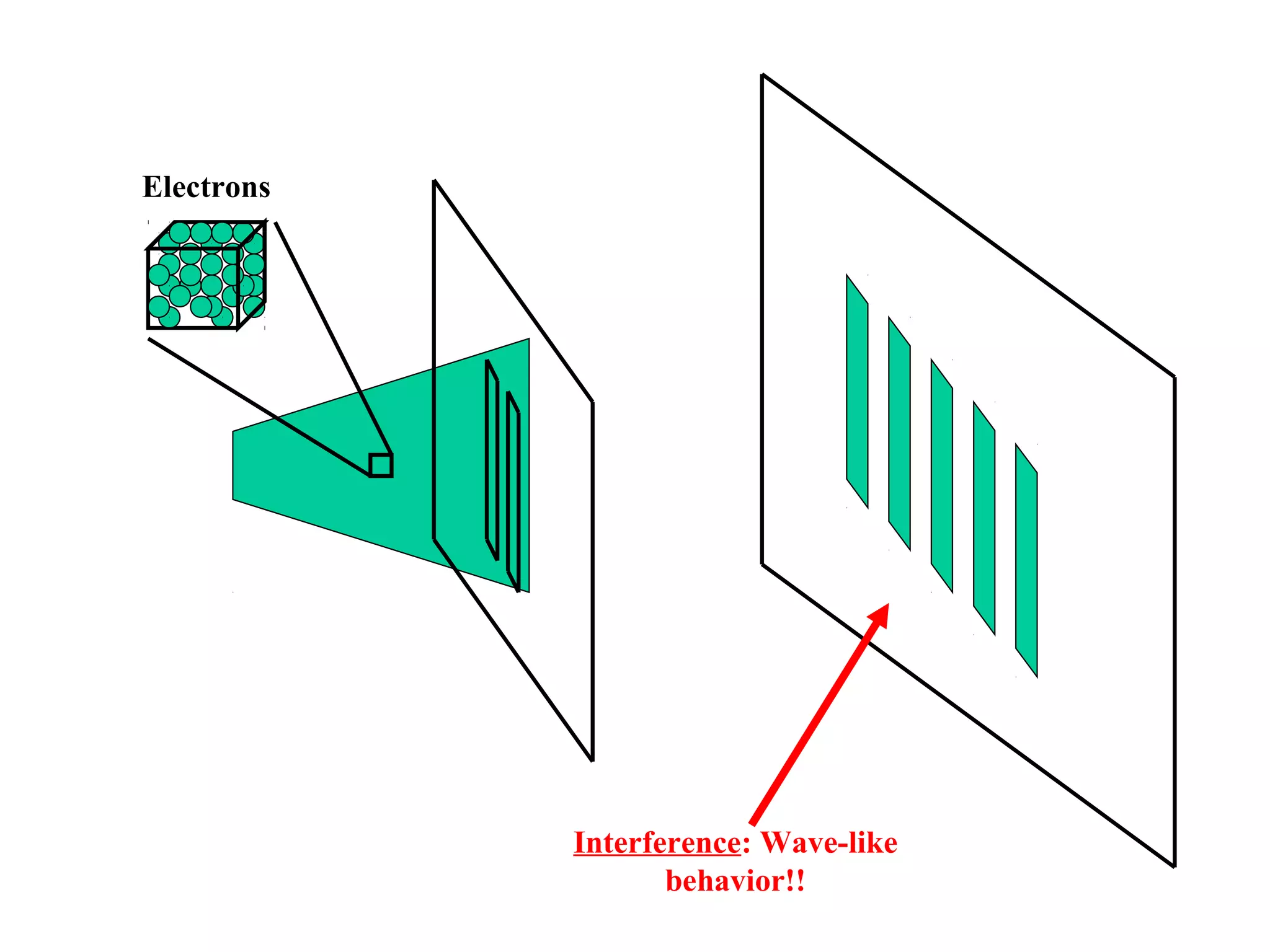
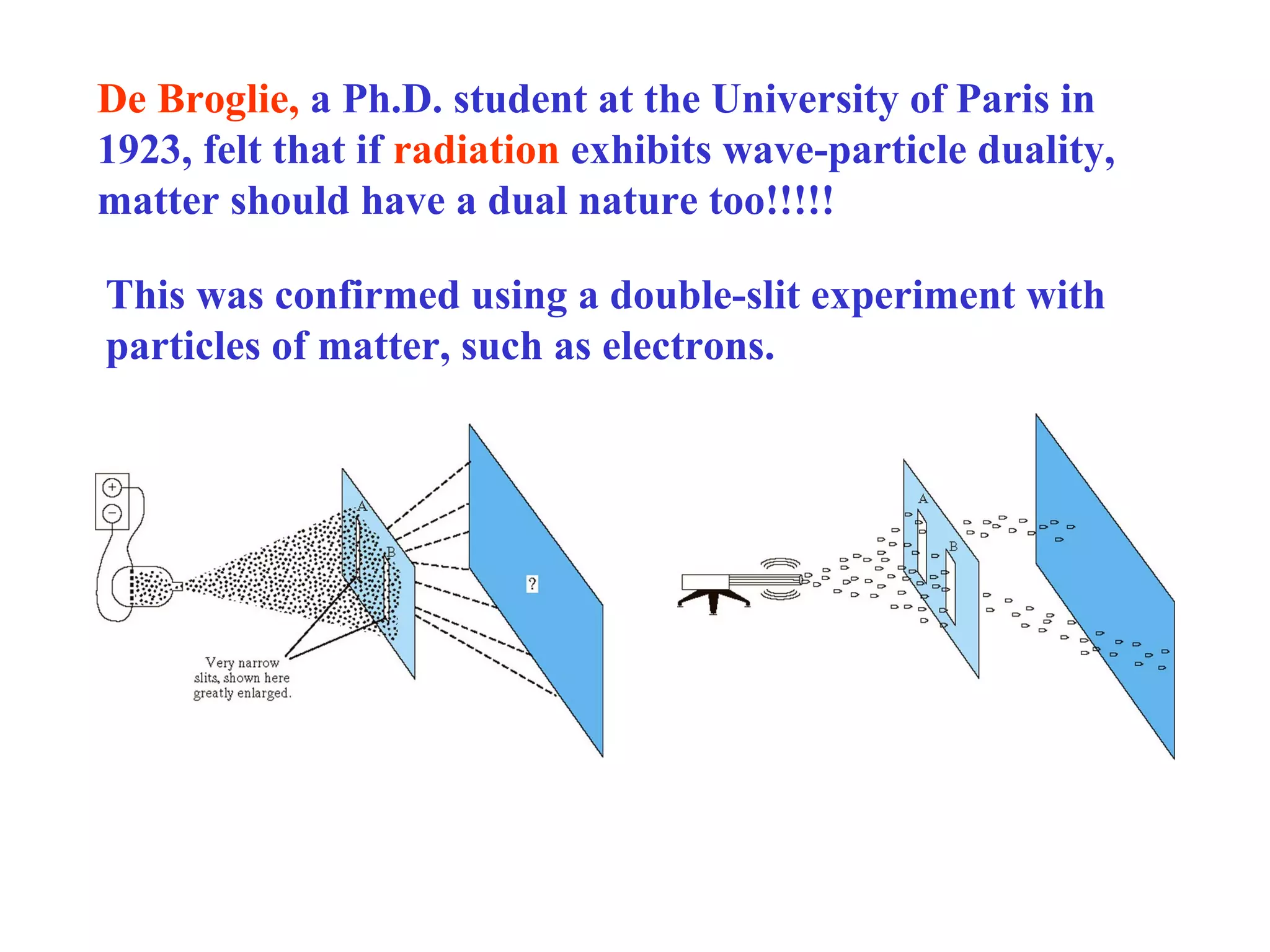
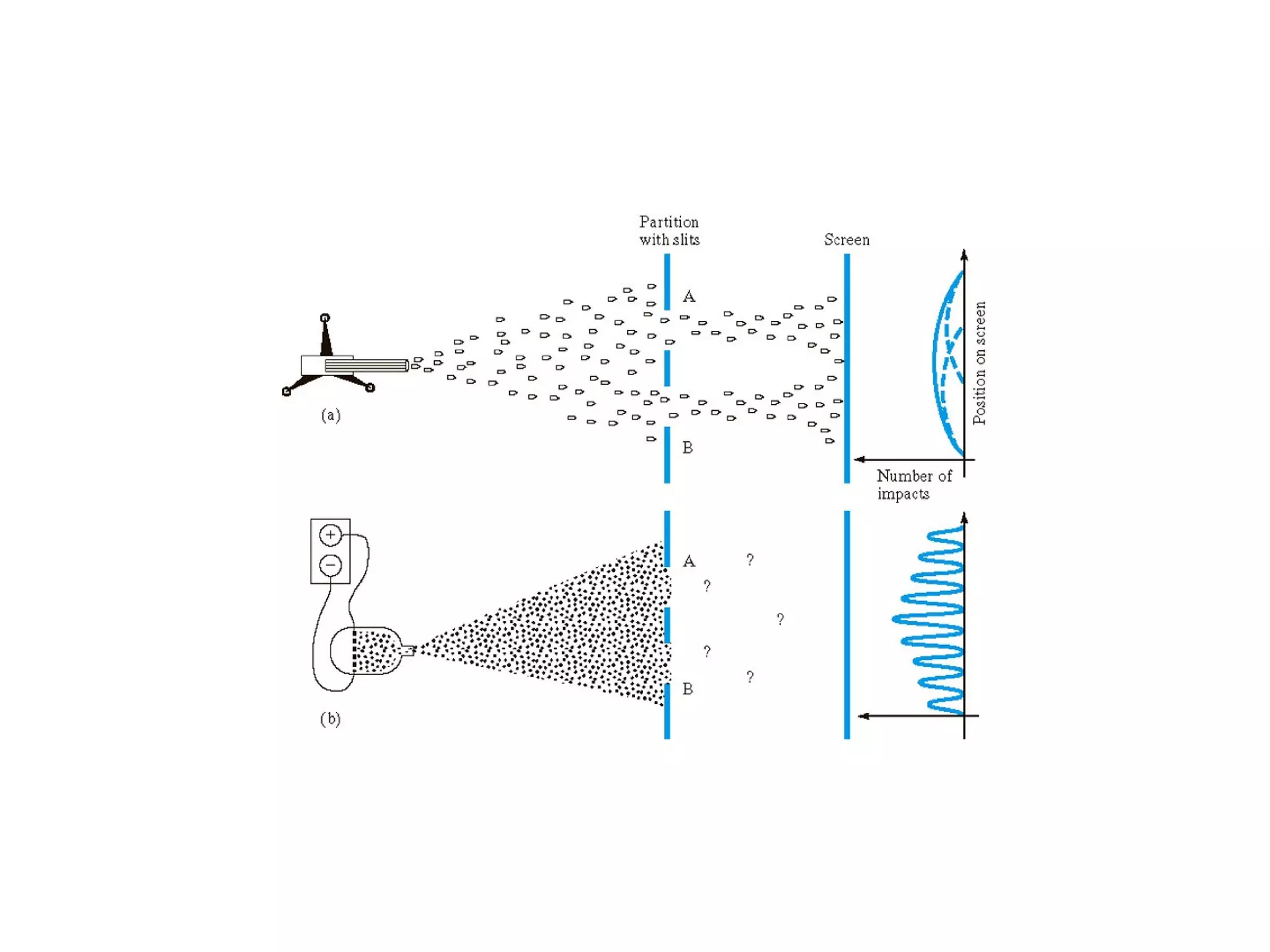
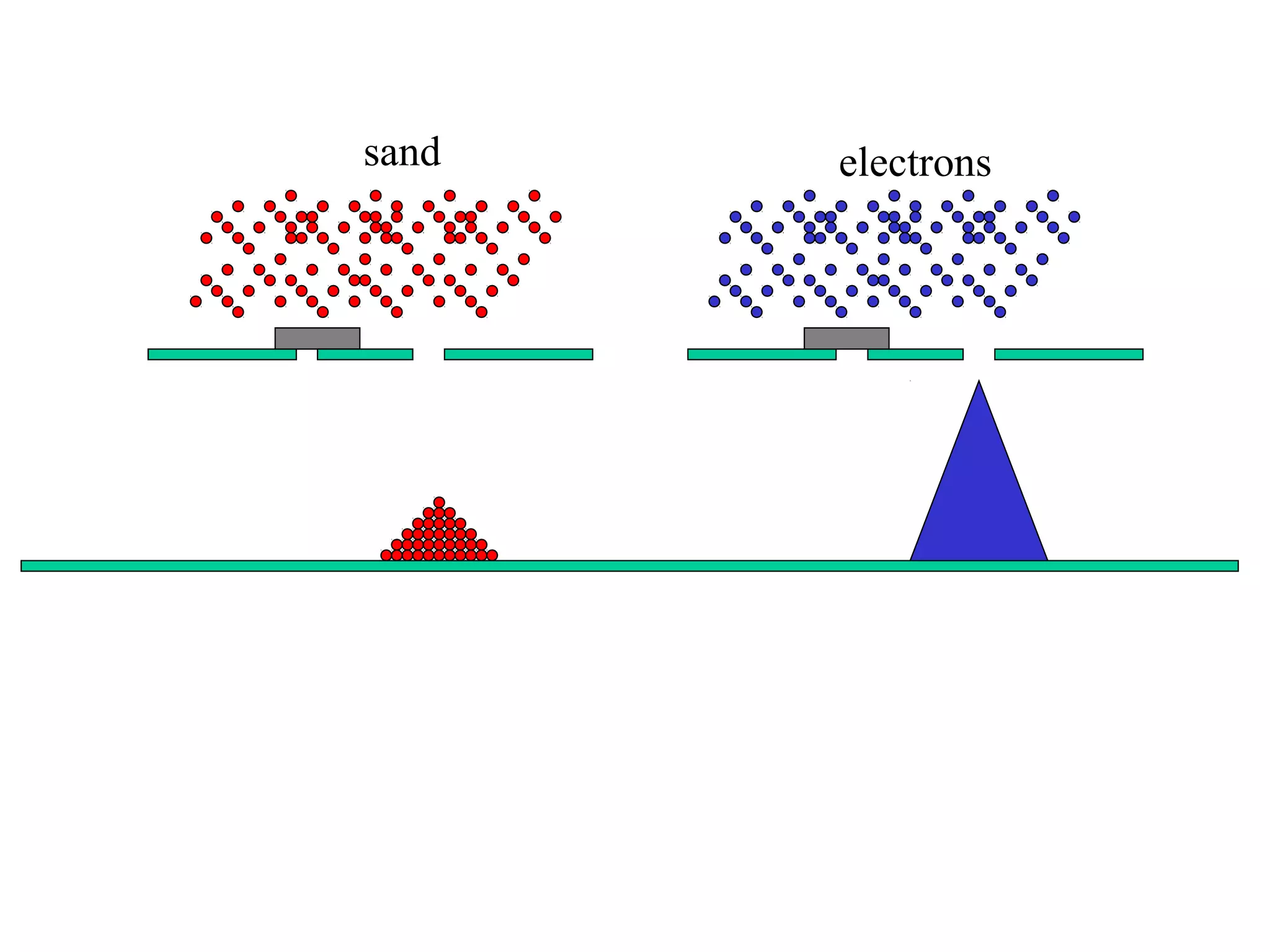
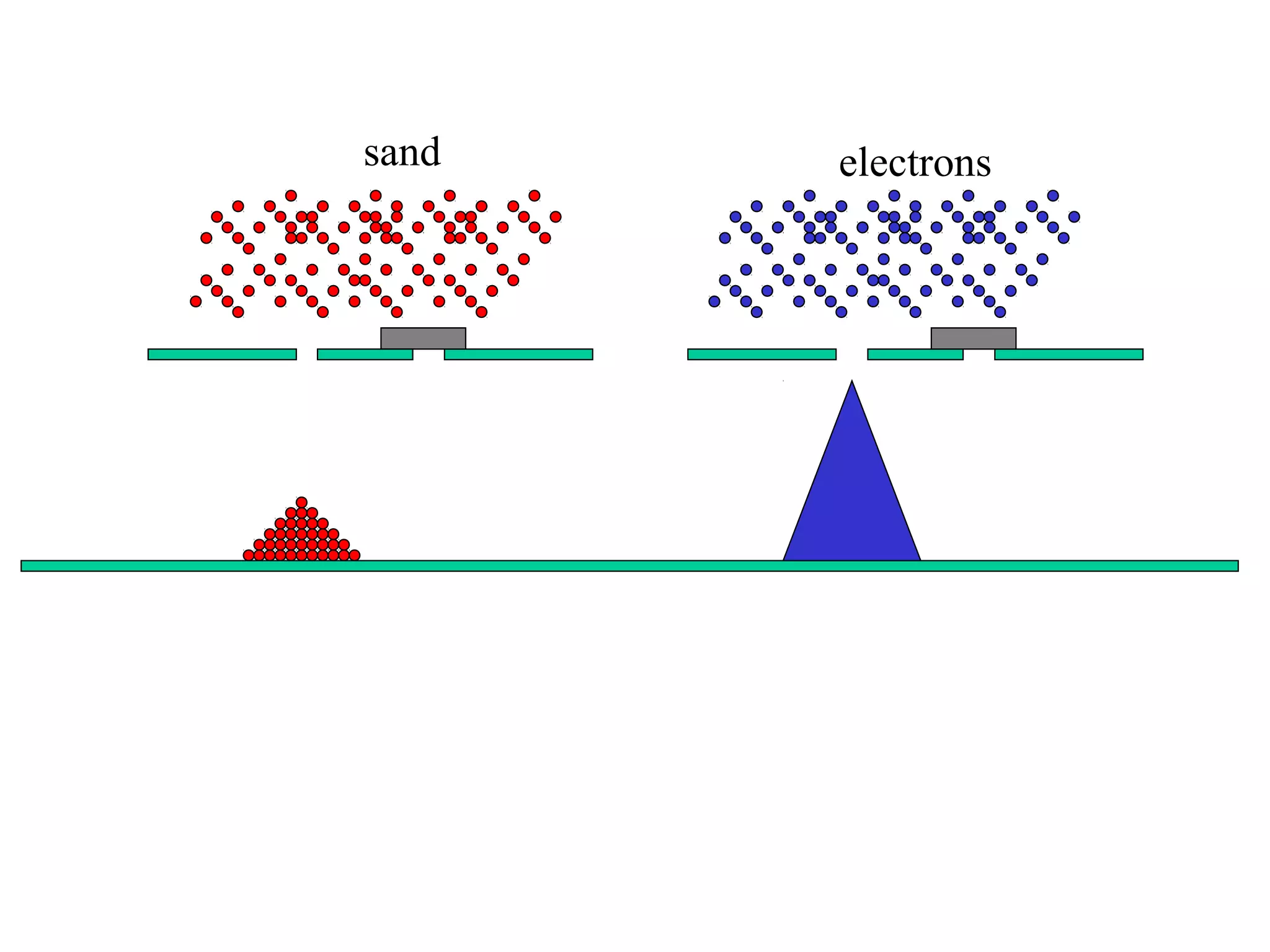
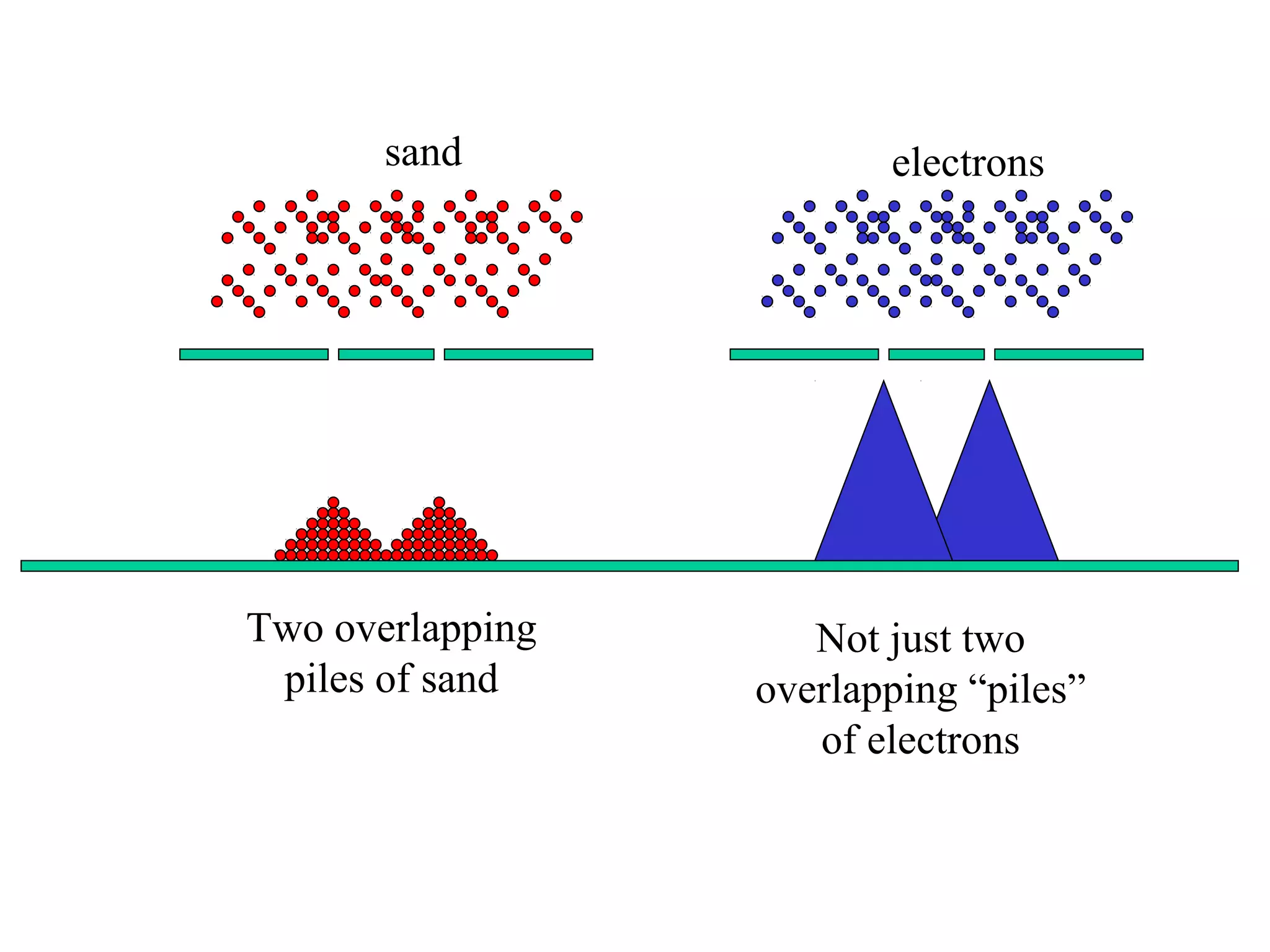
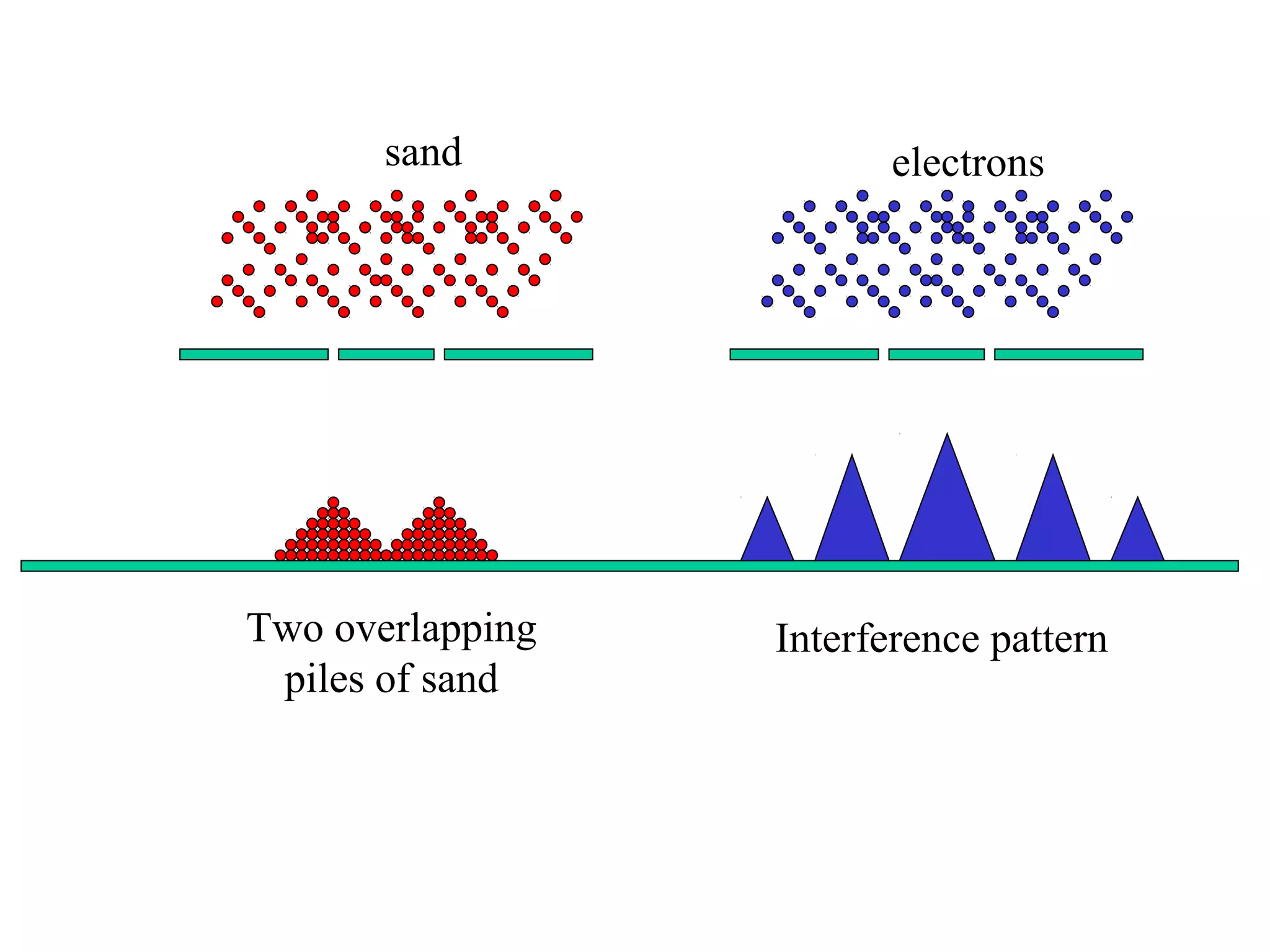
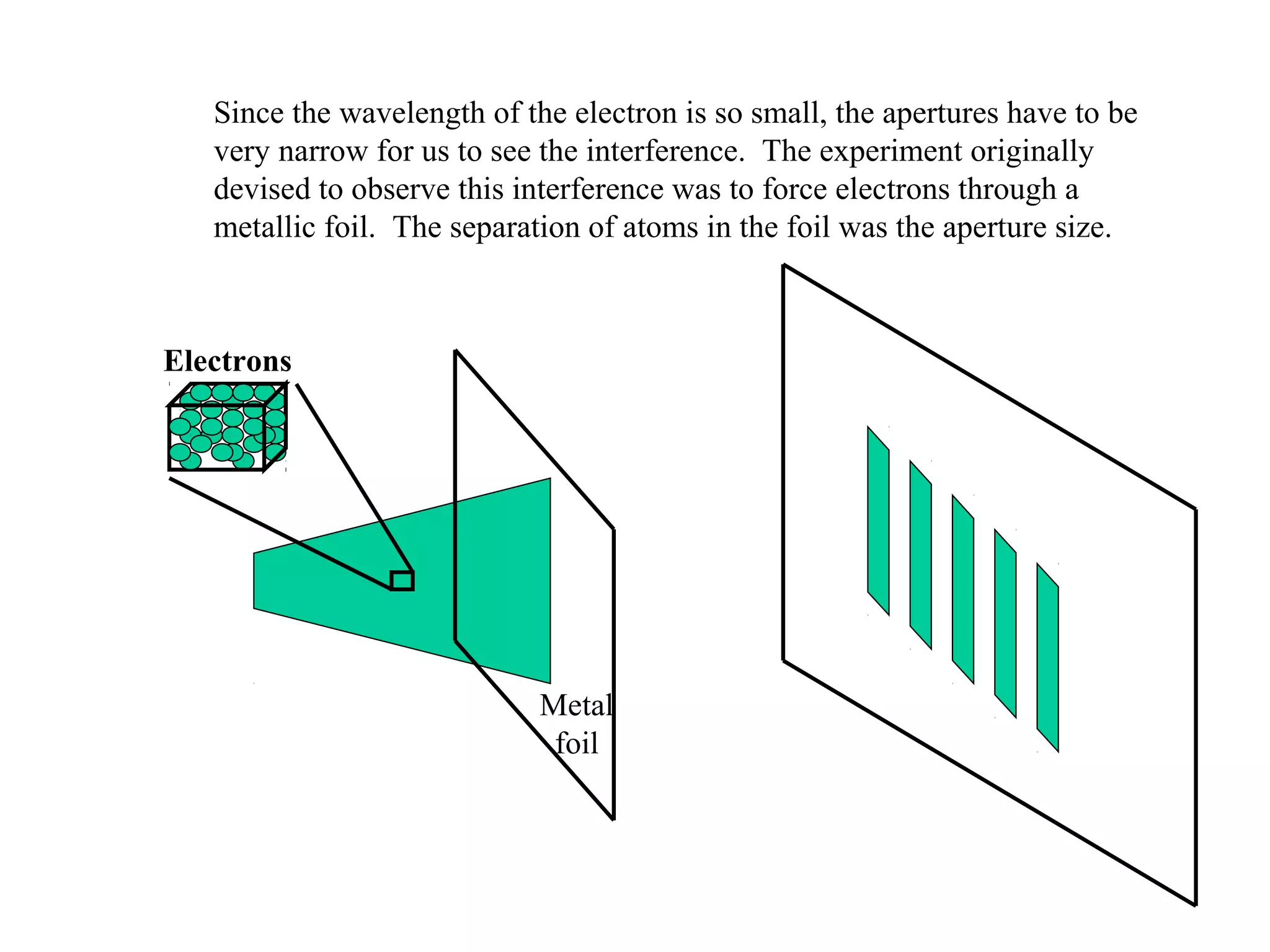
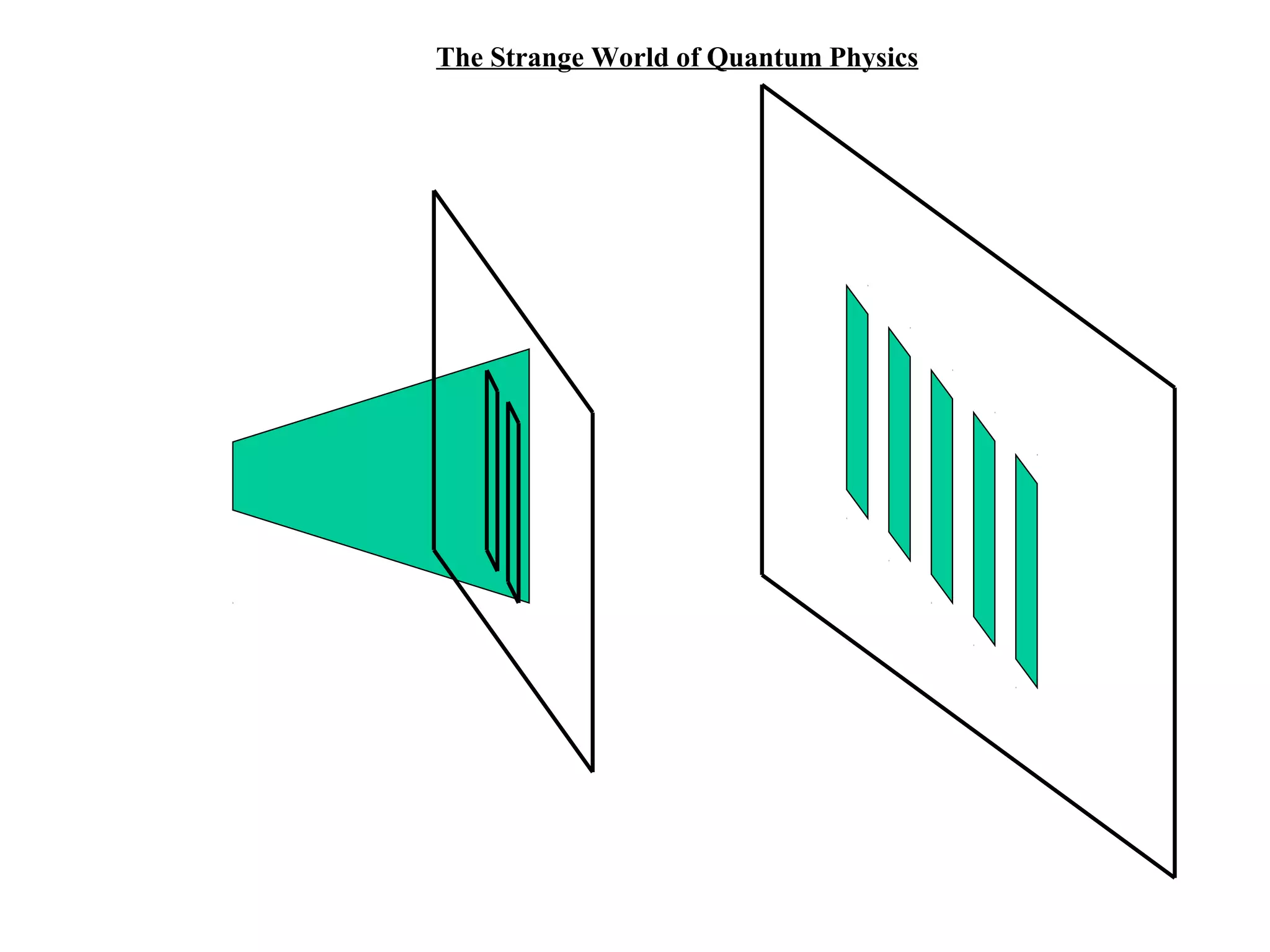
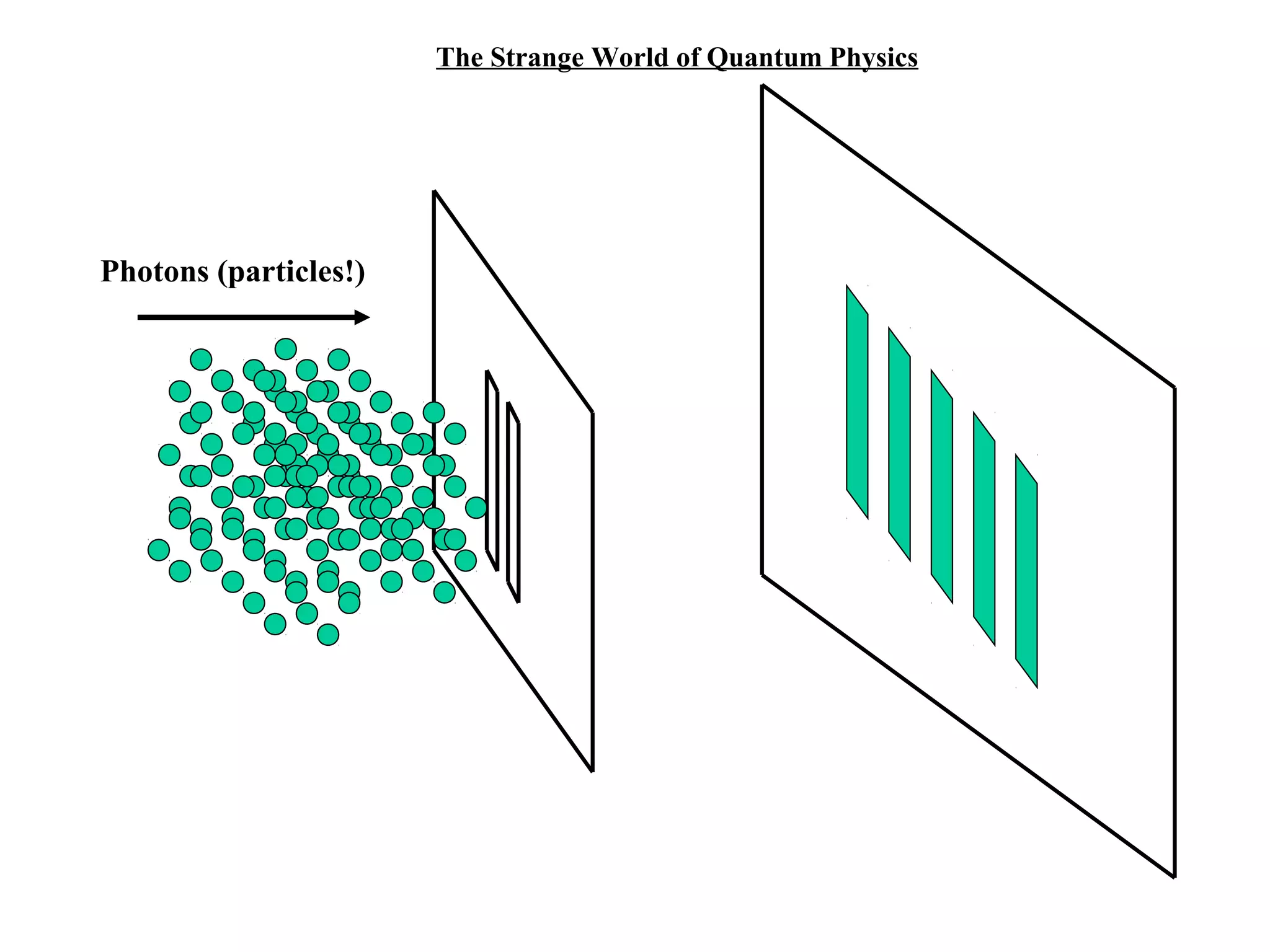
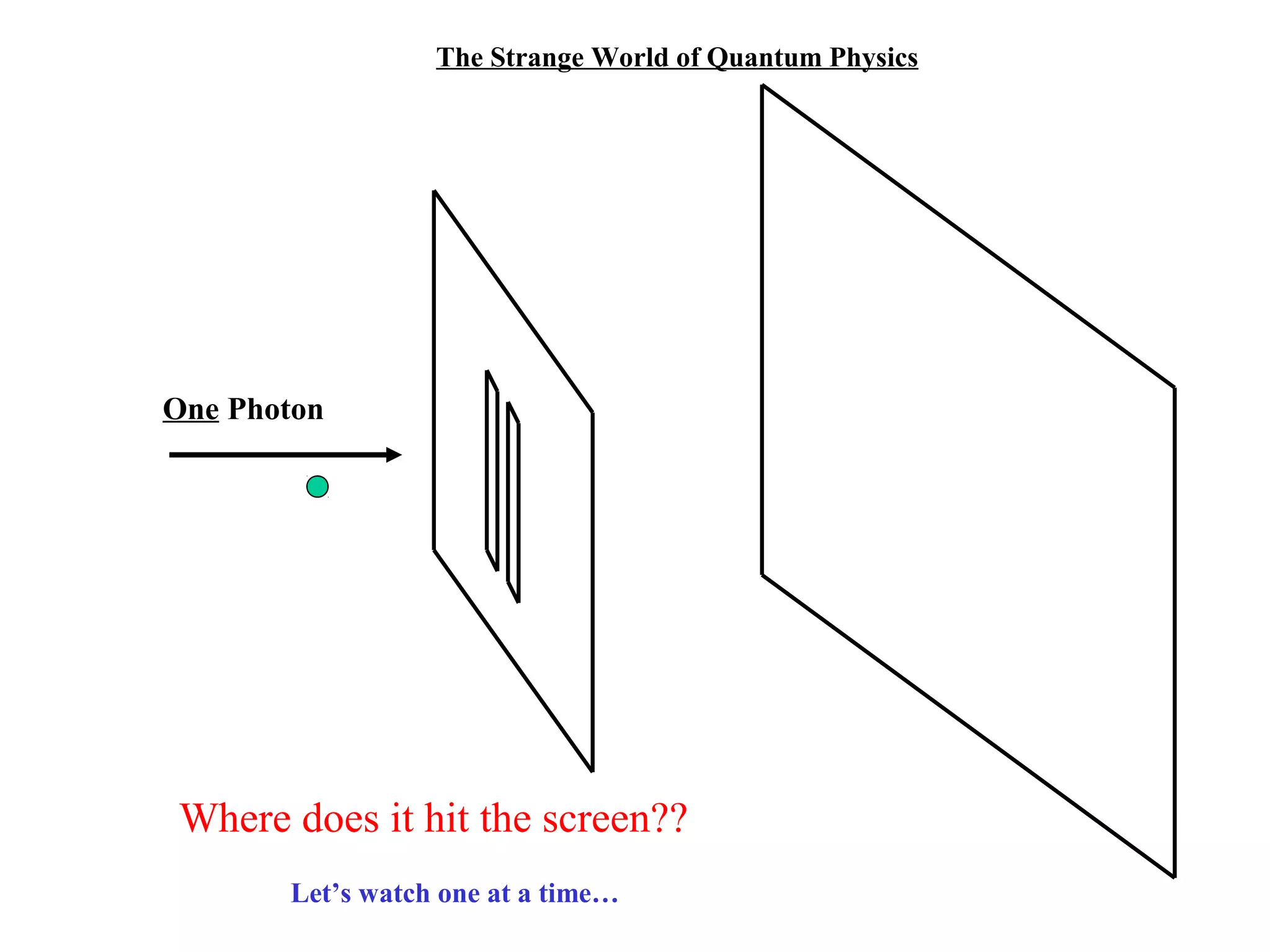
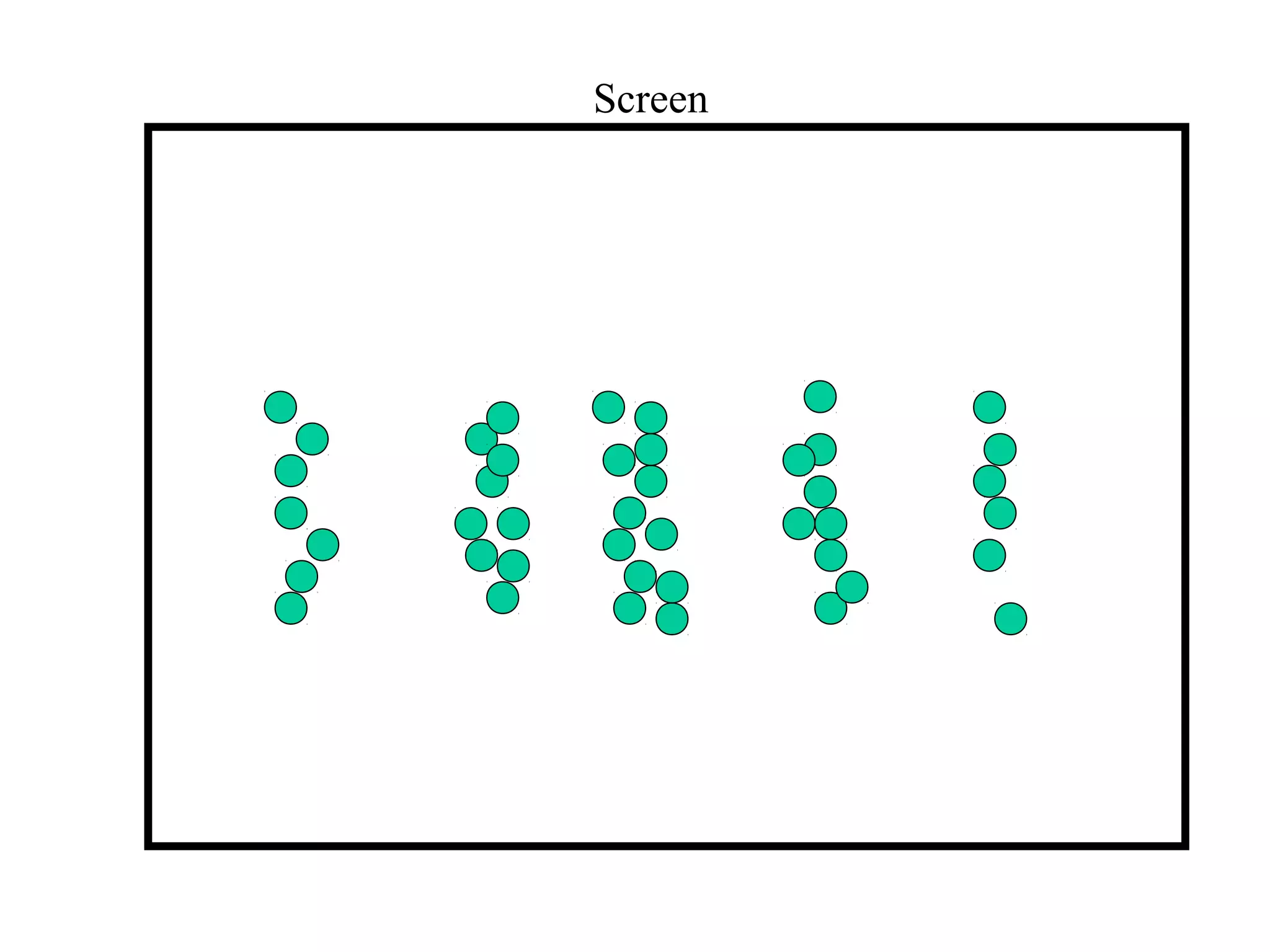
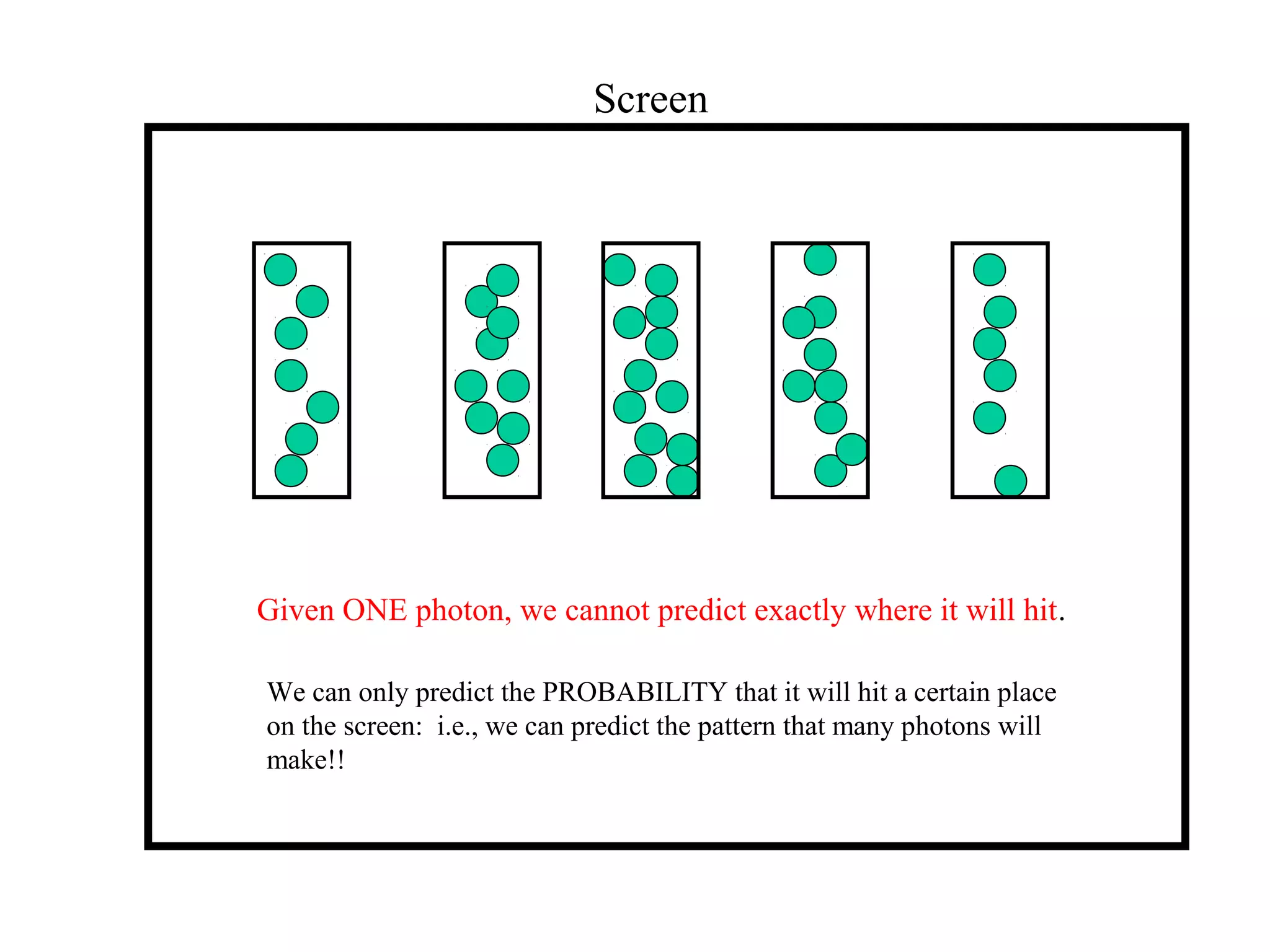
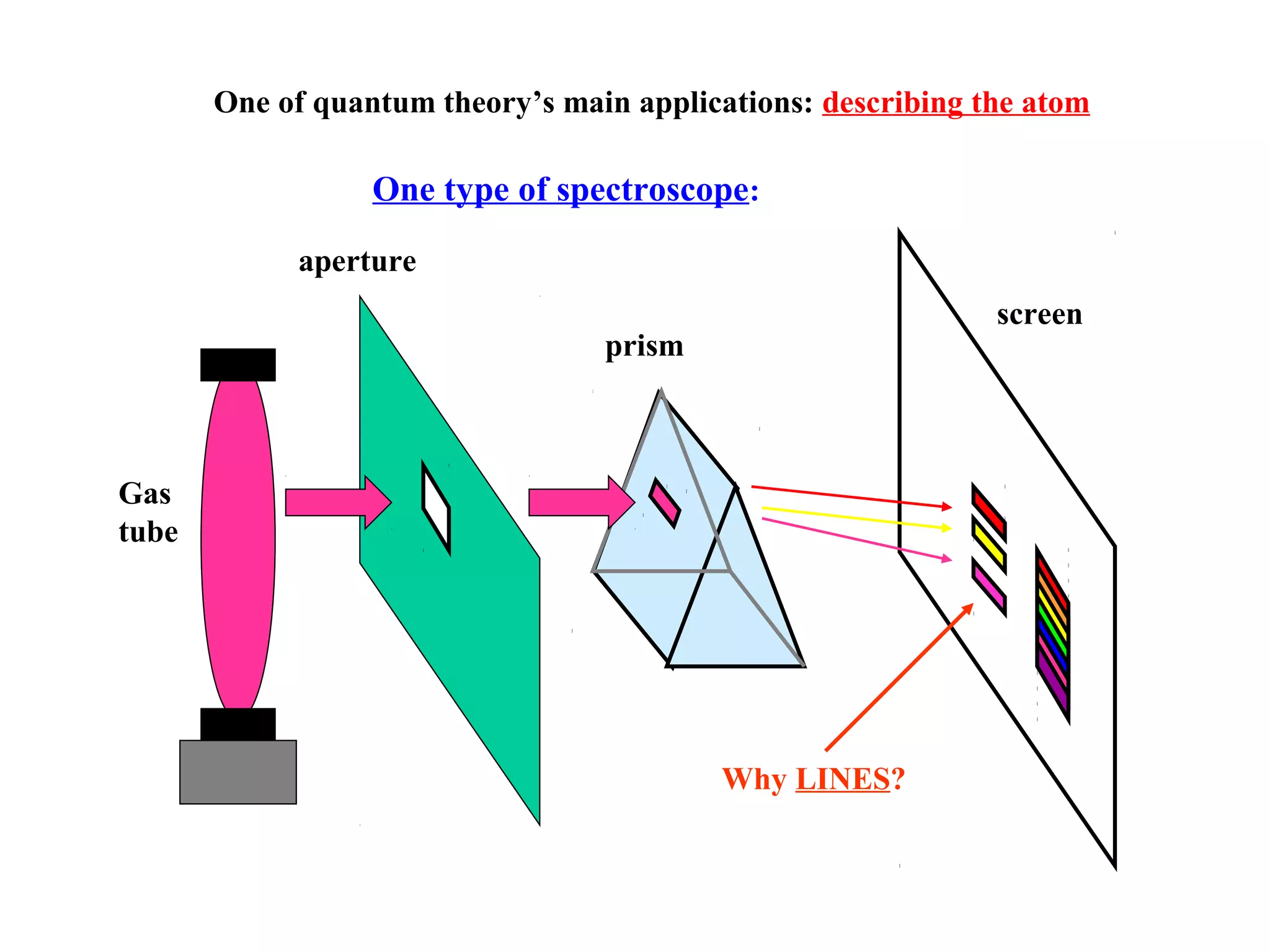
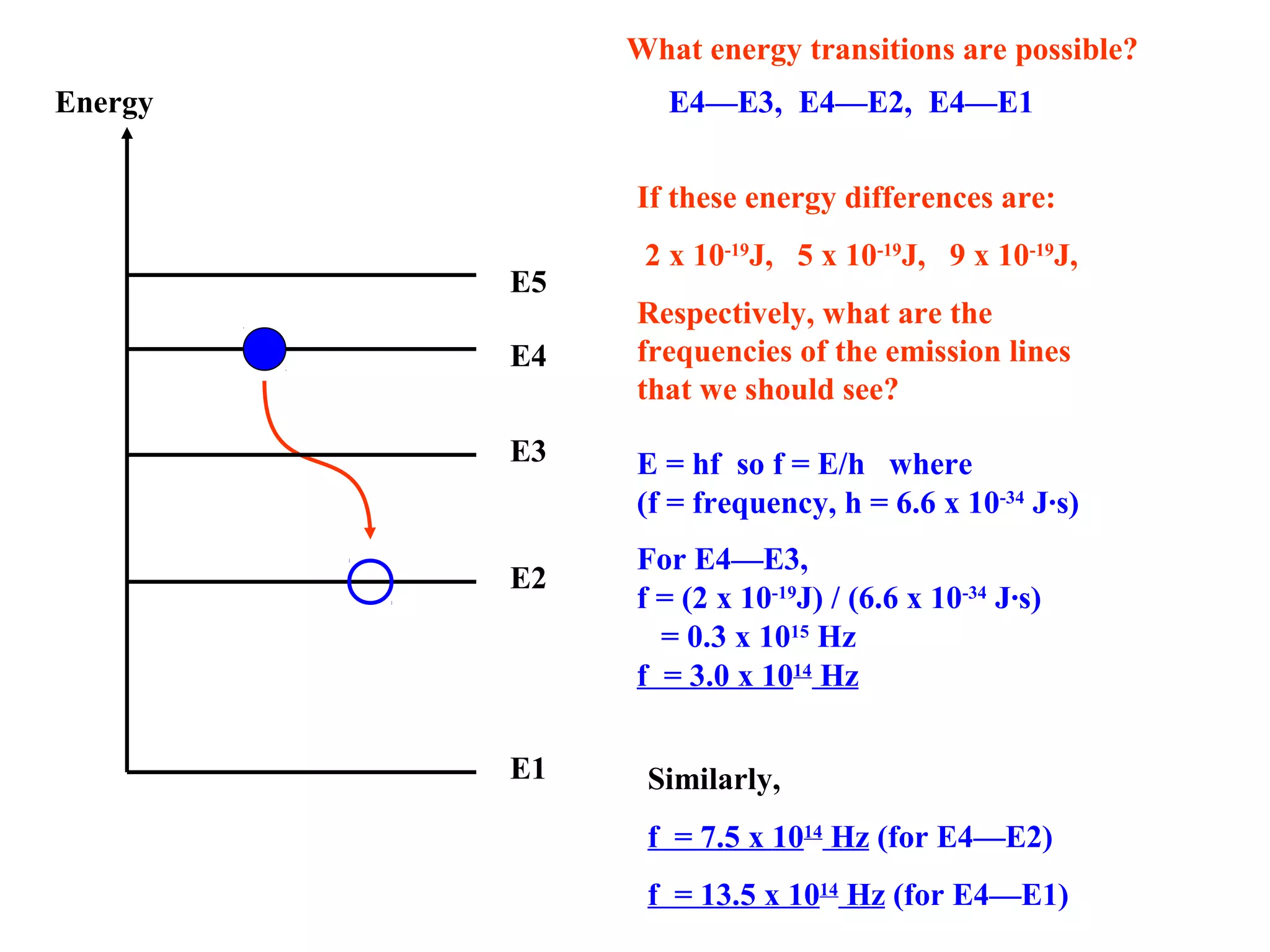
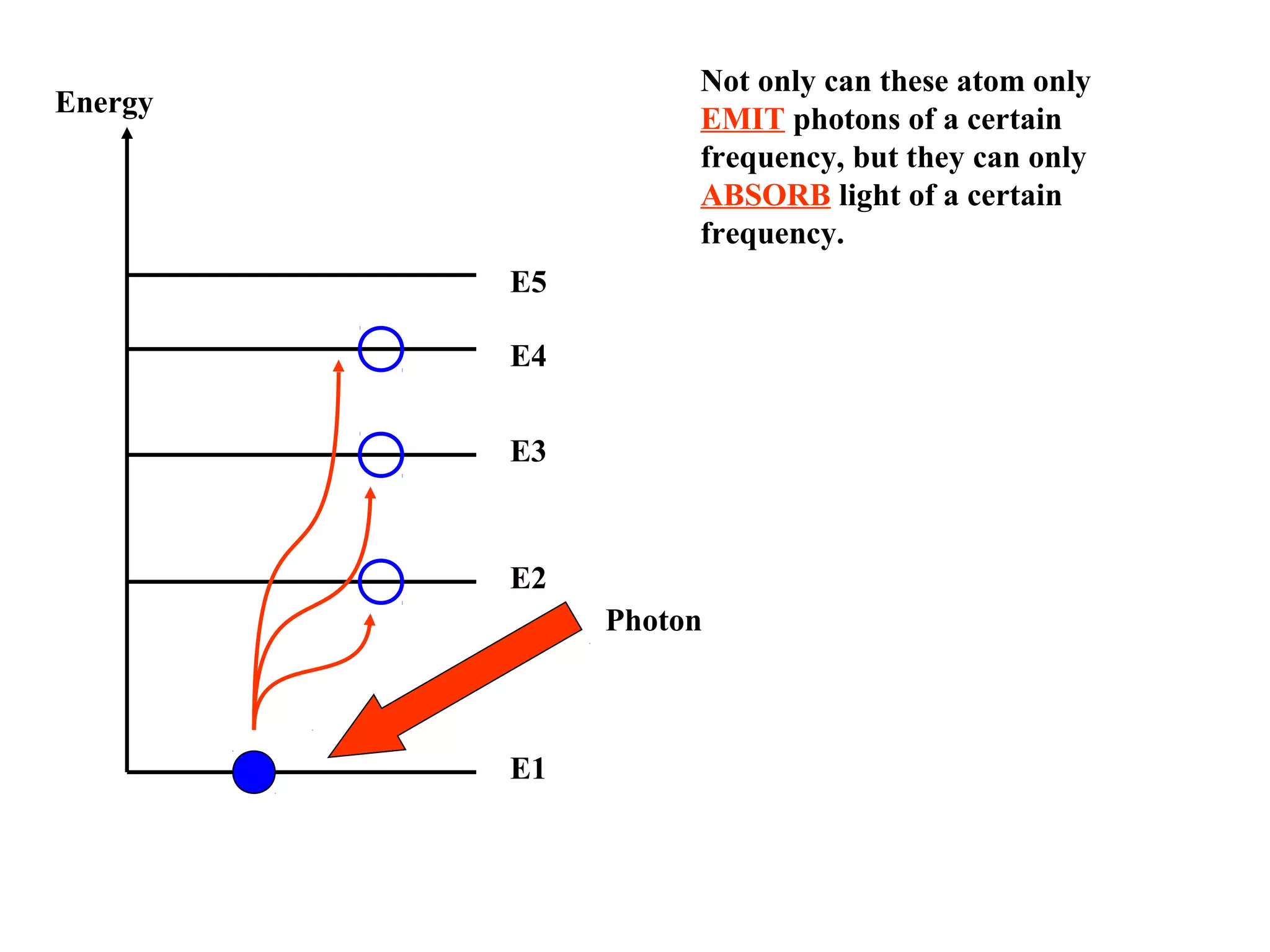
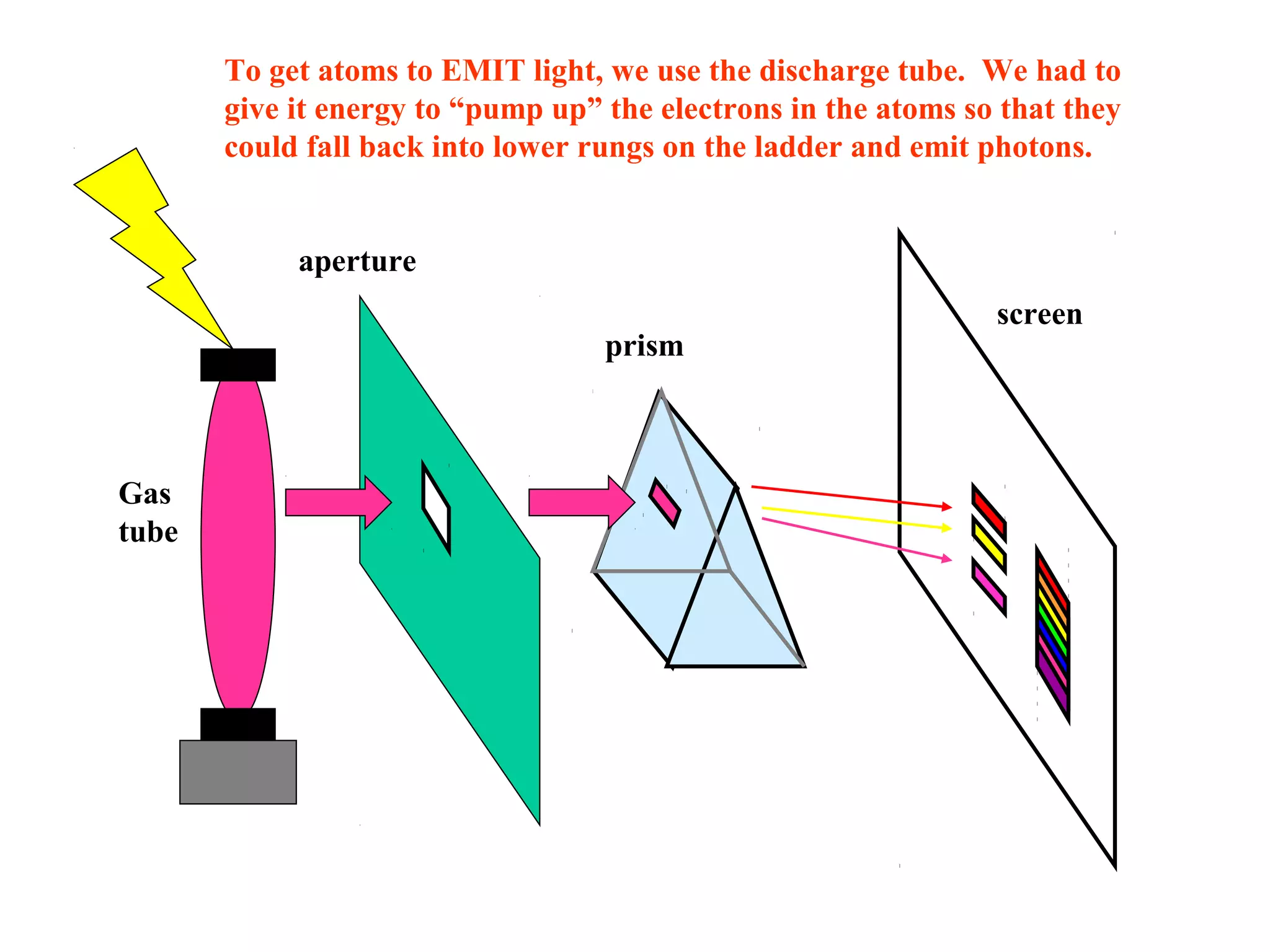
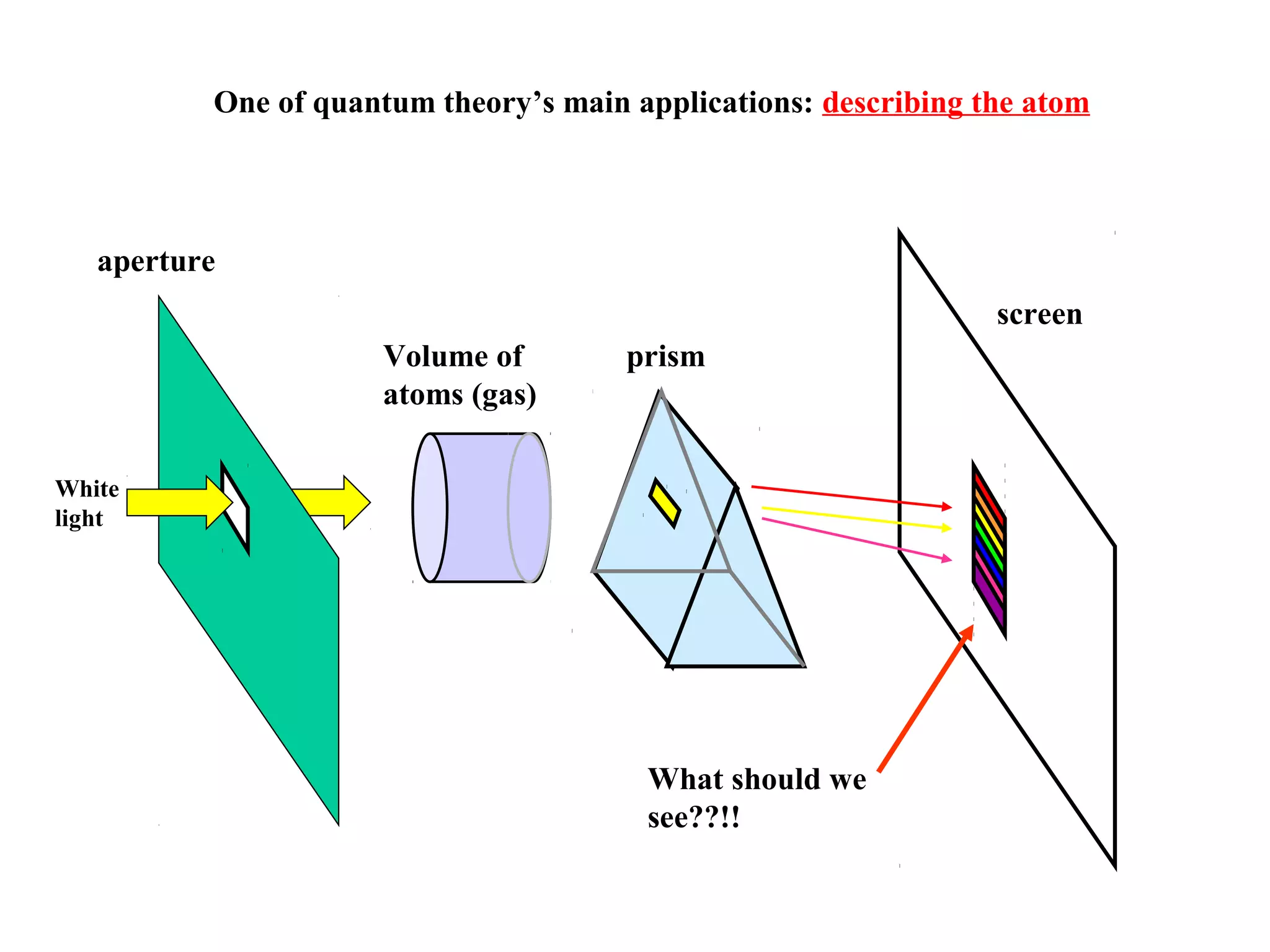
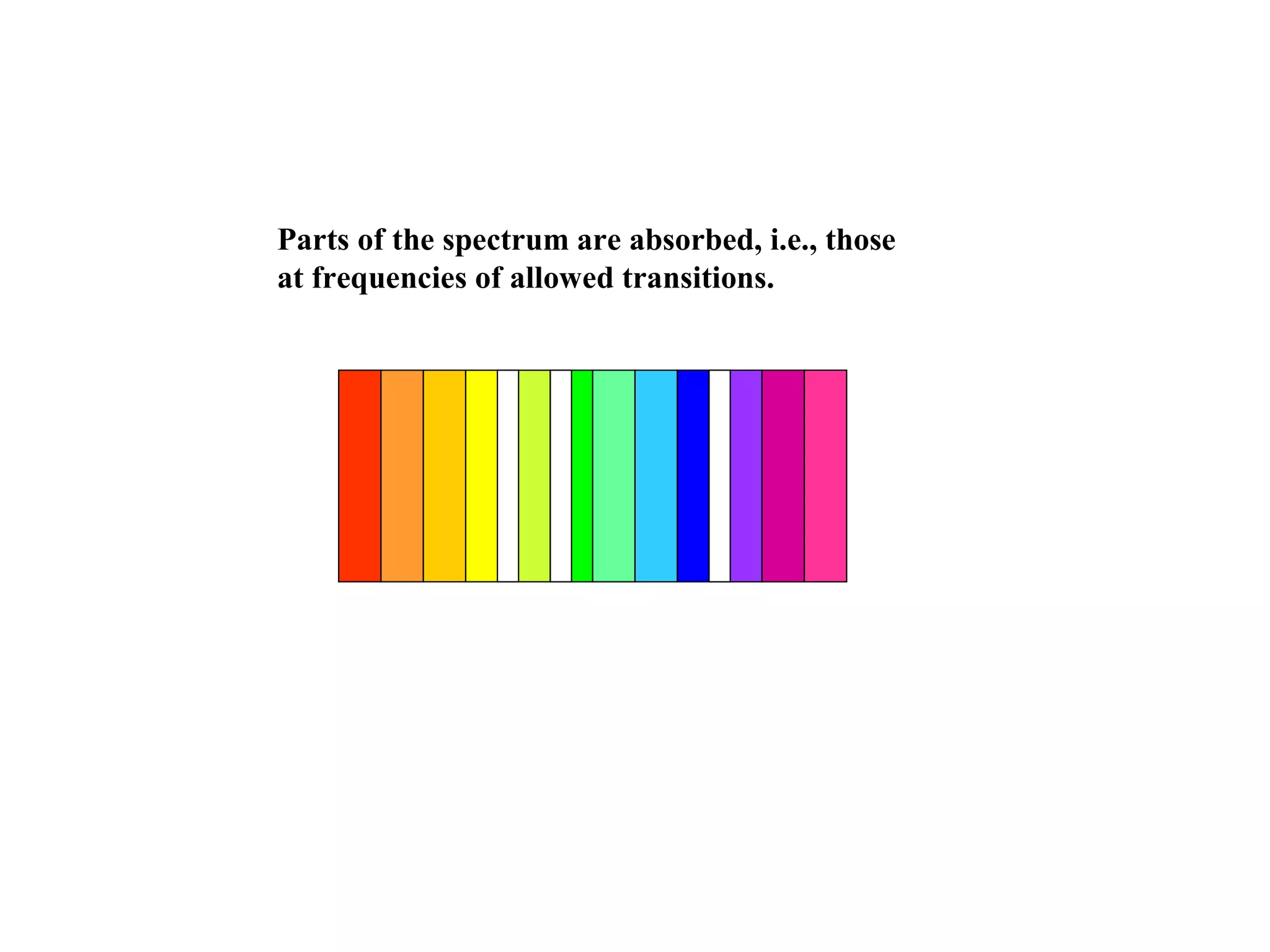
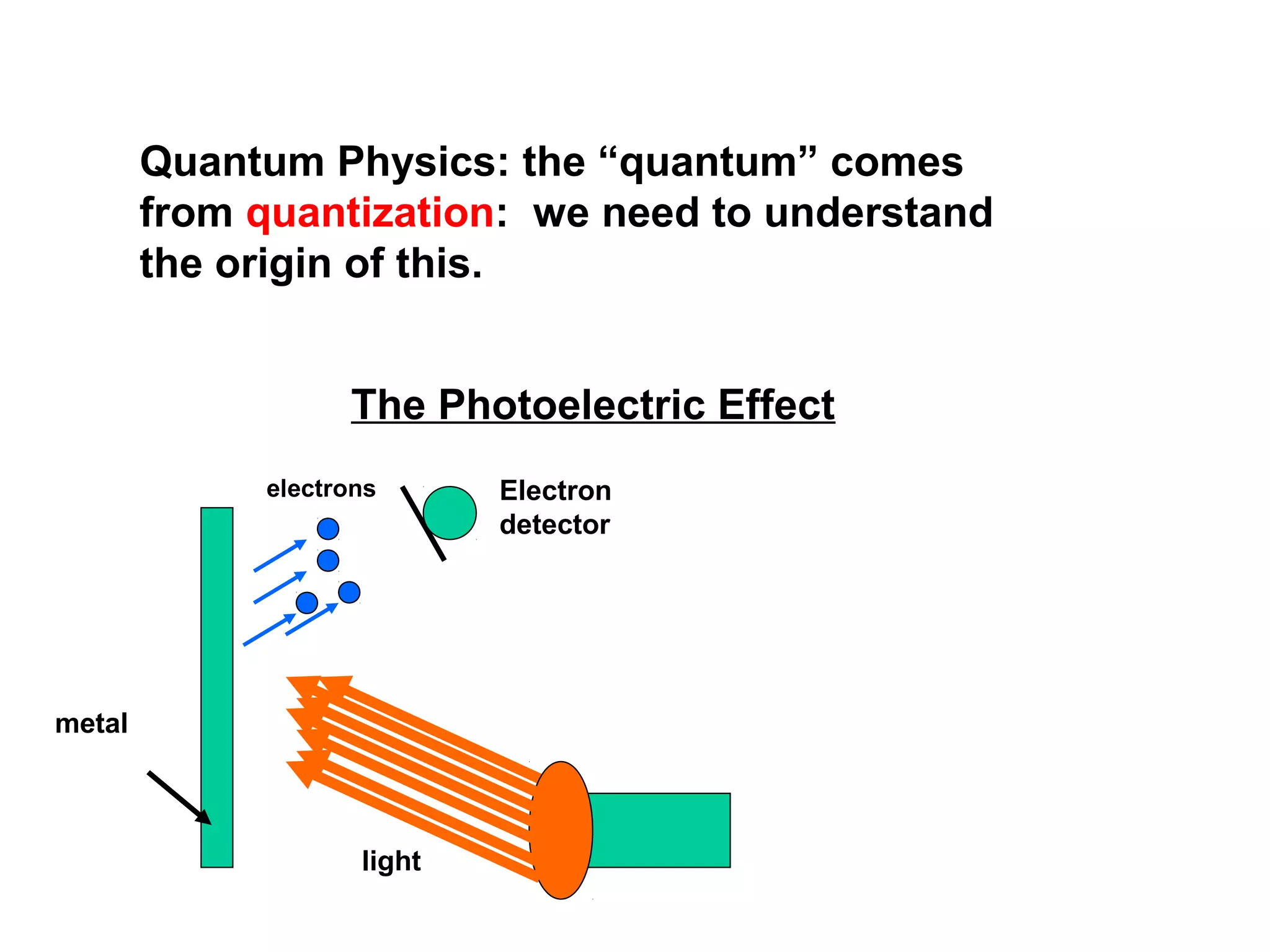
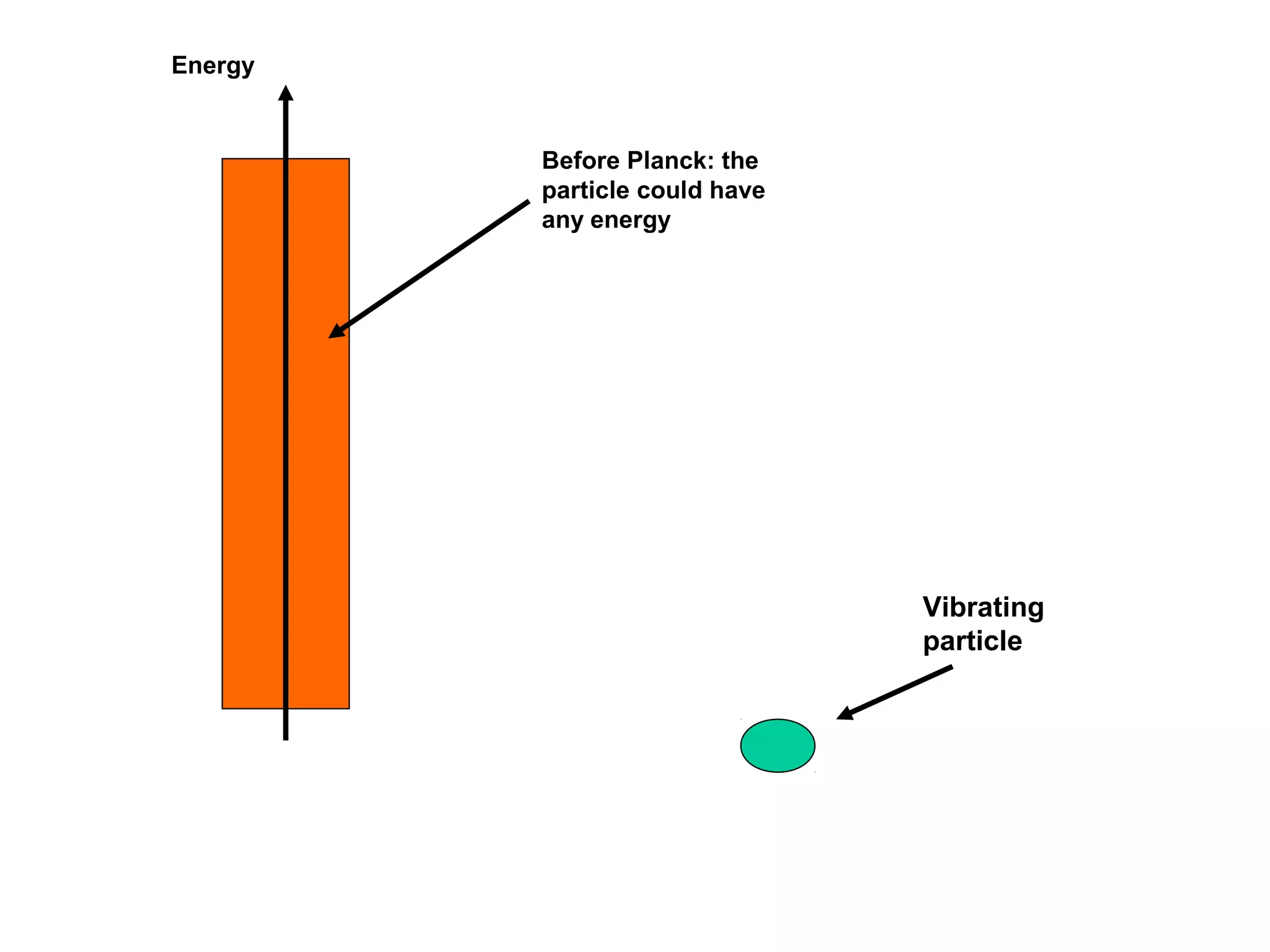
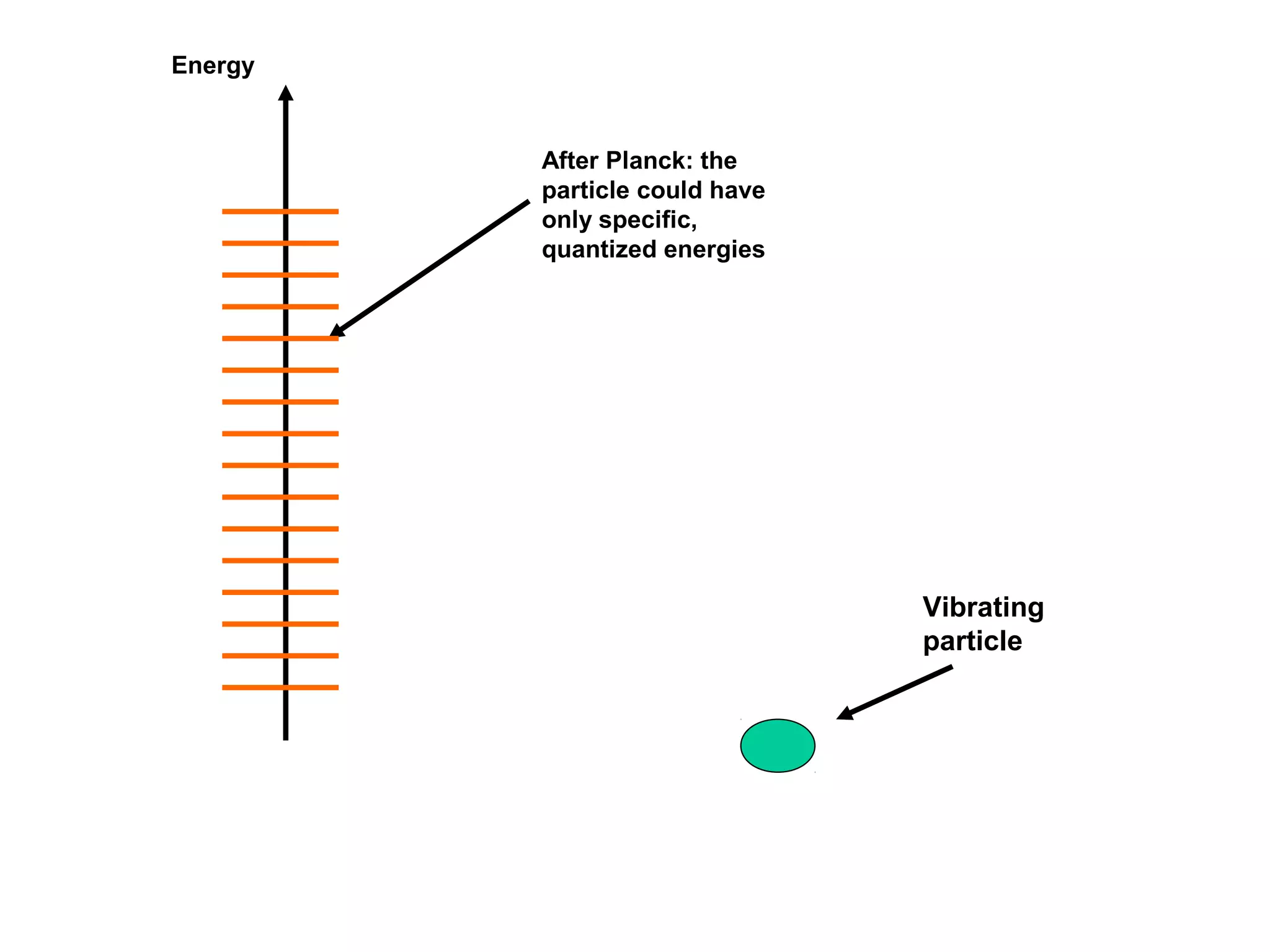
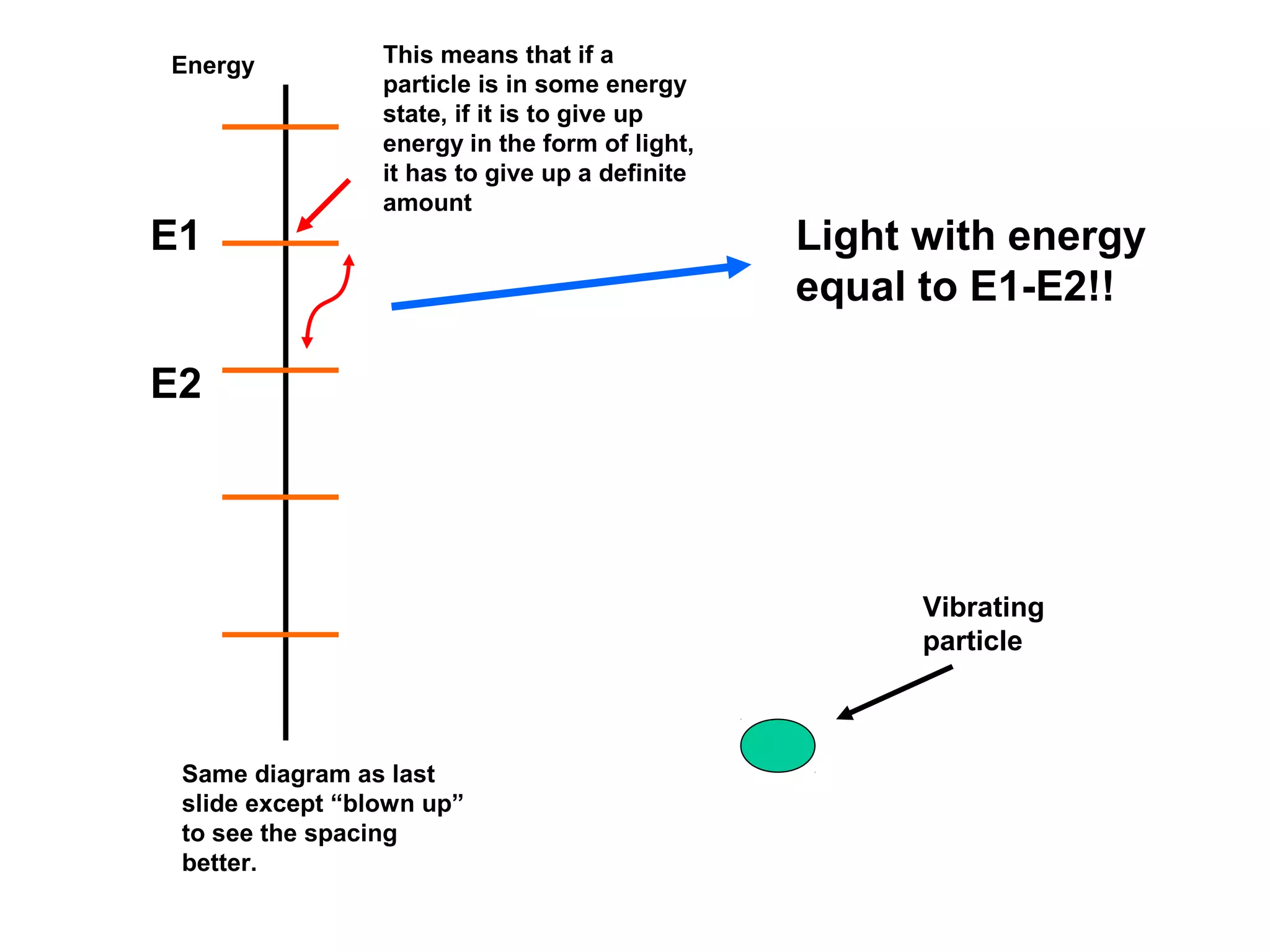
Quantum theory provides a framework to understand phenomena at the atomic scale that cannot be explained by classical physics. It proposes that energy is emitted and absorbed in discrete units called quanta. This explains observations like the photoelectric effect where electrons are only ejected above a threshold frequency. Light behaves as both a wave and particle - a photon. Similarly, matter exhibits wave-particle duality as demonstrated by electron diffraction. At the quantum level, only probabilities, not definite values, can be predicted. Quantum mechanics is applied to describe atomic structure and spectra.












![Actual Experimental Observations:
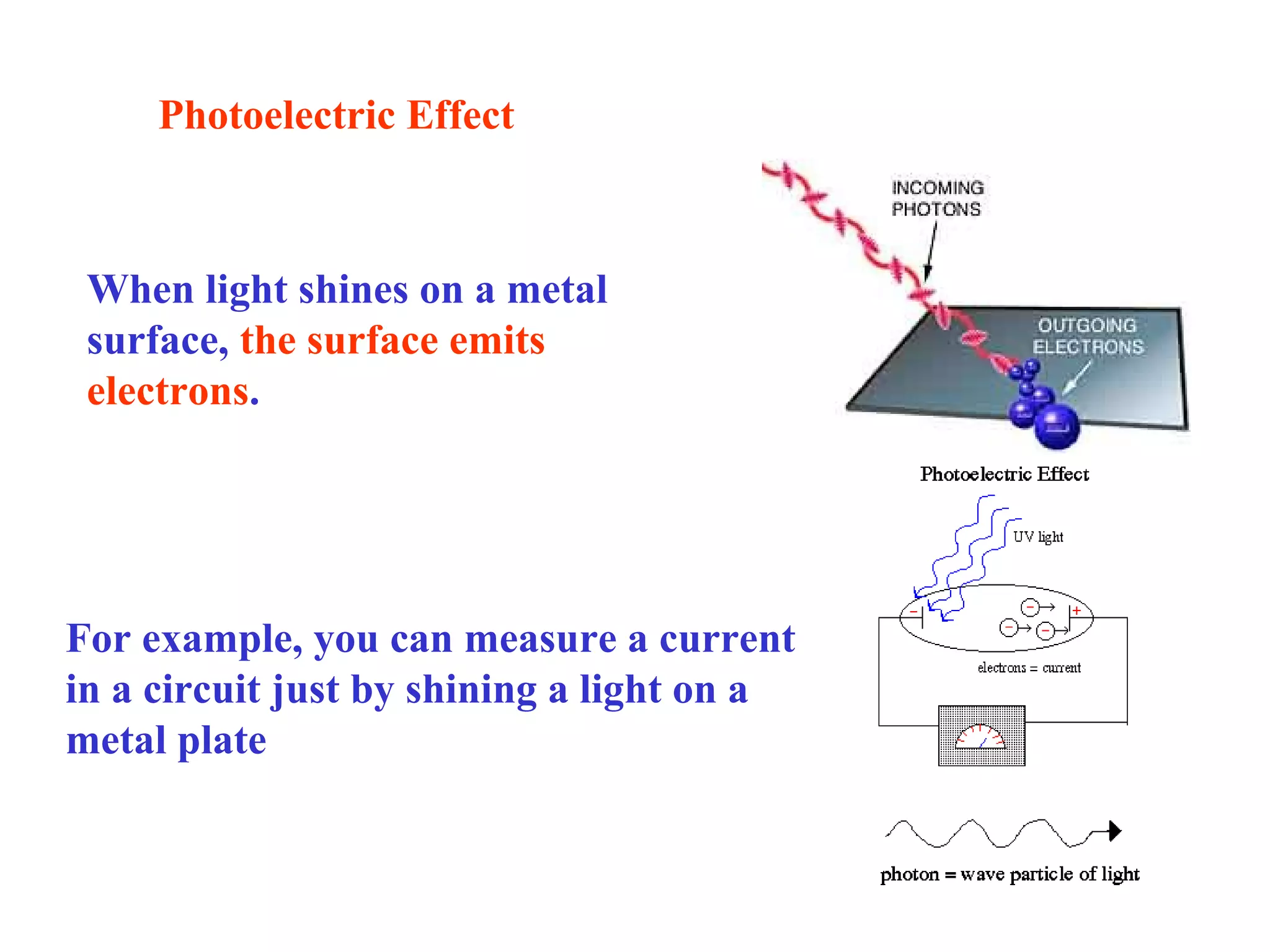
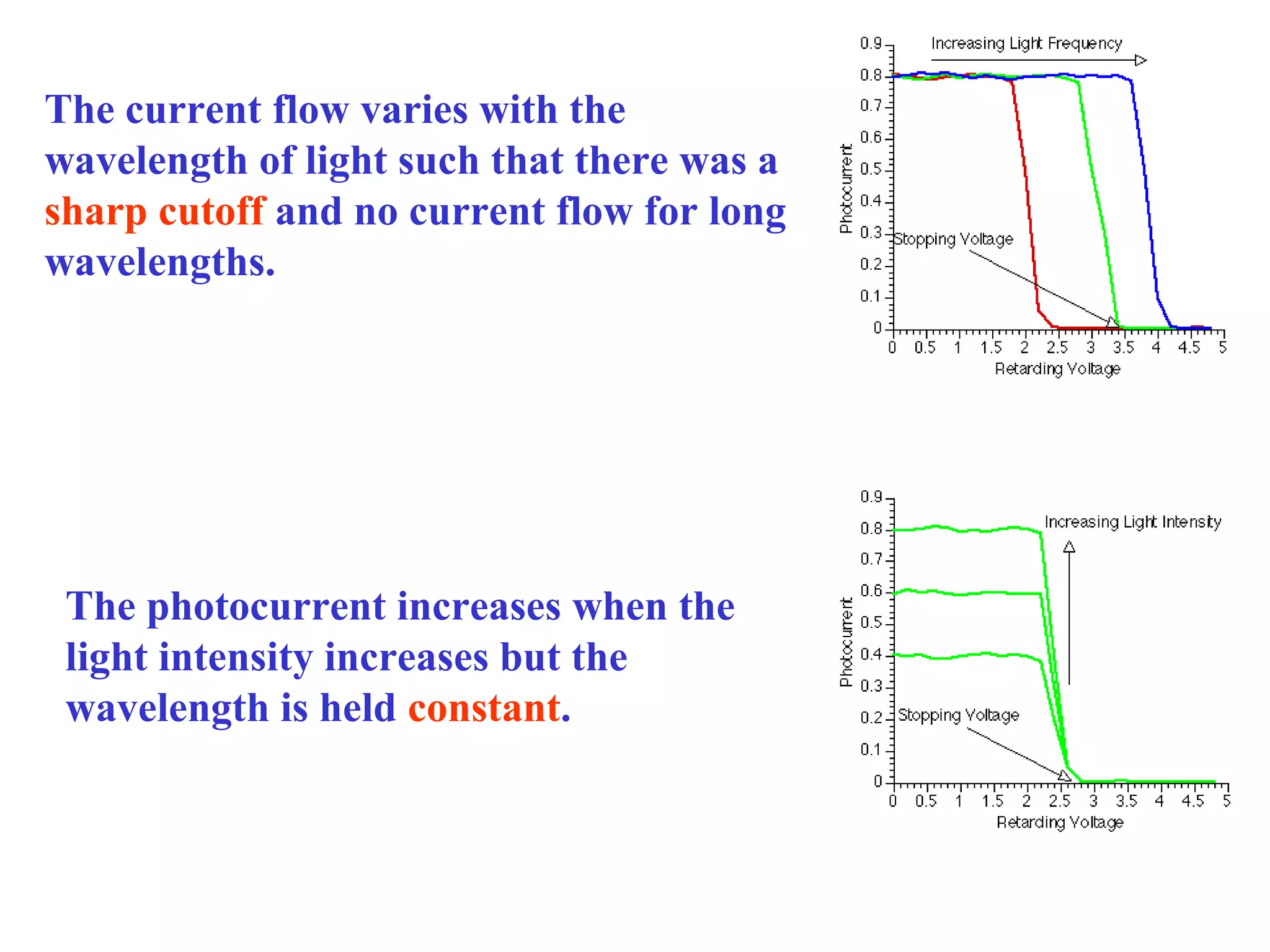
[1] There is no delay between the light hitting the surface and
the electrons being ejected
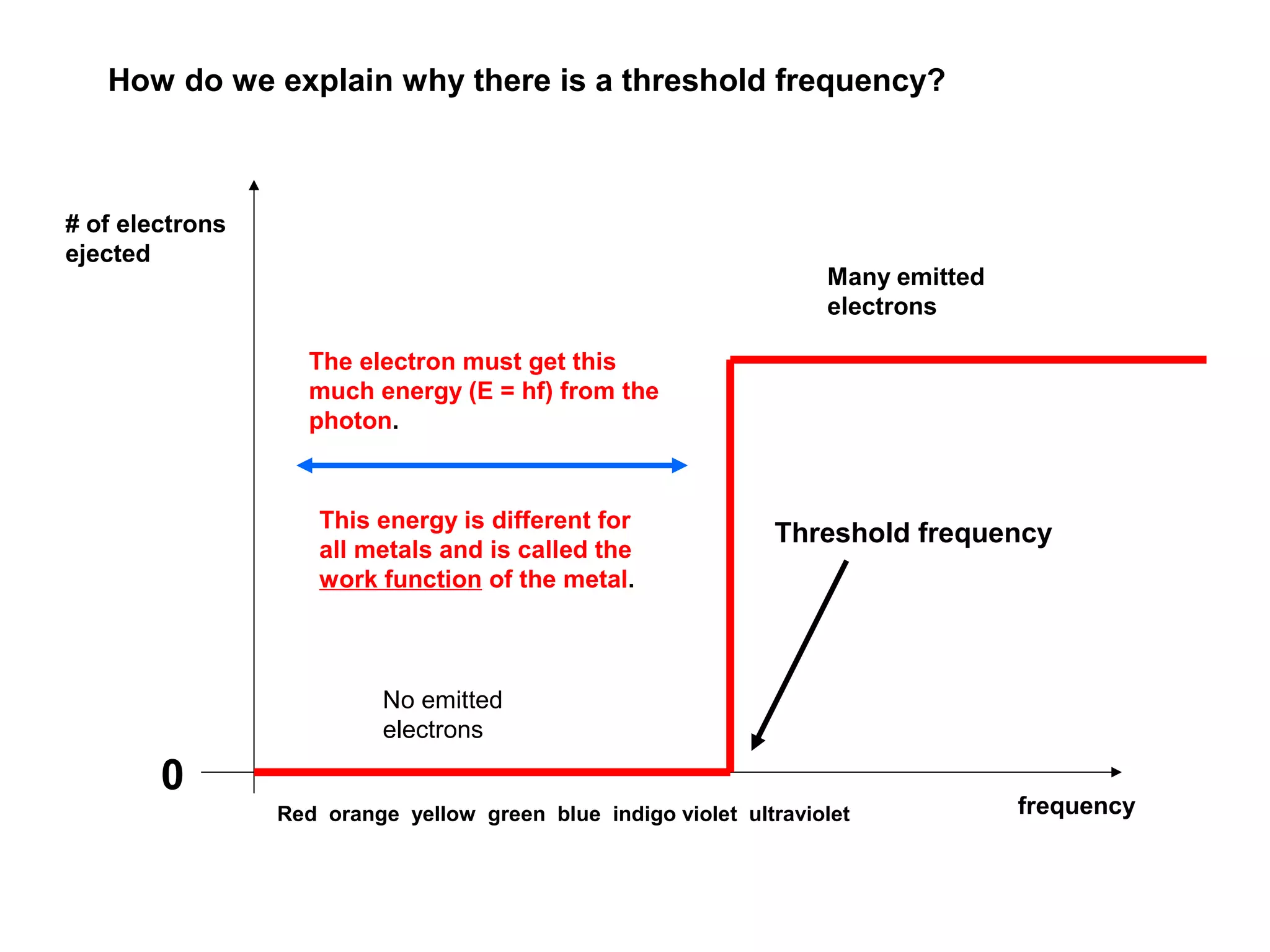
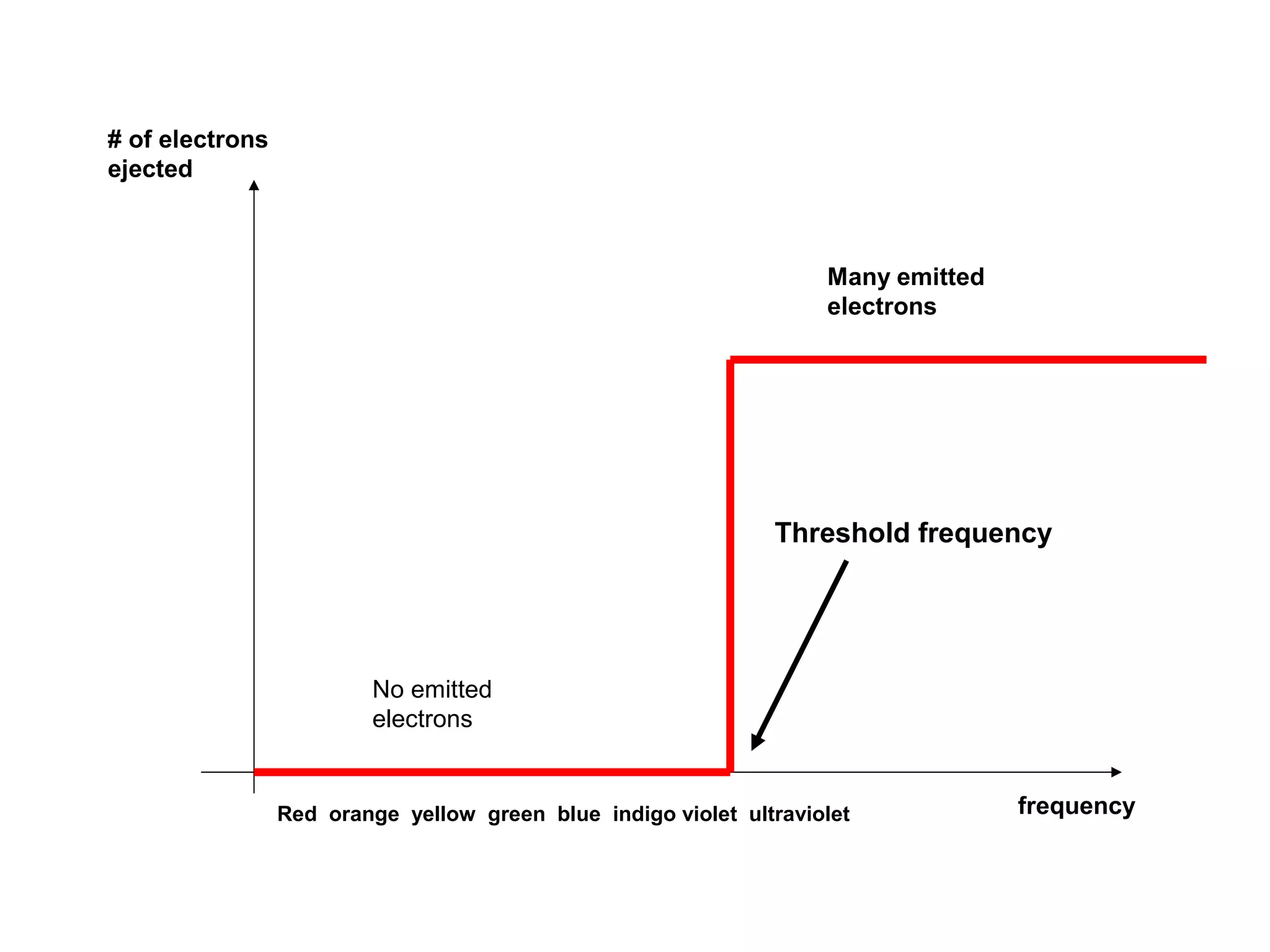
[2] Electrons are ejected only if the incident light has a frequency
above some threshold value (i.e., it depend on the color of the light!!)
electrons
metal
light
Electron
detector](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumtheoryppt2-131107003044-phpapp01/75/Quantum-theory-ppt-18-2048.jpg)





![Einstein argued that the emission of the light must occur
in instantaneous bursts of radiation.
He then took this one step further: he said that all light had the
following properties:
[1] All radiation occurs as tiny bundles (particles).
[2] The bundles always move a lightspeed (c).
[3] They have zero rest-mass.
[4] The energy of a photon is given by
E = hf
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 x 10-34 J x s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumtheoryppt2-131107003044-phpapp01/75/Quantum-theory-ppt-28-2048.jpg)