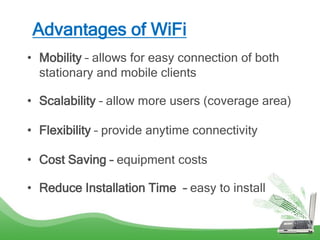
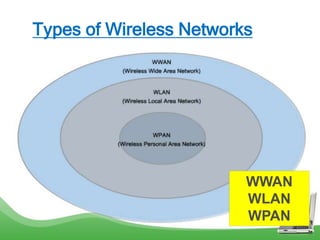
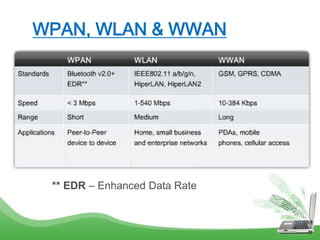
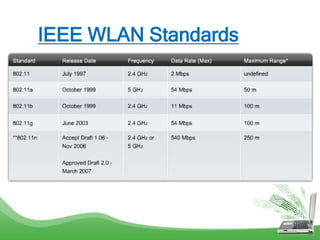
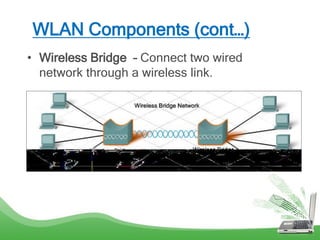
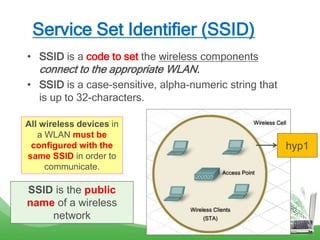
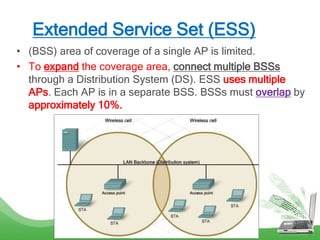
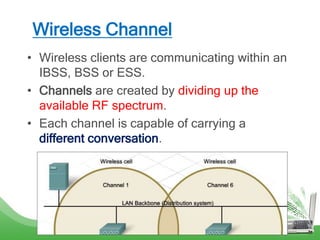
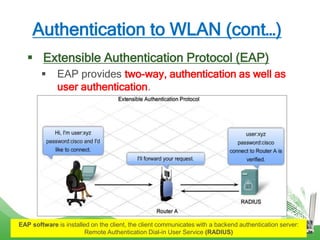
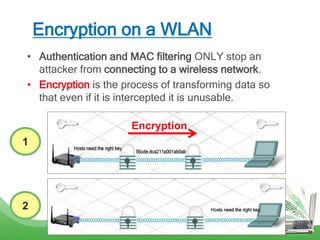
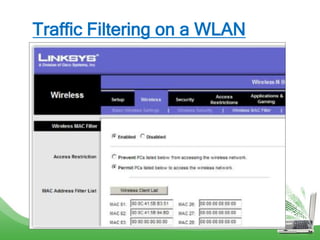
The document discusses learning outcomes related to wireless technologies, building wireless LANs, and implementing wireless LAN security. It covers topics such as wireless standards, WLAN components, setting up infrastructure and ad-hoc modes, wireless channels, authentication methods, encryption protocols like WEP and WPA, and traffic filtering. The goal is to understand wireless concepts and how to properly setup and secure a wireless local area network.