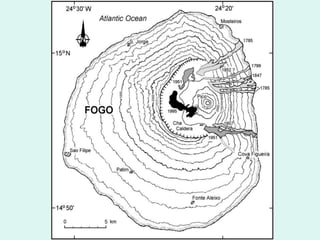
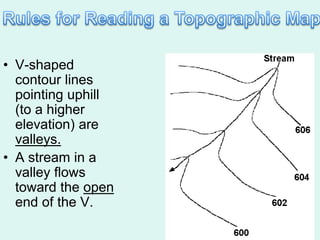
The document discusses how to read maps and globes. It explains key concepts like scale, latitude and longitude, and how they are used to locate points on maps and globes. Specifically, it details how latitude is measured north and south of the equator in degrees, and longitude is measured east and west of the prime meridian in degrees. Topographic maps represent elevation using contour lines that connect points of equal height.