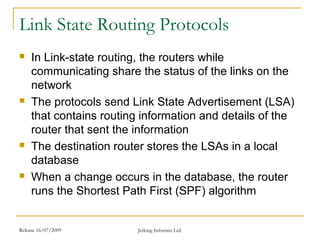
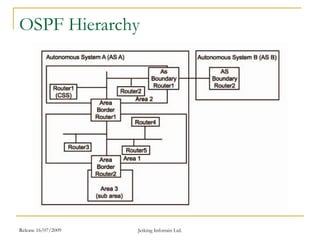
The document discusses several interior gateway routing protocols: IGRP is a distance-vector protocol that uses a composite metric and supports unequal-cost load balancing and multipath routing. EIGRP is a hybrid link-state and distance-vector protocol that provides fast convergence, less overhead, and supports six path load balancing. OSPF is a link-state protocol that uses the Shortest Path First algorithm to determine the shortest route and provides advantages like being open, loop-free, scalable, and hierarchical with multicasting support. It maintains a two-layer hierarchy of backbone and off-backbone areas to conserve router resources and handle external routes.