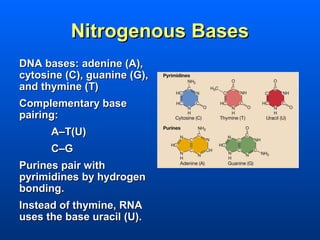
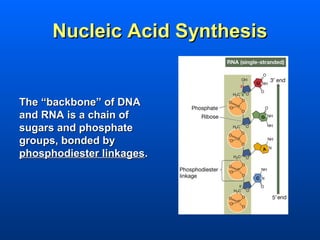
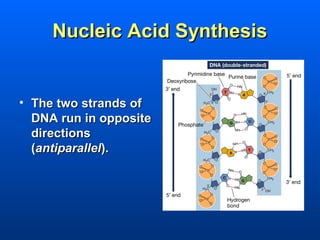
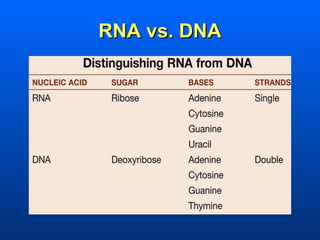
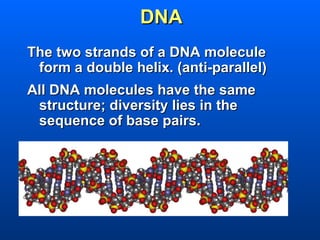
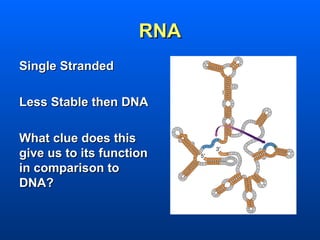
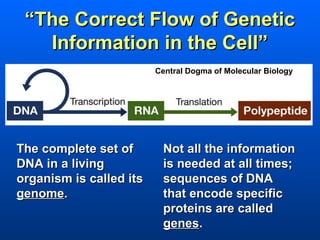
This document discusses nucleic acids and their role in genetic information. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are made up of nucleotides and store and transmit genetic information. DNA exists as a double helix with complementary base pairing between adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine. RNA is single stranded and less stable than DNA, suggesting it plays a role in expressing genetic information from DNA. The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins.