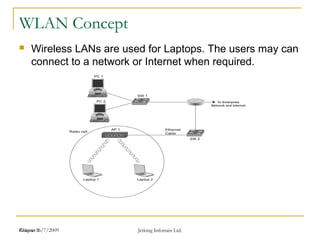
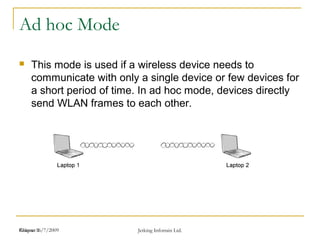
The document discusses wireless local area networks (WLANs) and security. It describes WLAN concepts including ad hoc and infrastructure modes. It covers WLAN security standards such as WEP, WPA, and 802.11i. It also discusses Cisco's unified wireless solutions including mesh networks, LWAPP, and AWPP protocols.