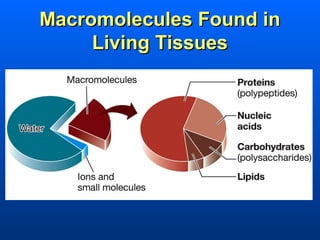
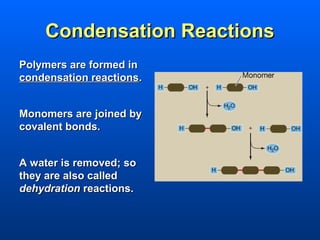
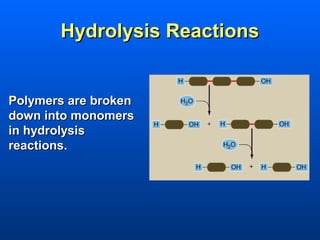
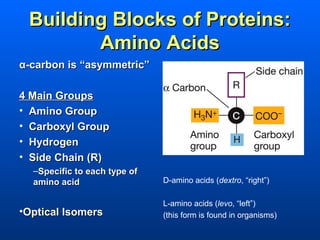
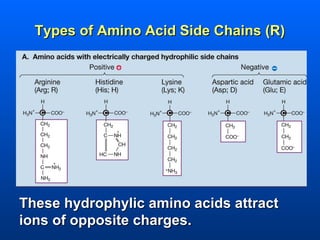
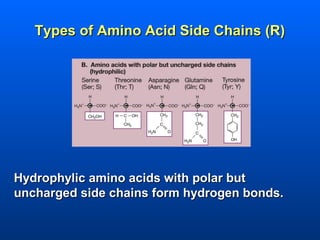
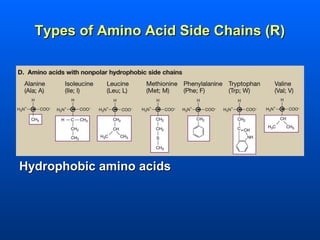
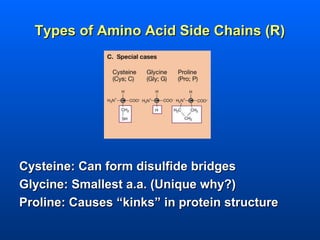
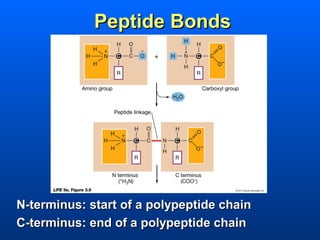
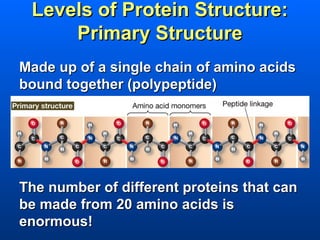
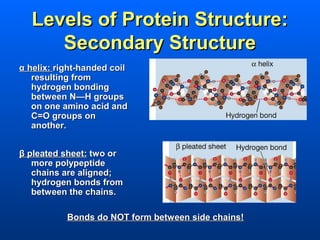
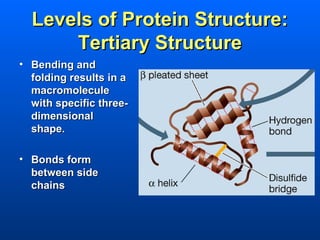
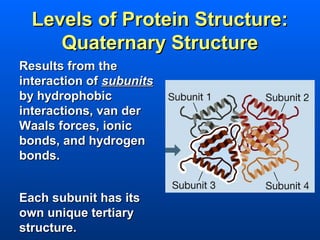
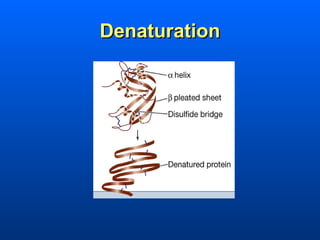
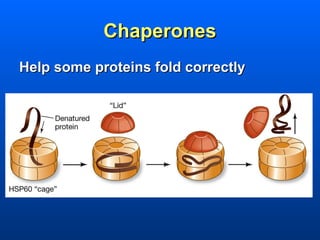
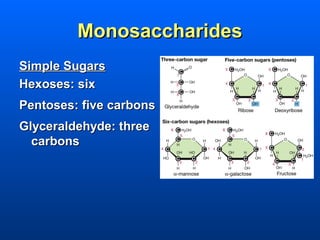
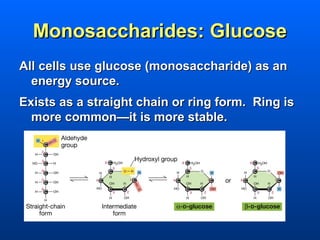
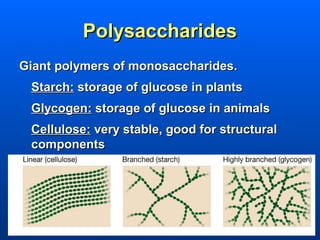
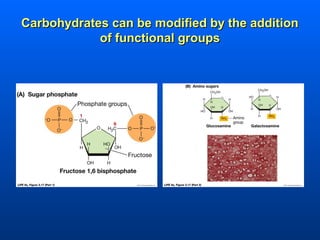
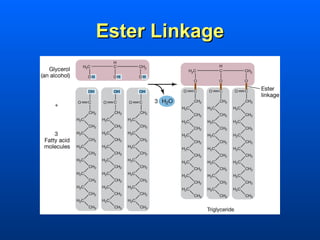
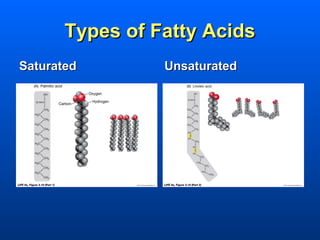
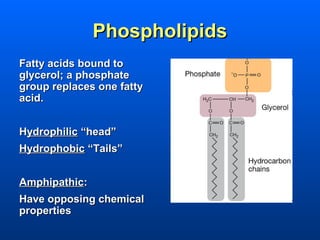
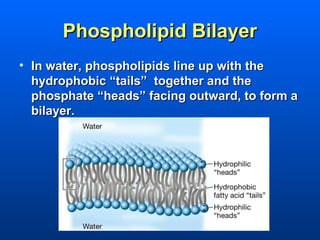
This document discusses macromolecules and their structure and function. It focuses on proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Proteins are polymers of amino acids and their structure ranges from primary to quaternary levels. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides like starch and cellulose. Lipids are nonpolar and include triglycerides, fatty acids, and phospholipids that form cell membranes. The document explains the structure and properties of these macromolecules.