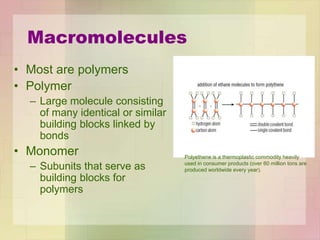
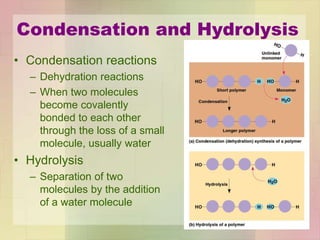
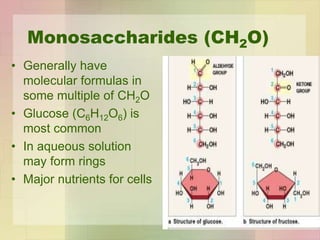
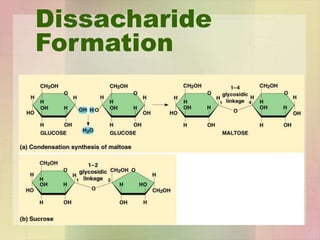
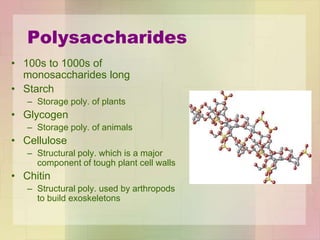
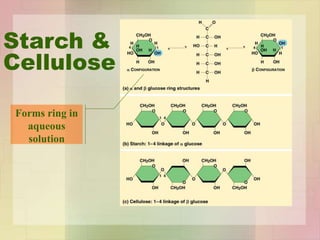
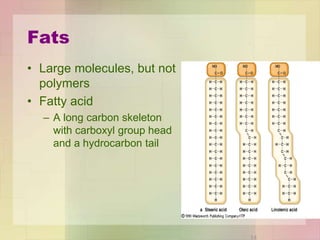
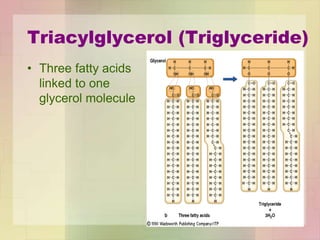
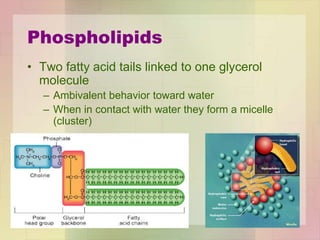
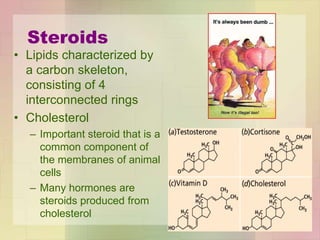
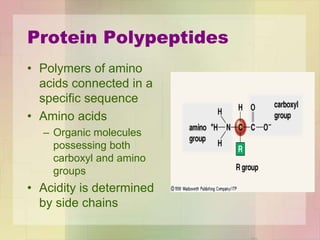
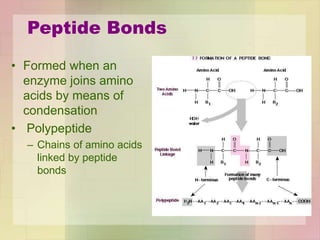
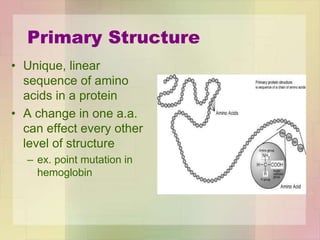
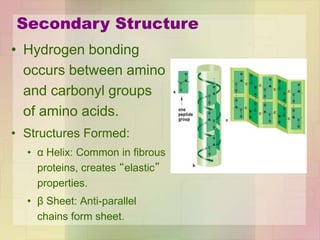
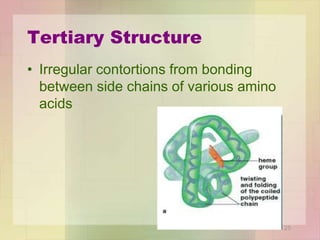
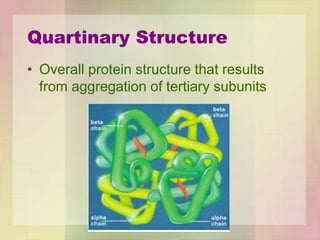
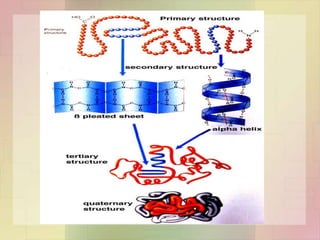
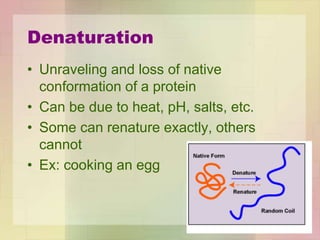
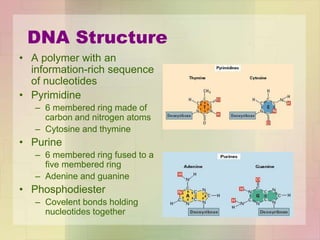
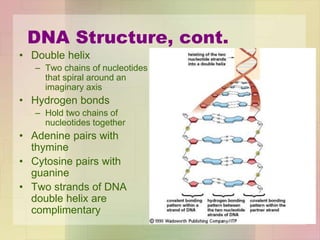
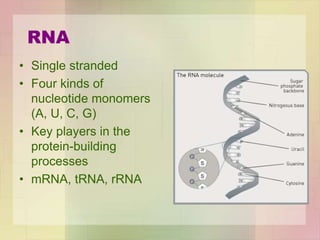
This document provides an overview of macromolecules including their structure, function, and importance in living organisms. It discusses the key macromolecules of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. For each macromolecule, it describes the monomers used to build polymers, examples of different types, and their roles in cells. The document emphasizes that macromolecules are constructed through condensation reactions from simple monomers into complex polymers with unique properties essential for life.