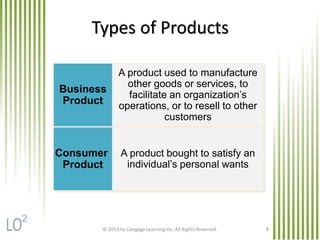
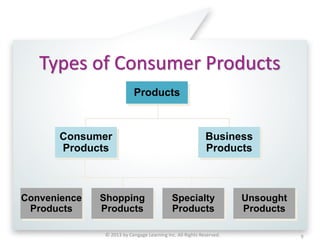
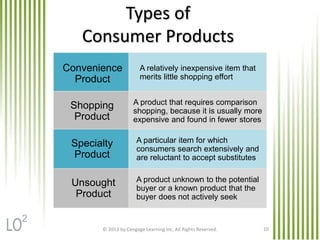
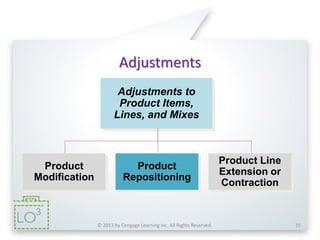
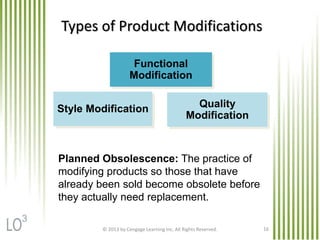
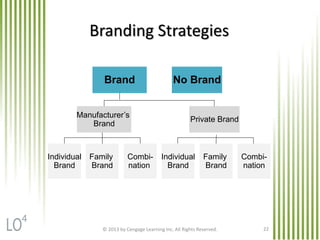
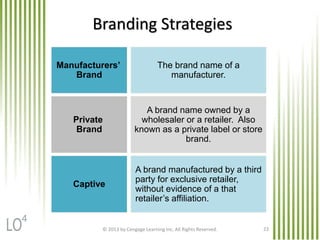
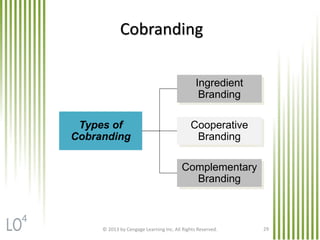
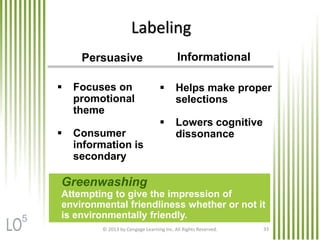
The document discusses key marketing concepts related to products. It defines products, consumer products, and different types of consumer products. It also defines product items, product lines, and product mixes. The document then describes marketing uses of branding, packaging, labeling, and product warranties. It discusses how branding can benefit companies through product identification, repeat sales, and new product sales. Global issues in branding and packaging like adaptations and labeling requirements are also covered.