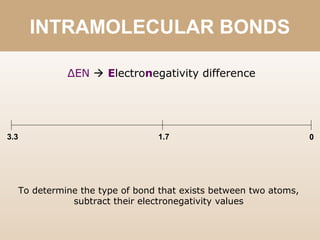
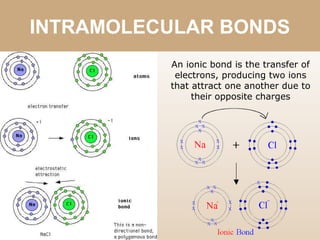
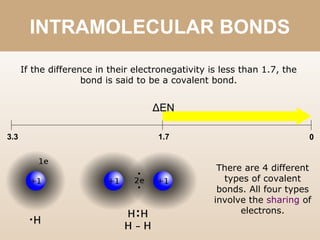
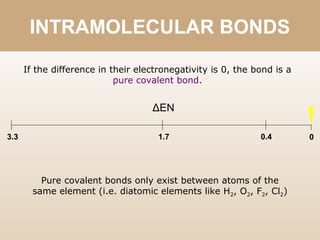
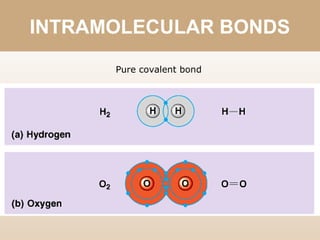
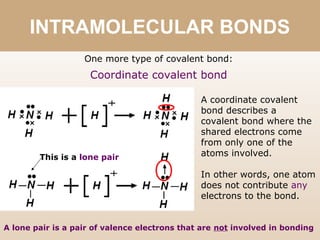
The document discusses different types of bonds between atoms. An ionic bond forms when there is a large electronegativity difference (>1.7) between atoms, causing one atom to transfer an electron to the other and form ions. A covalent bond forms when the electronegativity difference is less than 1.7, and involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Covalent bonds can be polar covalent if the difference is 1.7-0.4, nonpolar covalent if the difference is <0.4, or pure covalent between like atoms. A coordinate covalent bond involves one atom contributing both electrons through a lone pair.