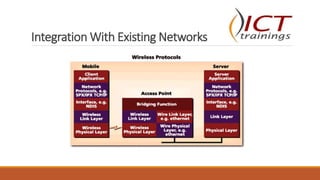
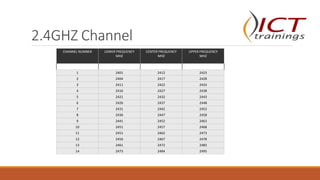
This document provides an overview of wireless communication and networking. It defines wireless communication and discusses wireless network topologies and integration with wired networks. It describes the IEEE 802.11 wireless standards including 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n. It also discusses wireless networking devices such as access points, wireless LAN controllers, and bridges. Finally, it covers common wireless security measures including SSID hiding, MAC address filtering, static IP addressing, 802.1X authentication, WEP, WPA, and WPA2 encryption.