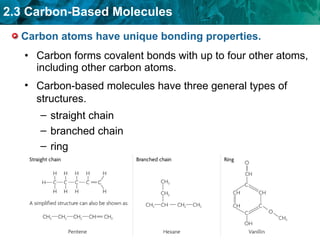
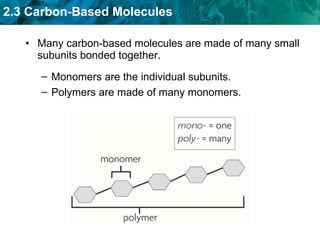
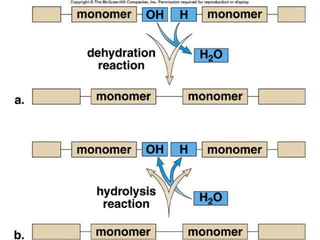
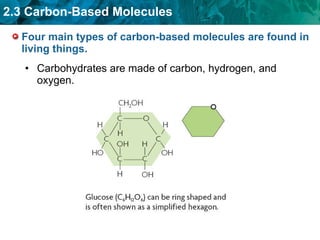
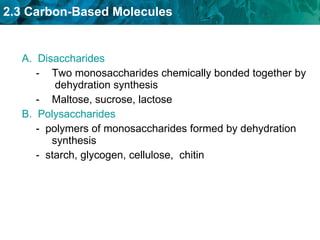
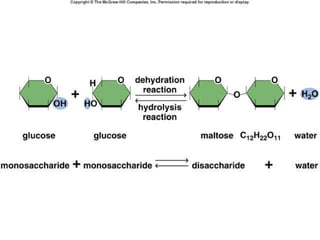
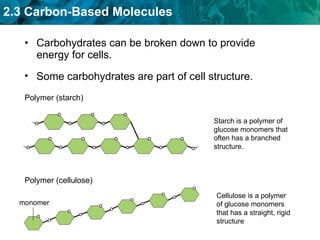
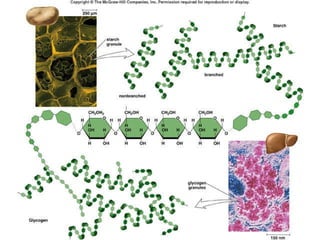
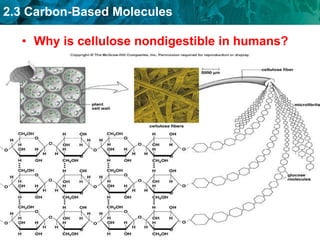
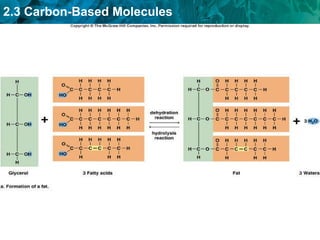
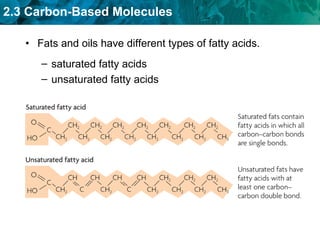
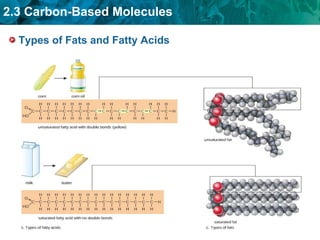
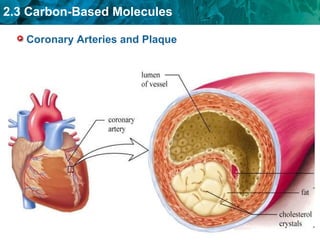
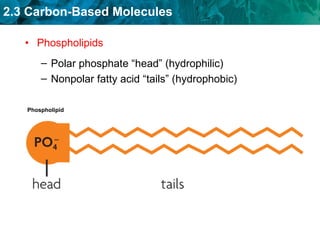
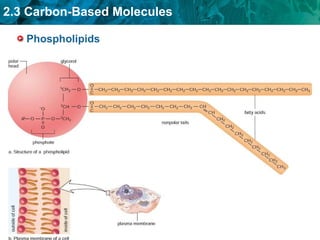
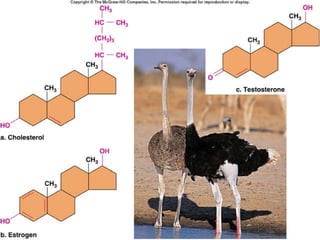
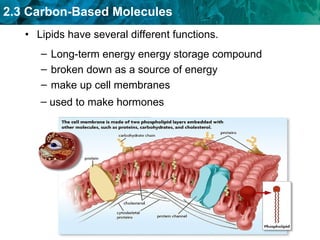
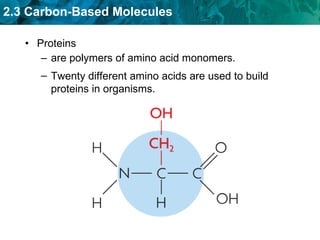
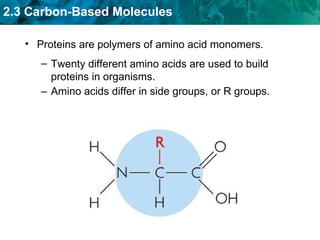
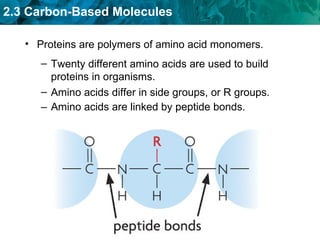
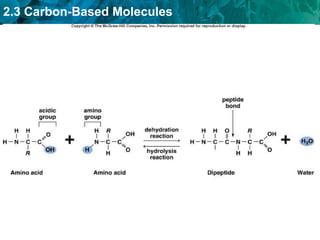
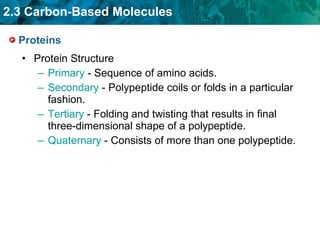
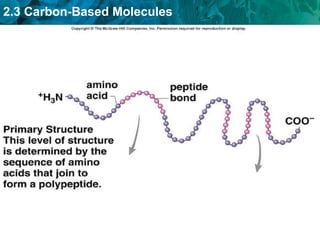
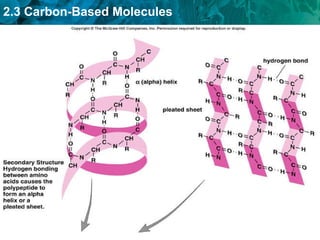
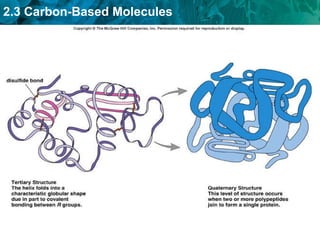
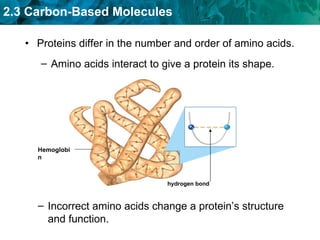
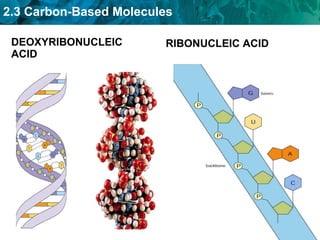
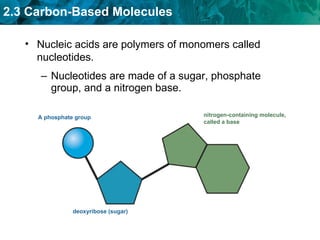
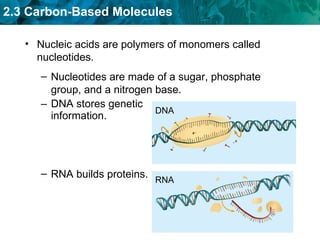
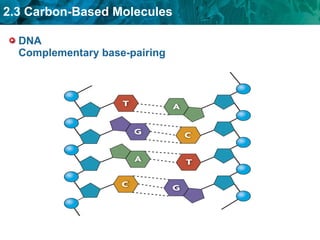
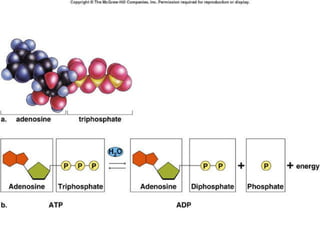
Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life and come in three main structures: straight chains, branched chains, and rings. The four main types of carbon-based molecules found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides like glucose and fructose that can link together to form polysaccharides like starch and cellulose. Lipids include fats, oils, and other nonpolar molecules that serve functions like energy storage. Proteins are polymers of amino acids that carry out important roles such as structure, movement, and catalysis. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides and store and use genetic information.