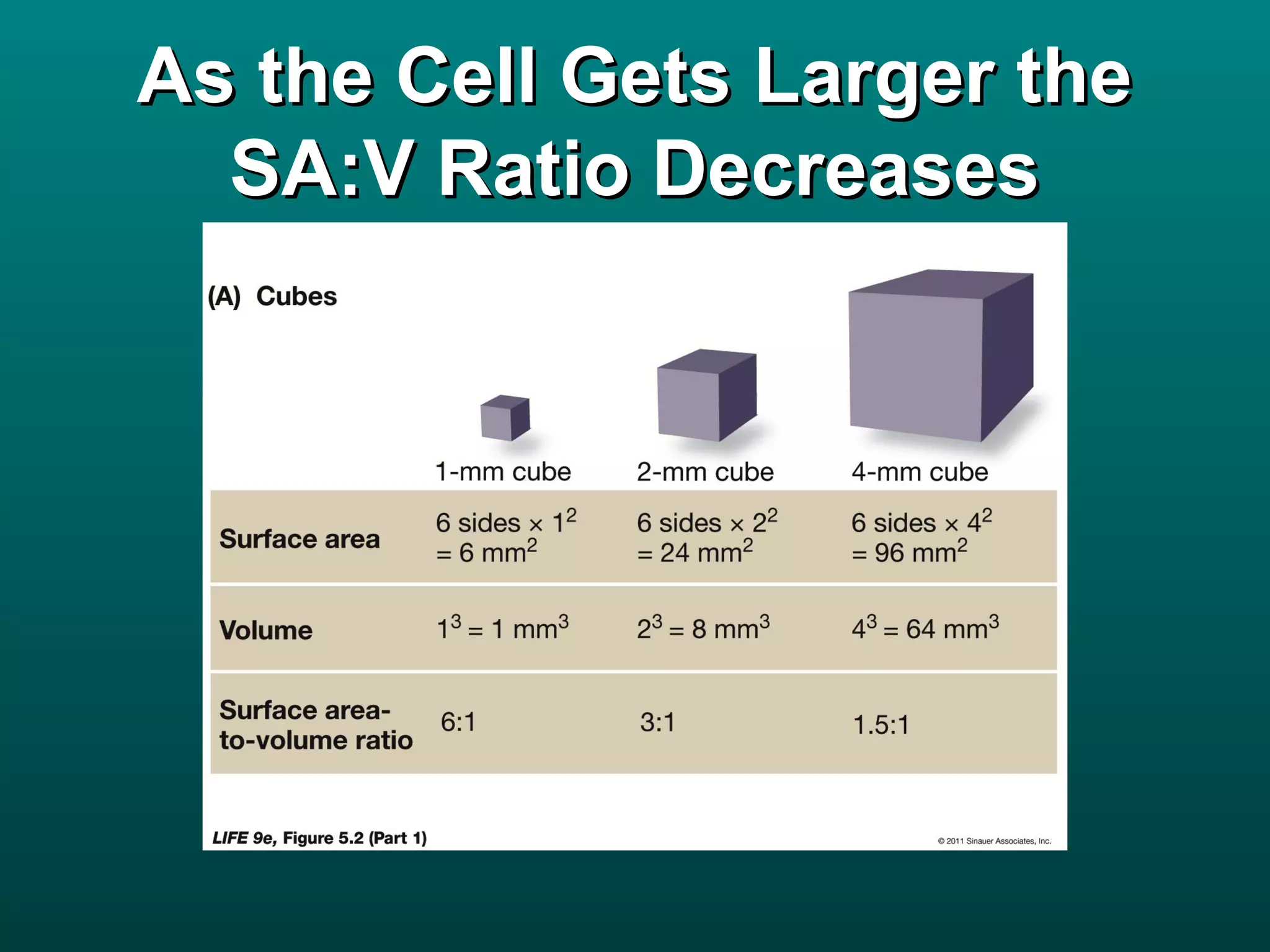
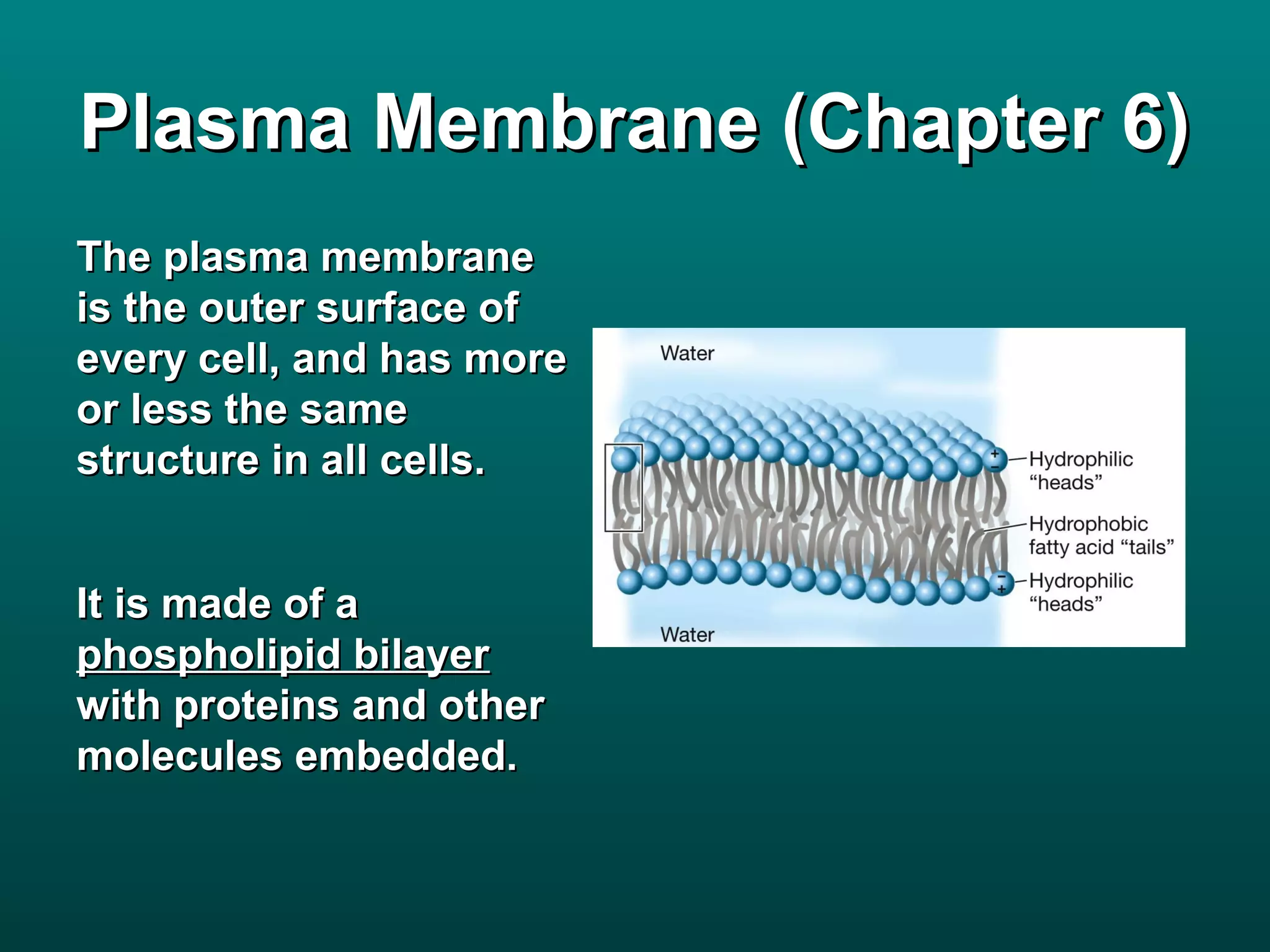
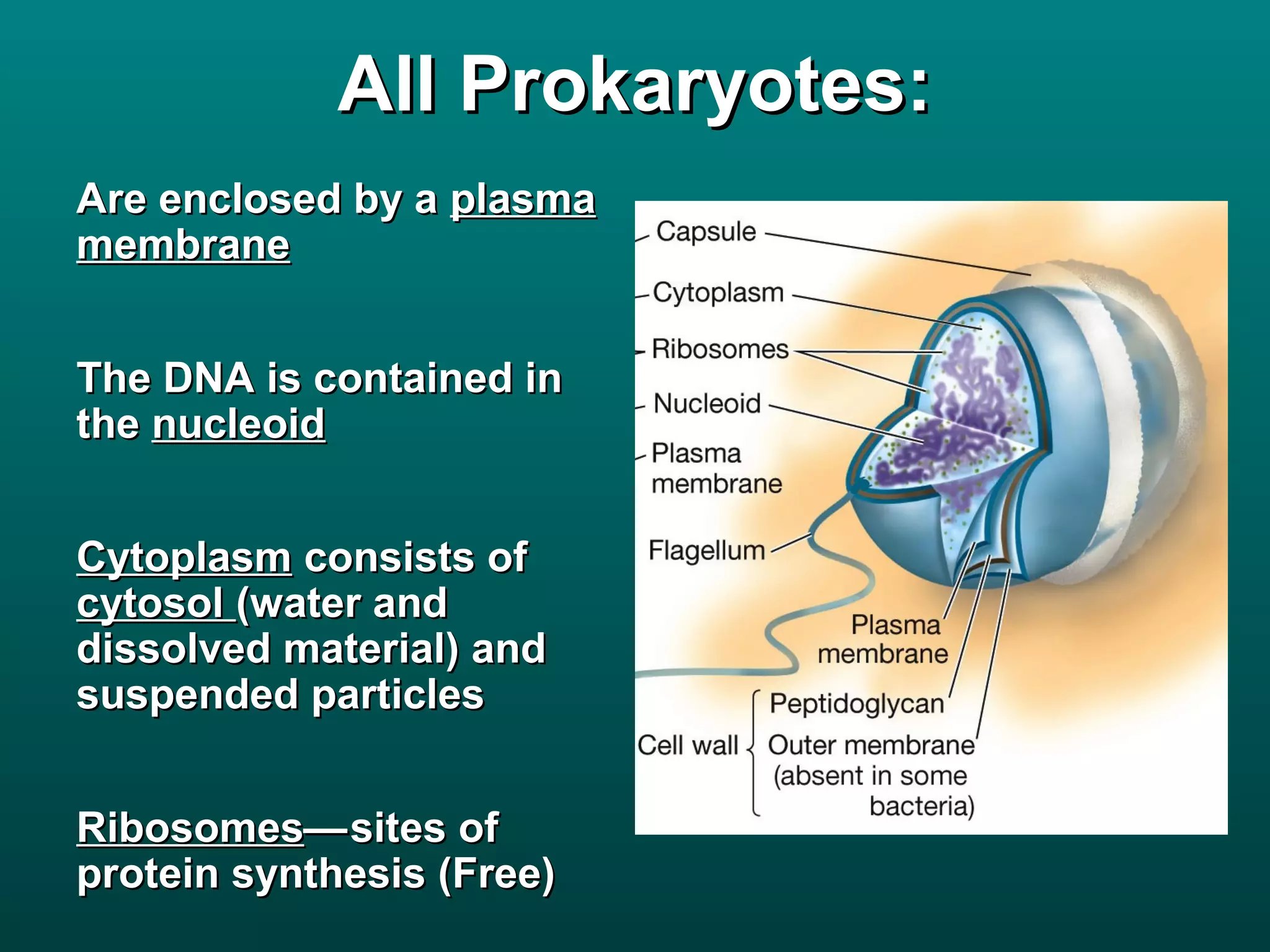
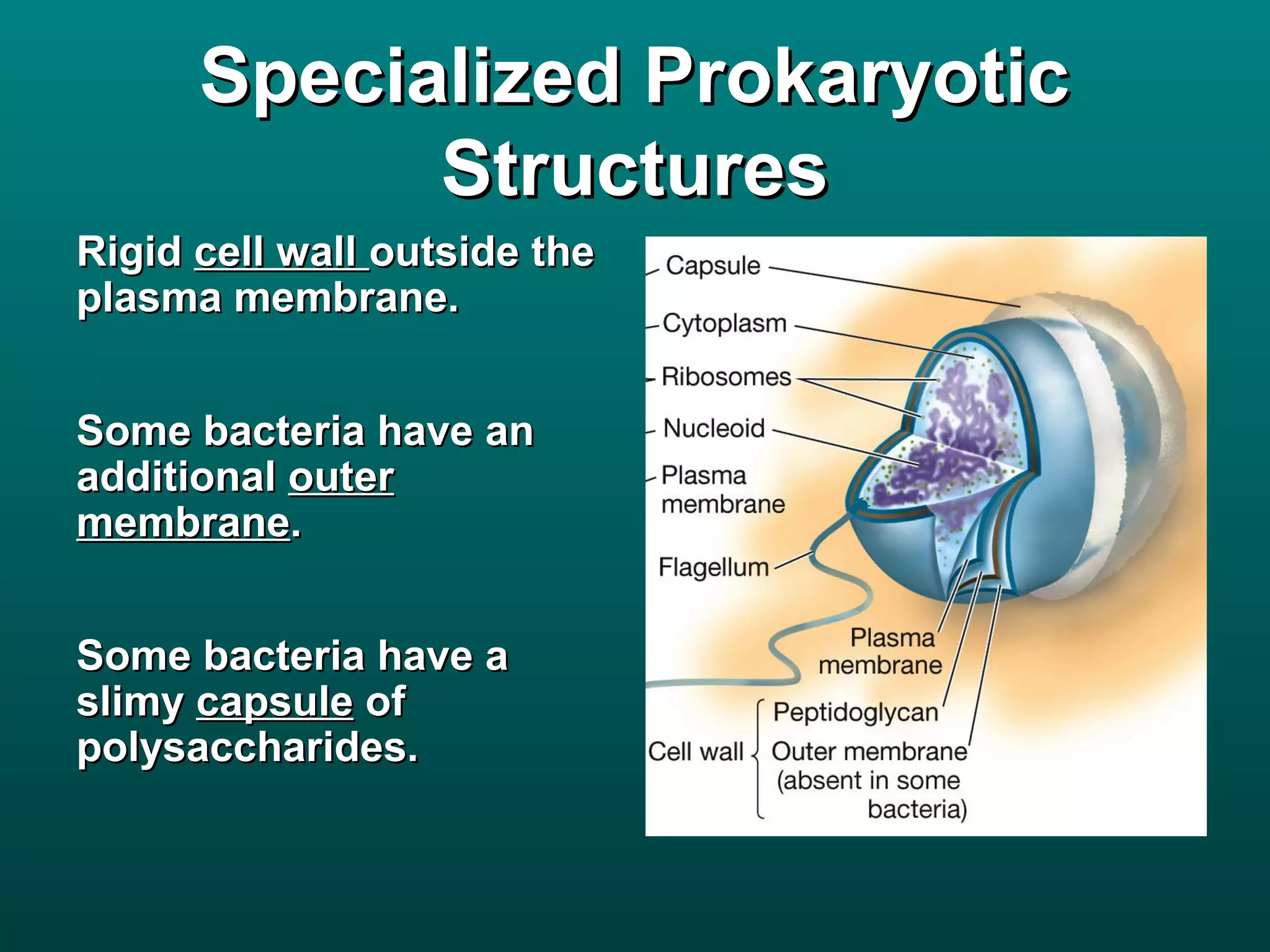
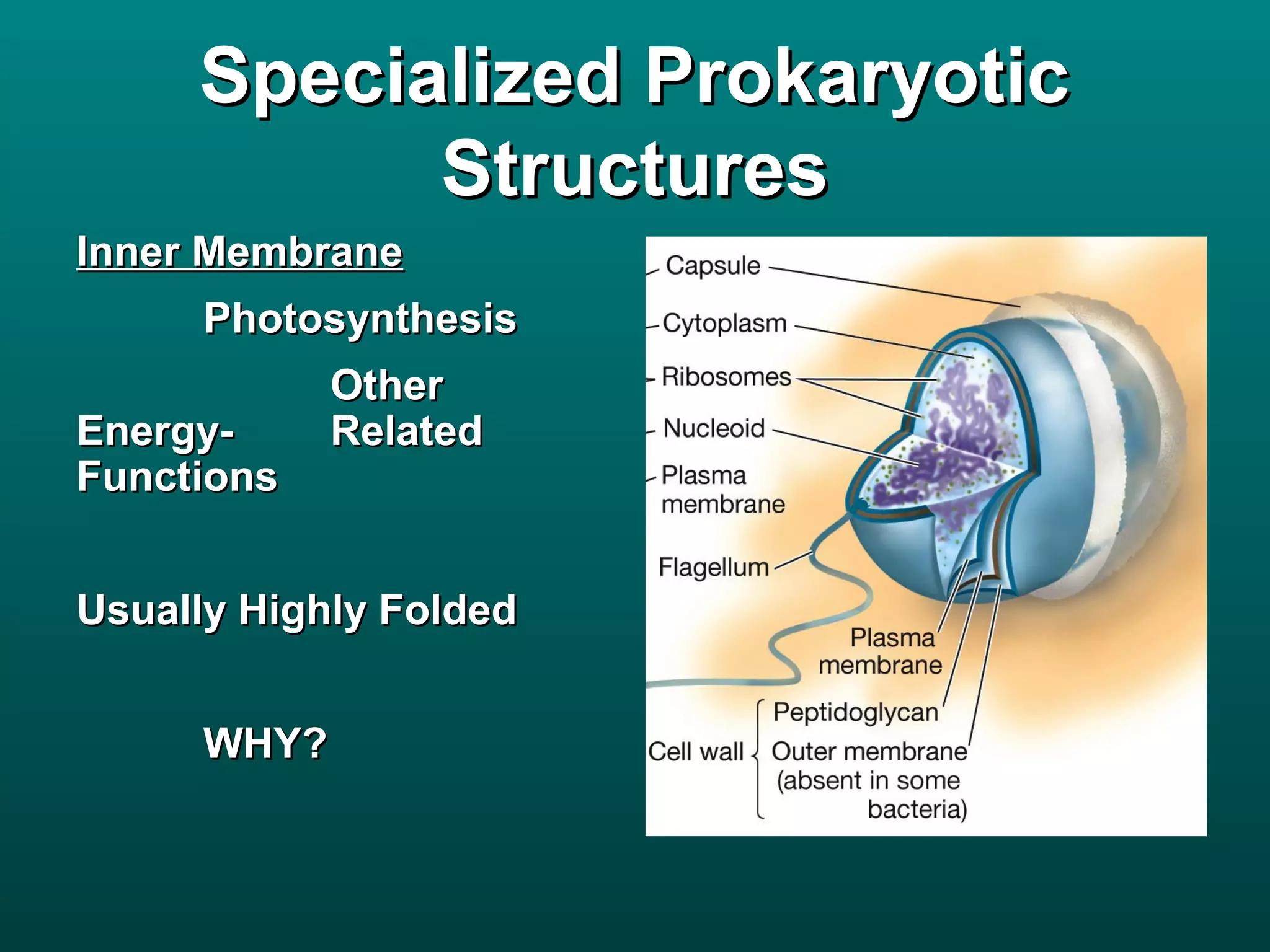
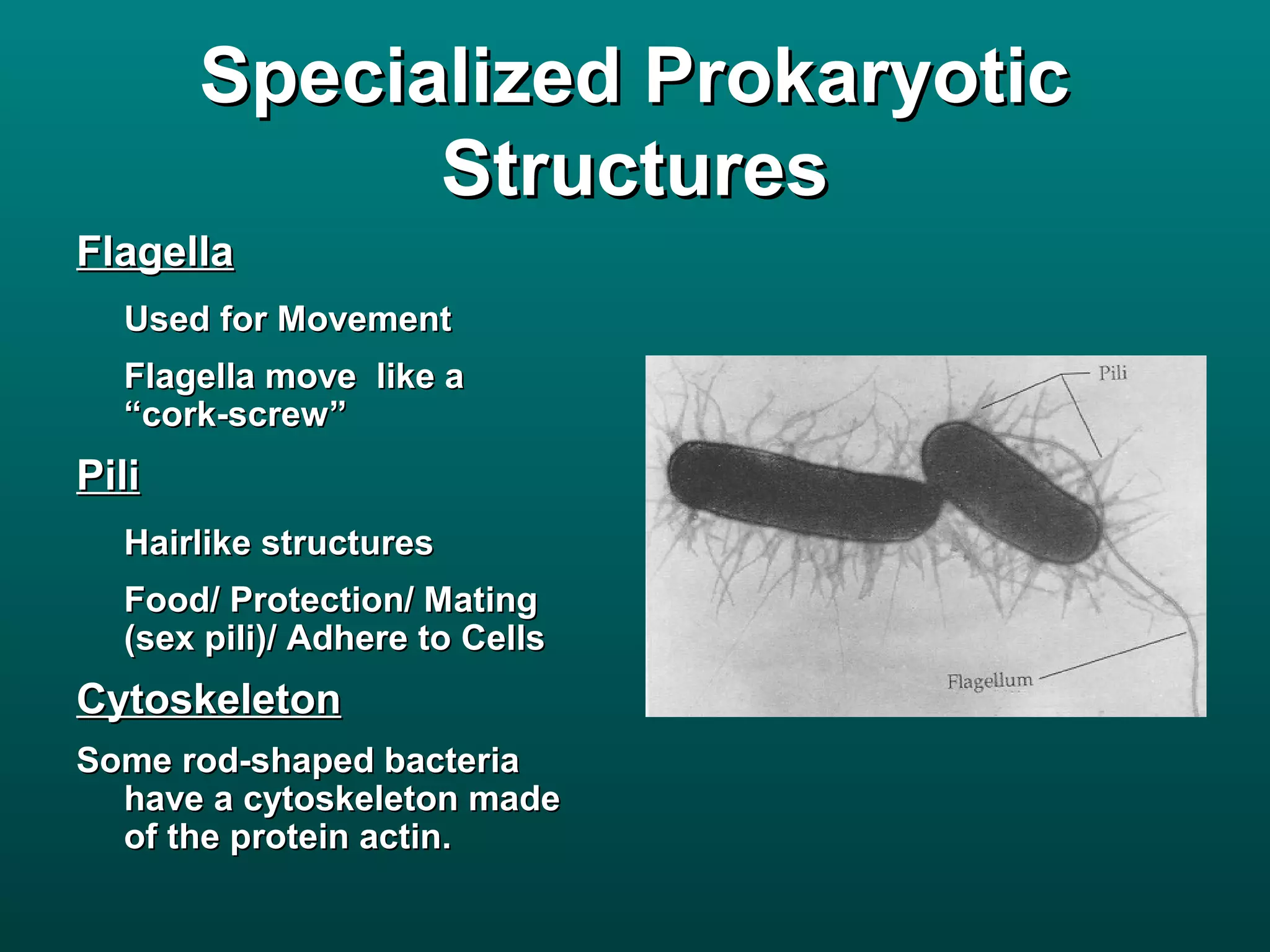
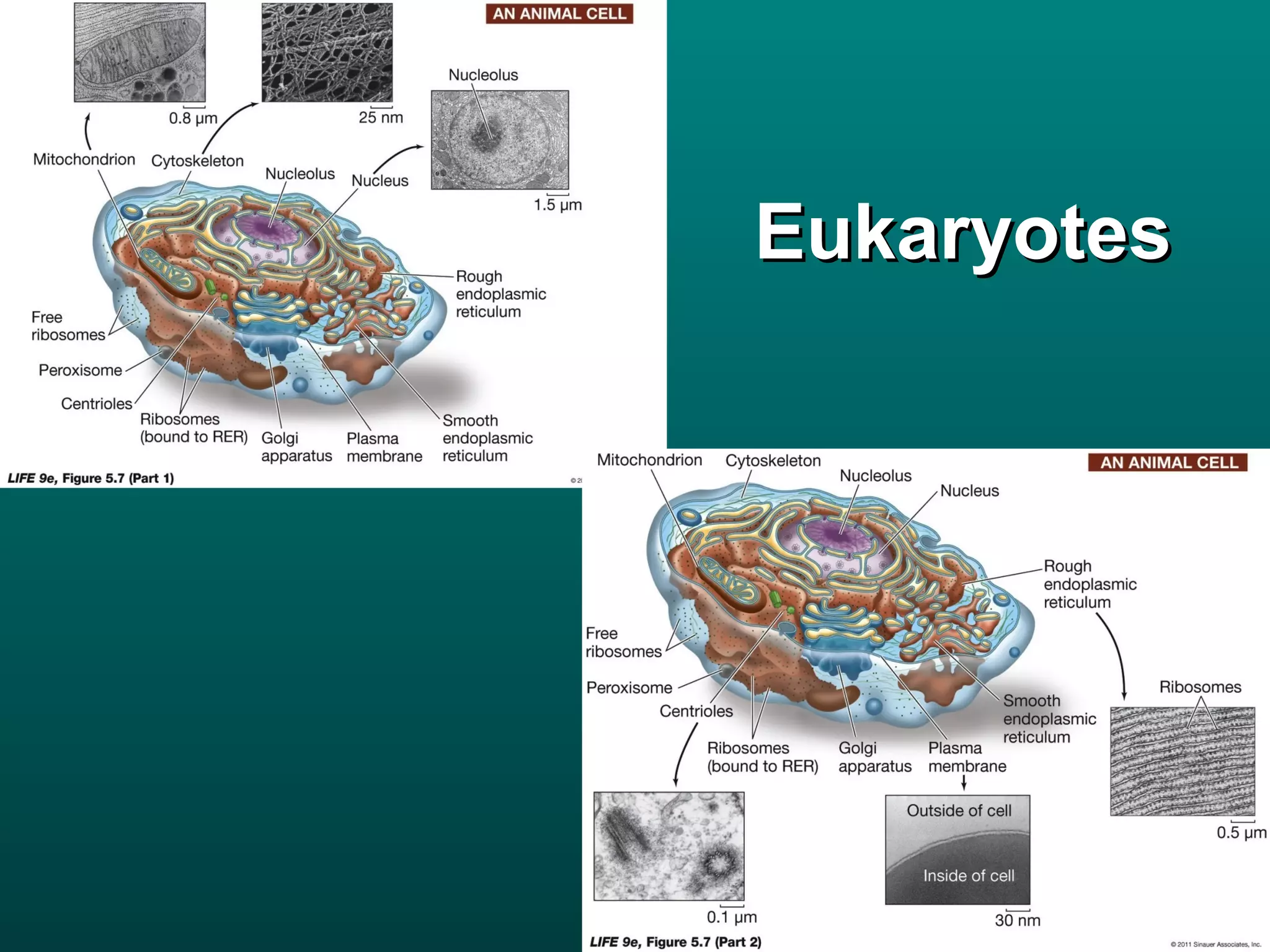
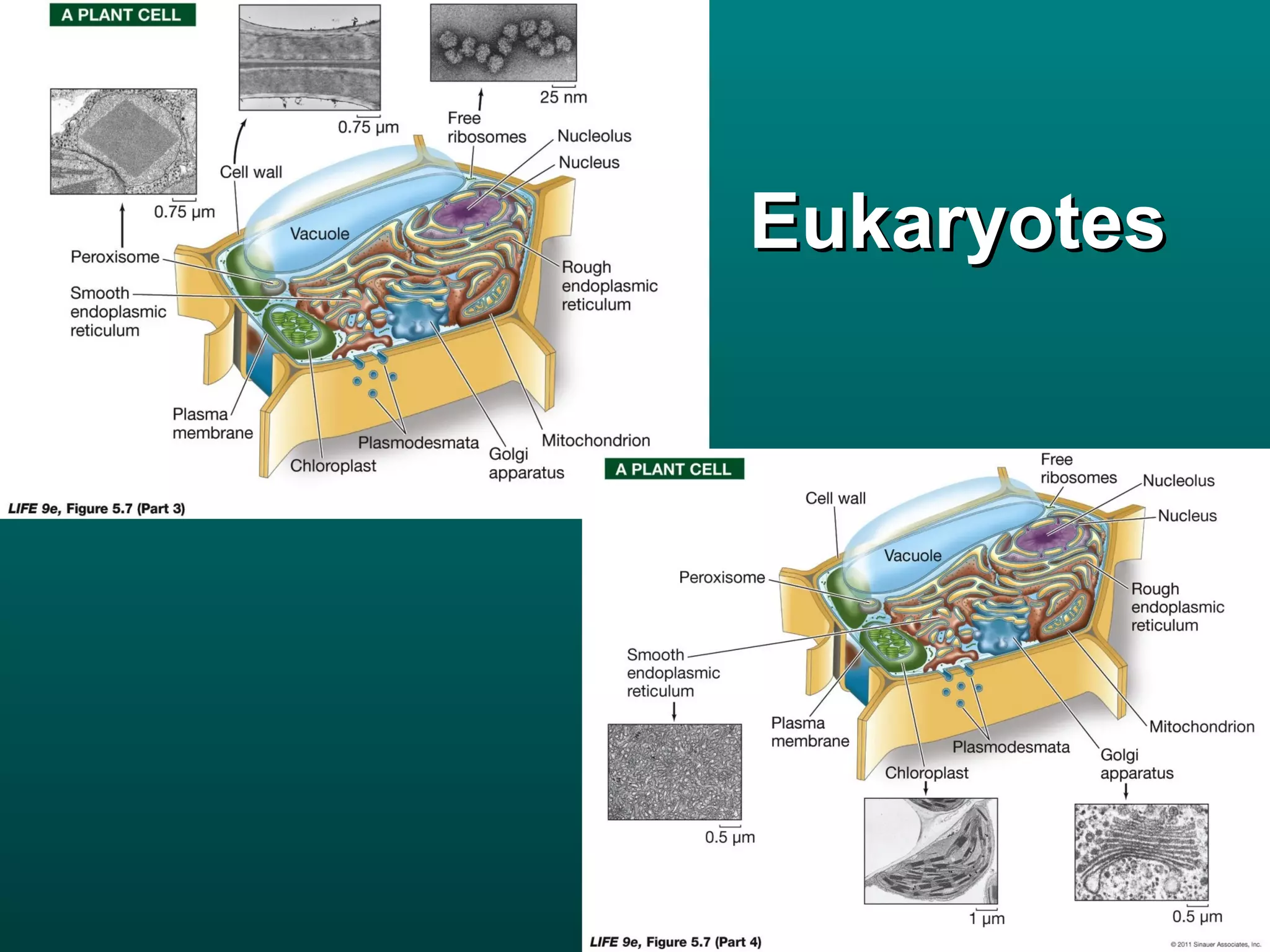
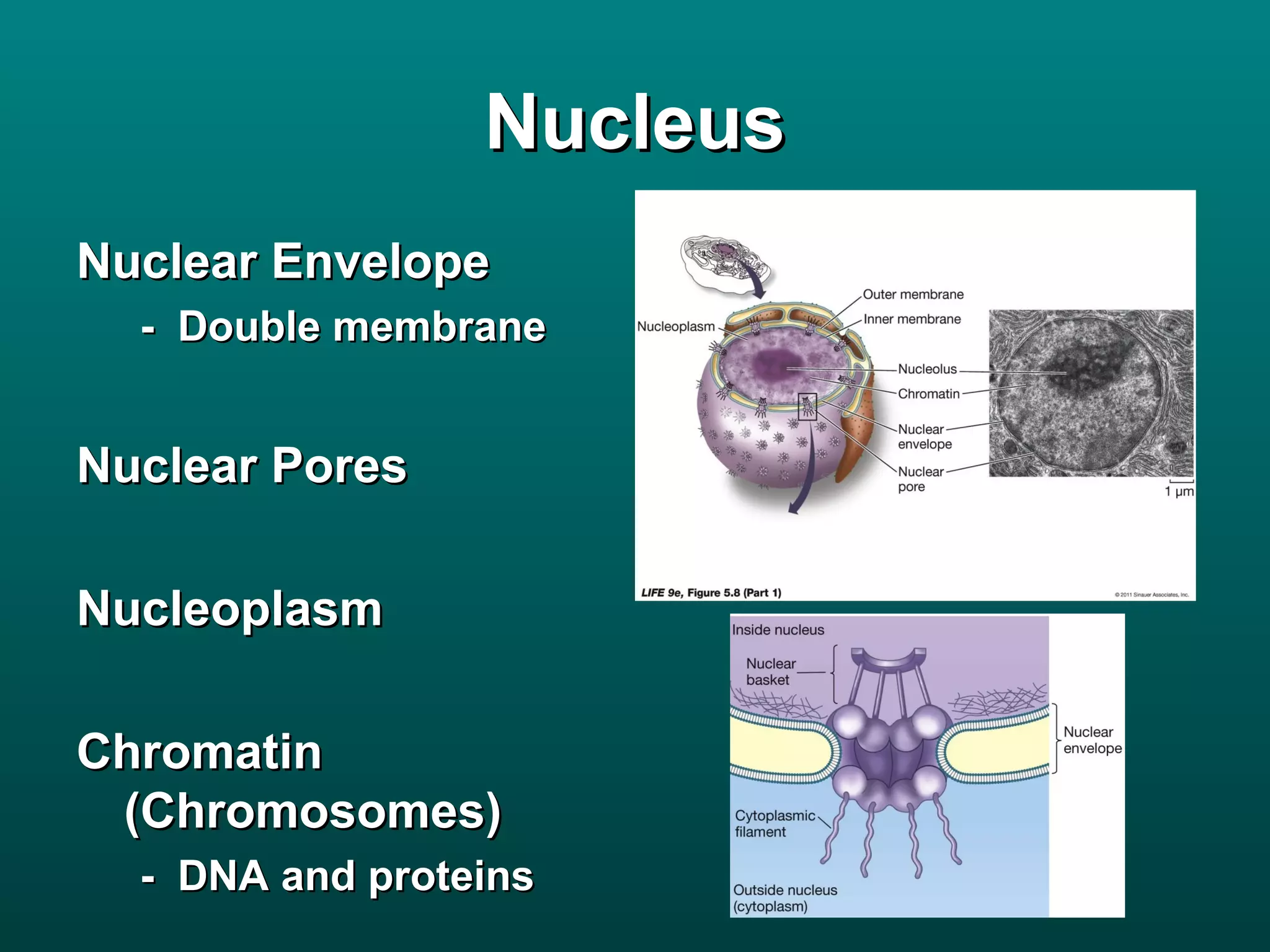
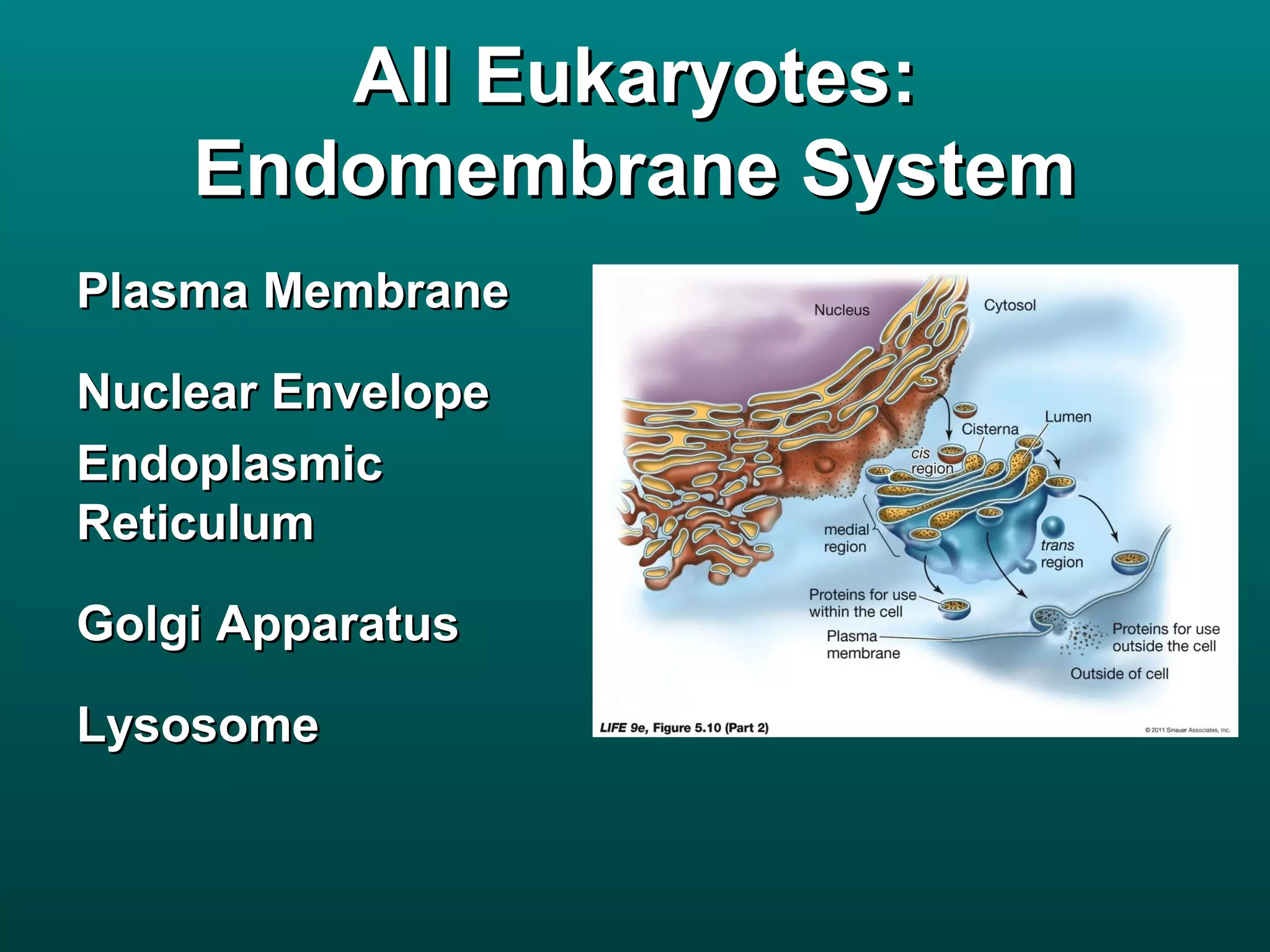
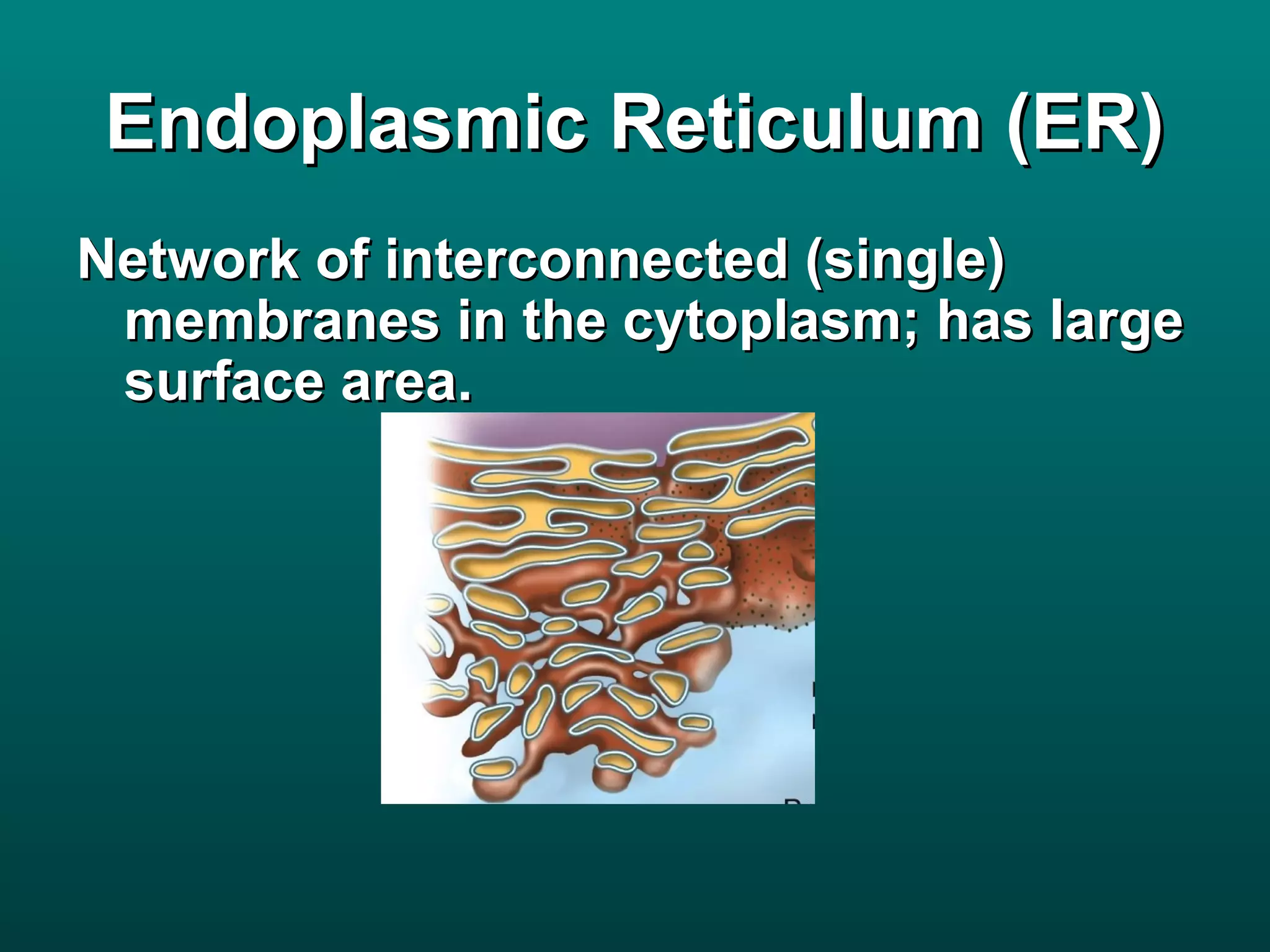
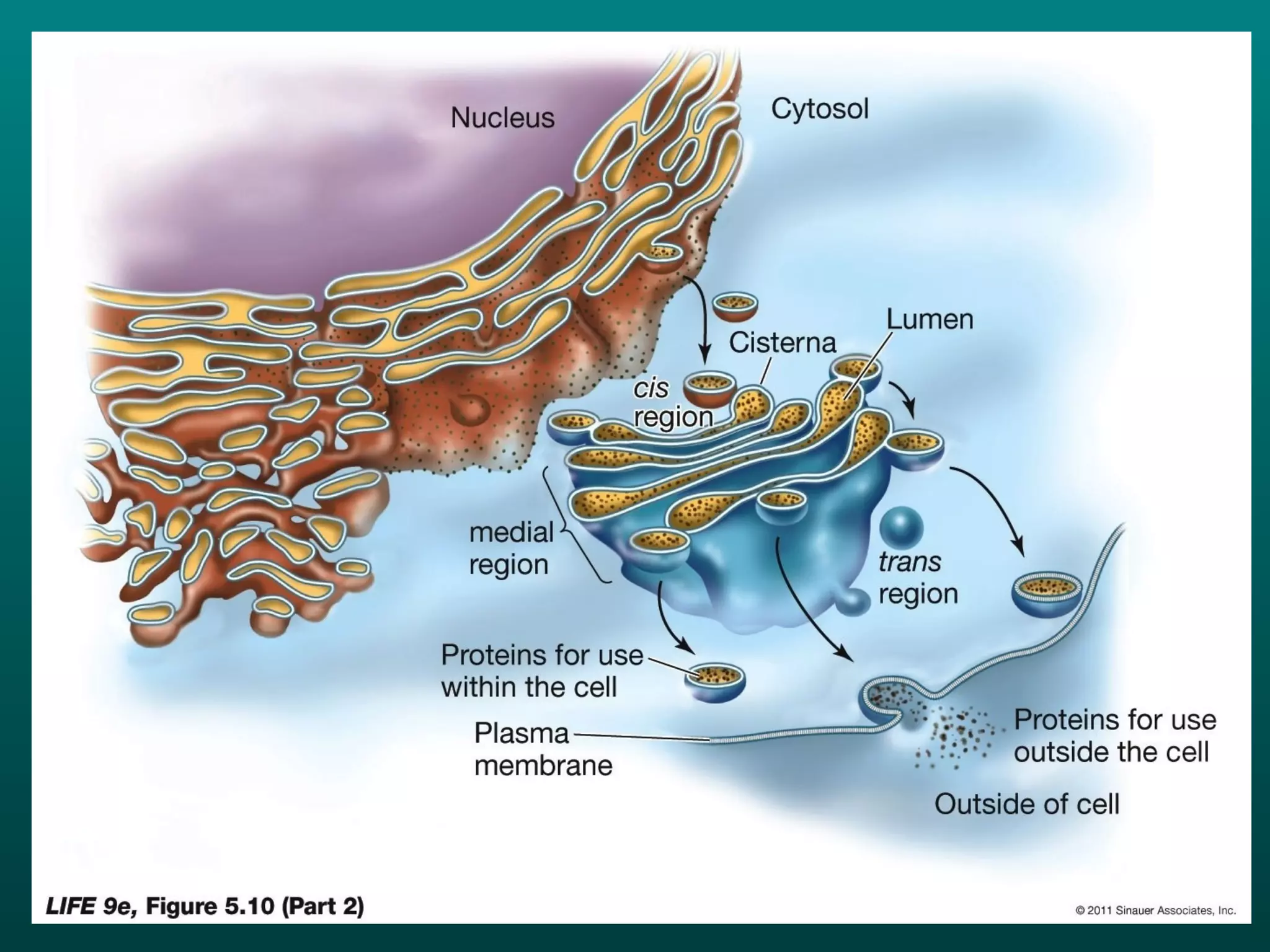
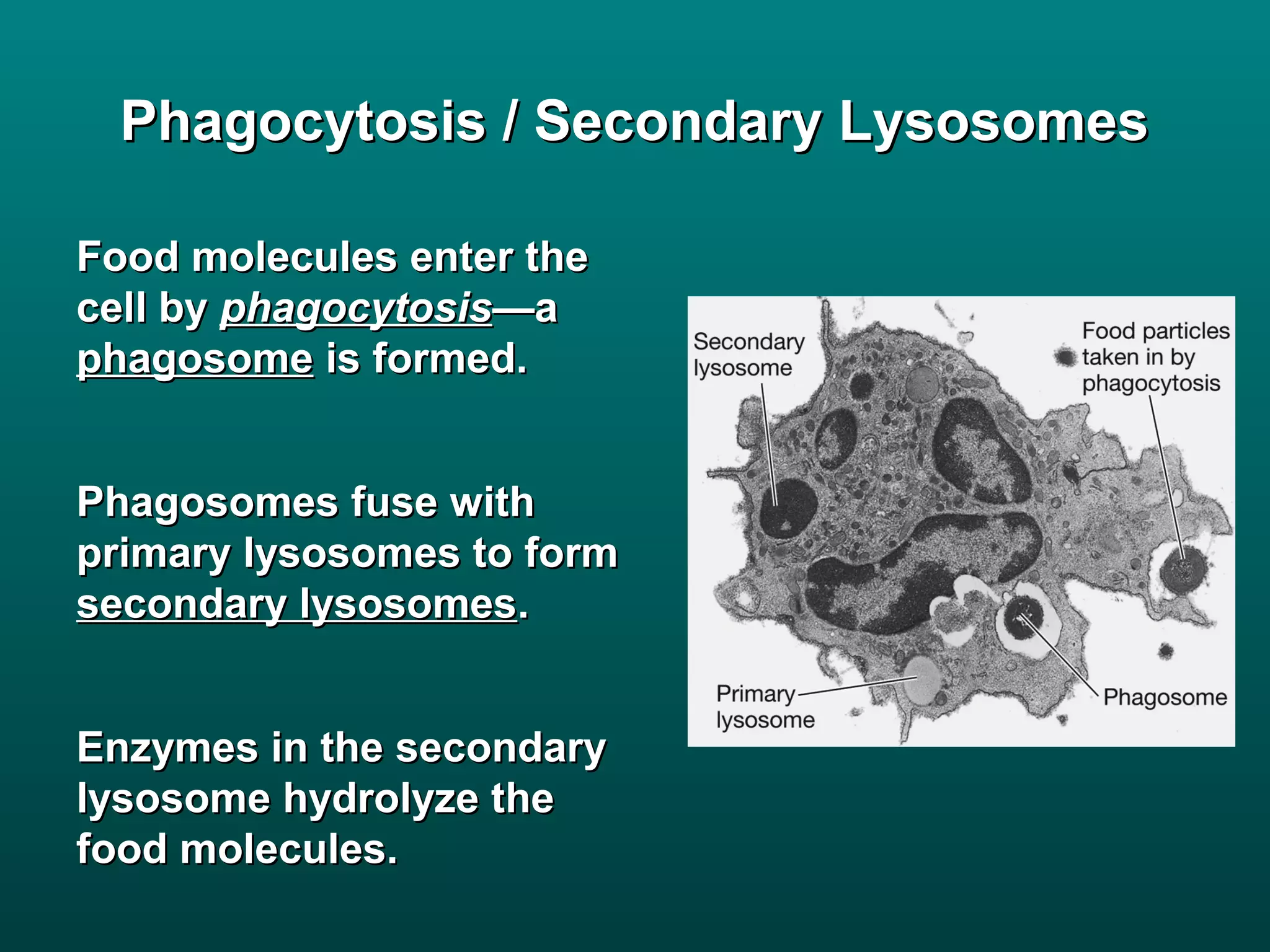
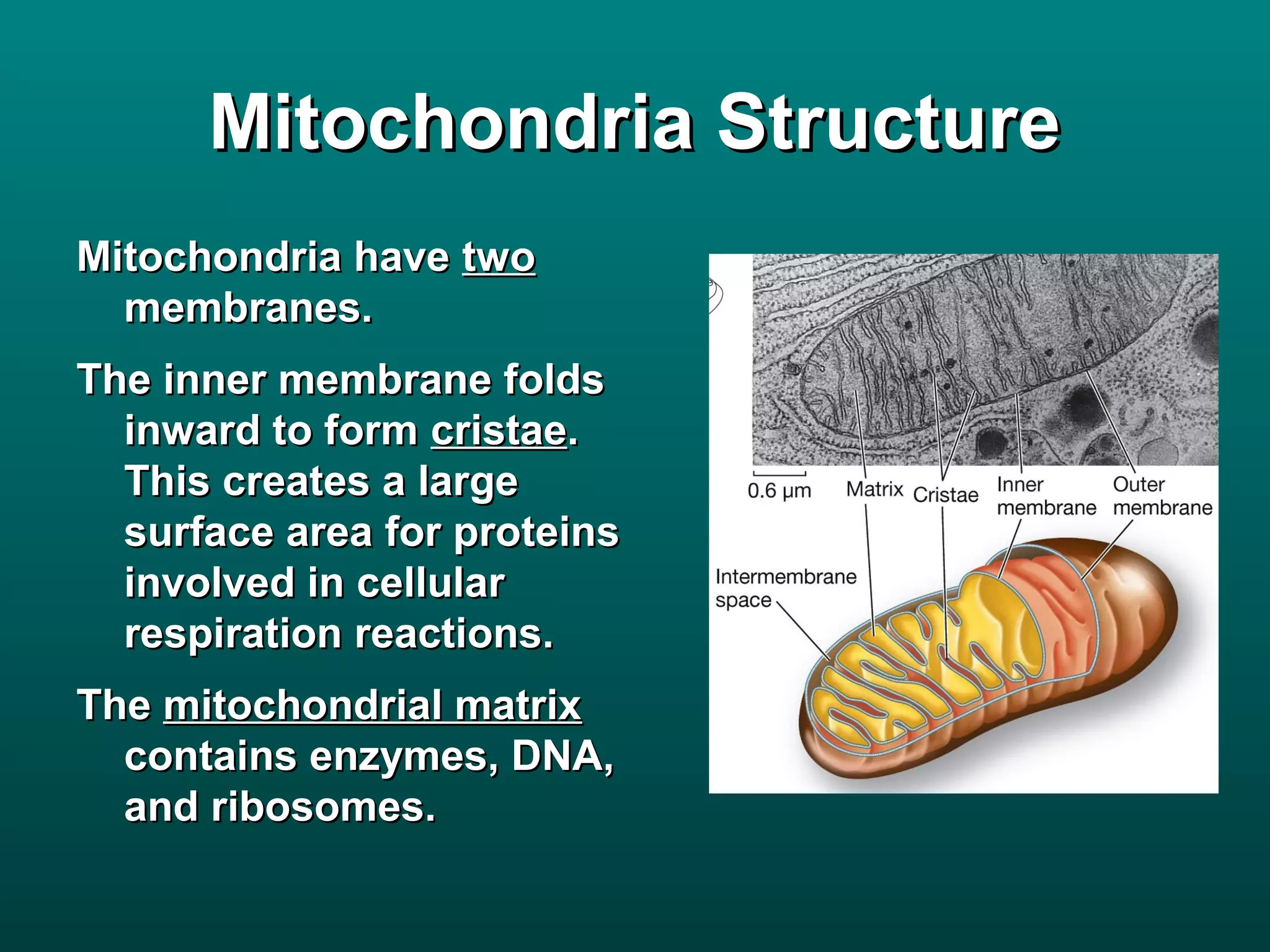
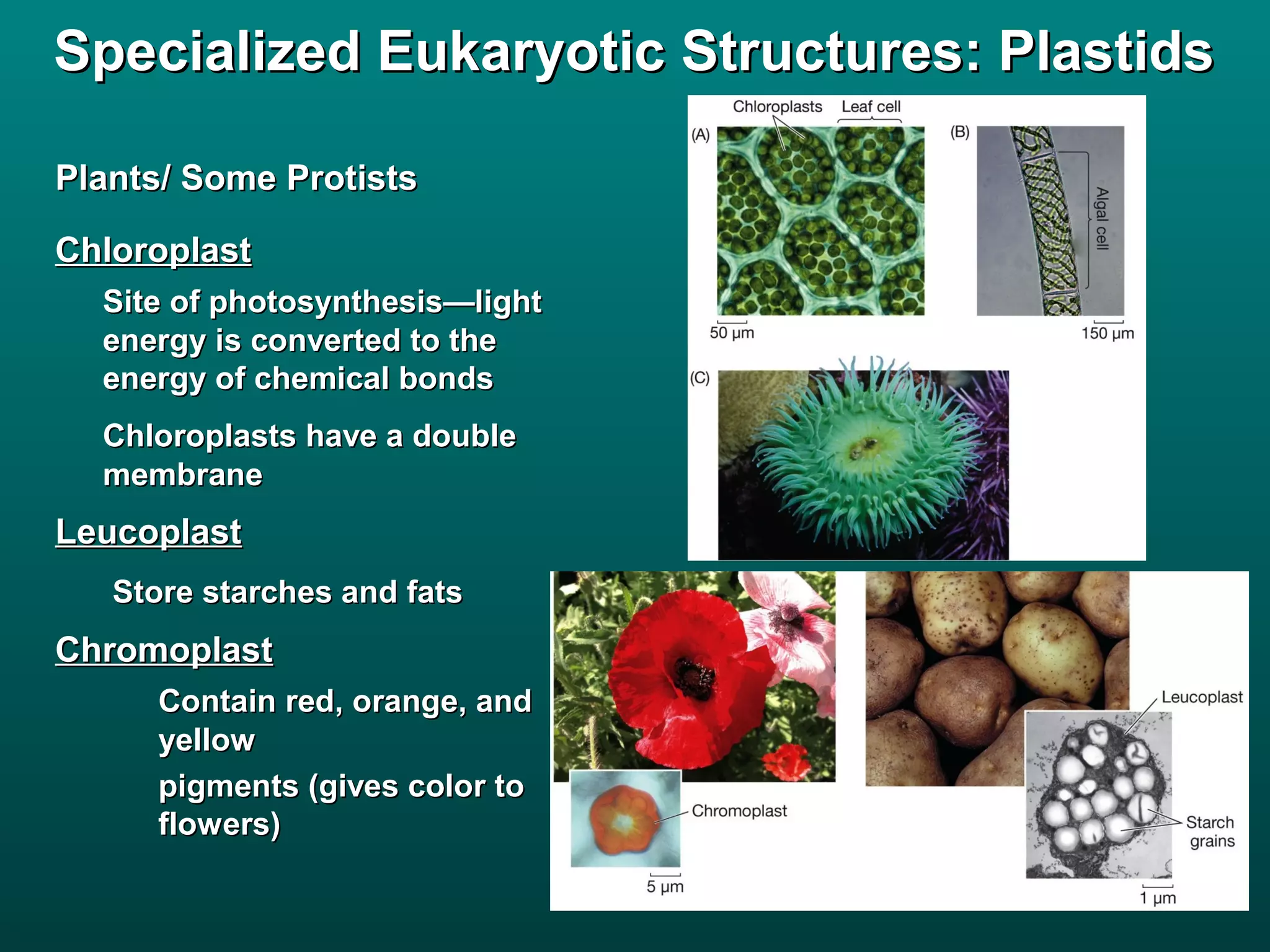
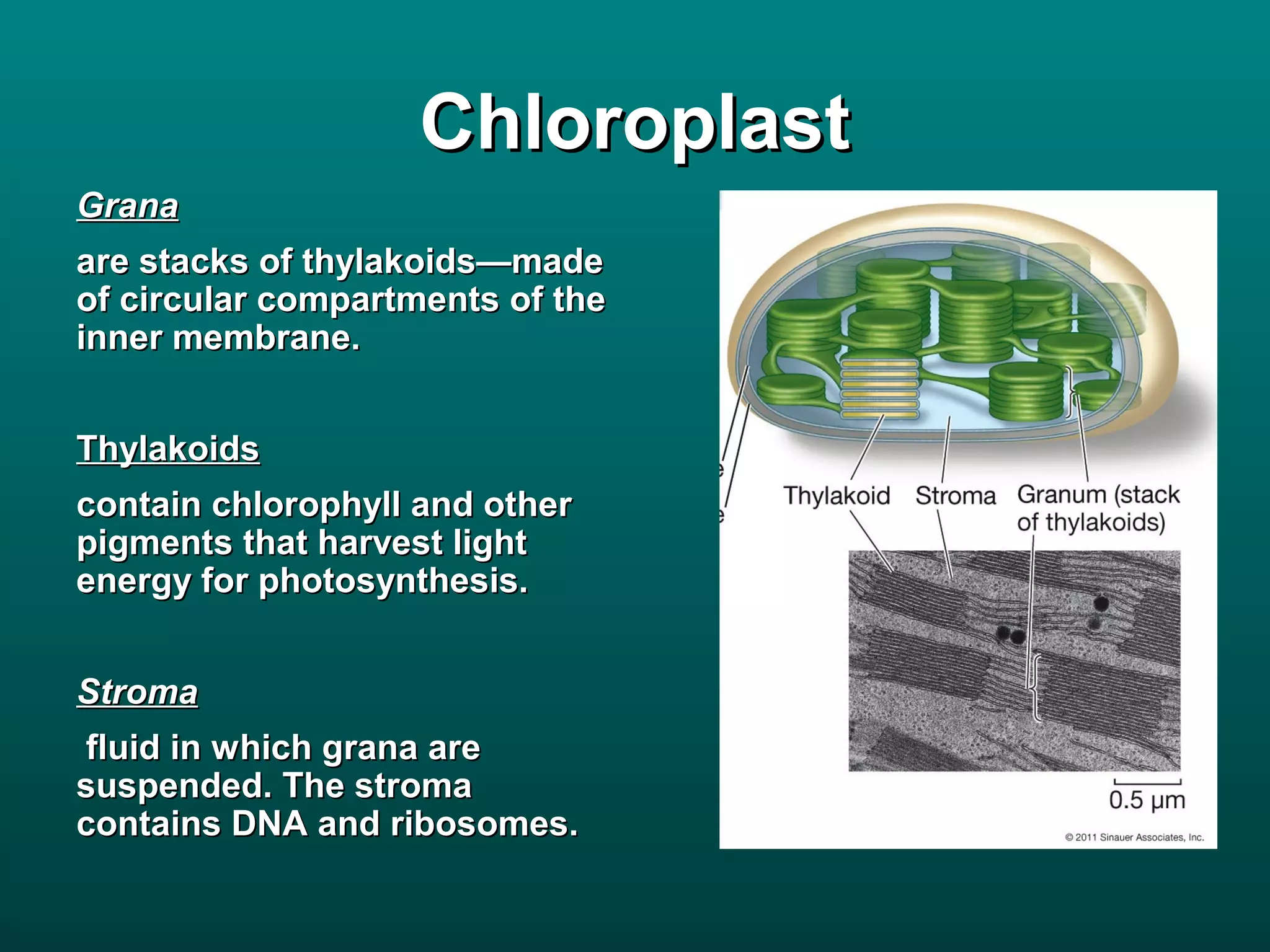
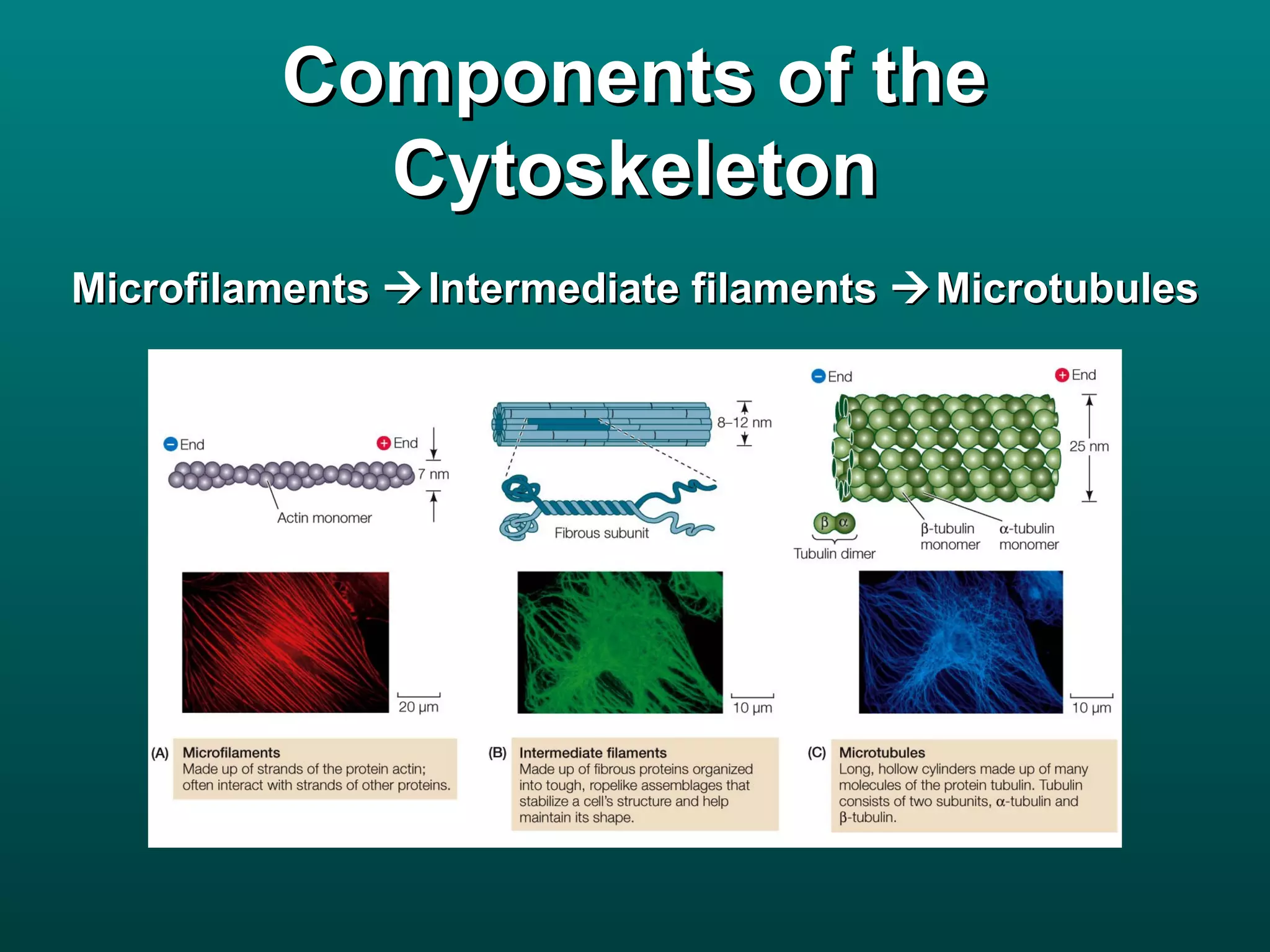
Cells are small to maintain a high surface area to volume ratio which allows for efficient exchange of substances. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic cells which are smaller and lack organelles, and eukaryotic cells which are larger and have membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized functions. Key organelles in eukaryotic cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, cytoskeleton, and vacuoles.