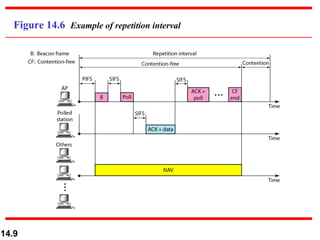
The document discusses wireless LAN standards including IEEE 802.11 and Bluetooth. It provides an overview of IEEE 802.11 specifications and architecture, addressing mechanisms, and physical layers. It also covers Bluetooth technology, describing its ad hoc network architecture and layers such as baseband and L2CAP. Various concepts are illustrated with figures including basic service sets, extended service sets, MAC layers, and frame formats.