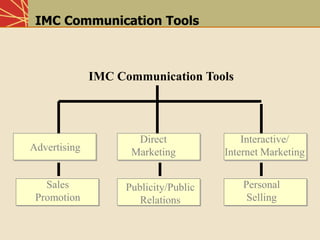
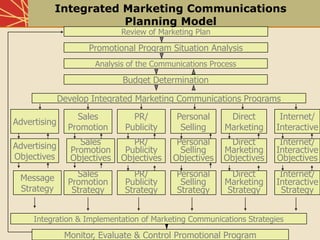
This document provides an overview of various integrated marketing communication (IMC) tools including advertising, direct marketing, interactive/internet marketing, sales promotion, publicity/public relations, and personal selling. It describes each tool, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. It also discusses considerations for developing an IMC promotional program such as situation analysis, objectives, strategy, integration, implementation, and evaluation. The goal of IMC is to coordinate these various promotional elements into a controlled, integrated marketing communications program.