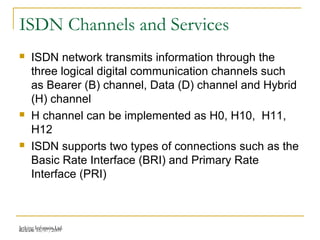
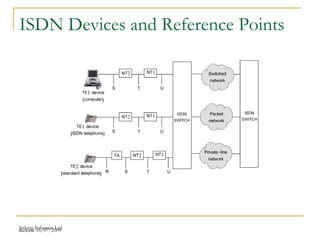
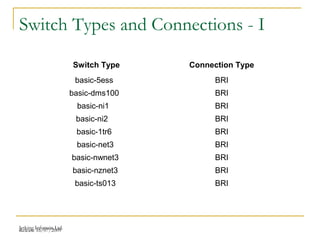
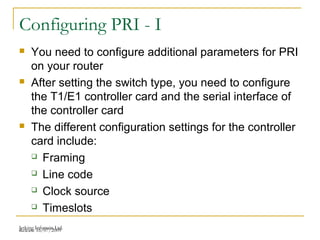
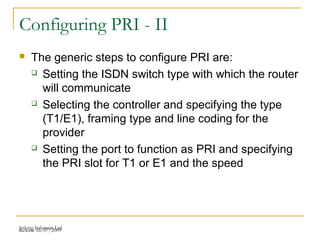
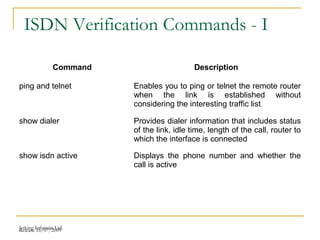
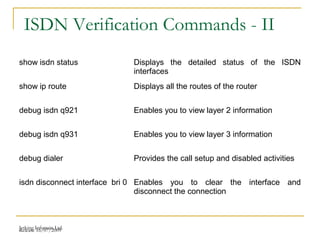
This document provides an overview of Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) configuration. It describes ISDN features like speed and multiple device support. It explains ISDN devices, connections using Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI), and the process of configuring BRI and PRI on routers. It also discusses verifying ISDN connections and configuring Dial on Demand Routing (DDR) to establish connections for specific interesting traffic.










![Release 16/07/2009Jetking Infotrain Ltd.
Configuring Static Routes
The DDR feature of Cisco allows you to prevent
unwanted traffic from making phone calls and
keeping the line busy
configuring static routes helps in avoiding other
traffic to trigger calls
The ip route command enables you to define the
static route. The syntax of this command is:
ip route network_IP_address_# subnet_mask
remote_router’s_IP_address|router_interface
[administrative_distance]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-141217100807-conversion-gate01/85/CCNA-CHAPTER-10-BY-jetarvind-kumar-madhukar-26-320.jpg)
![Release 16/07/2009Jetking Infotrain Ltd.
Specifying Interesting Traffic
Access Lists (ACLs) allows you to specify the
interesting traffic on the router
Using the dialer-list command, you can allow only
the IP traffic to establish connection
The dialer-list command enables you to specify
which traffic is interesting. The syntax of this
command is:
dialer-list [list_#] protocol [protocol_name] permit|
deny access-list [ACL_#]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-141217100807-conversion-gate01/85/CCNA-CHAPTER-10-BY-jetarvind-kumar-madhukar-27-320.jpg)

![Release 16/07/2009Jetking Infotrain Ltd.
Configuring Dialer Maps
Once you finish specifying the interesting traffic and
activating the dialer list on the DDR interface, you
can specify dialer information to the router
The dialer map command gives dialer information
for the router to make phone calls. The syntax of the
command is:
dialer map protocol_name
destination_router_address name [remote_router]
speed [56|64] [broadcast]
[destination_phone_number]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter10-141217100807-conversion-gate01/85/CCNA-CHAPTER-10-BY-jetarvind-kumar-madhukar-29-320.jpg)