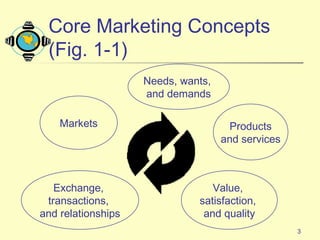
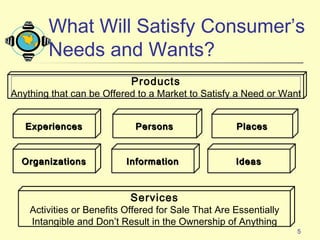
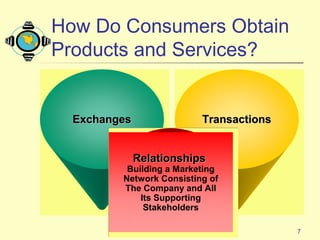
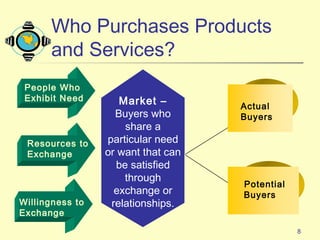
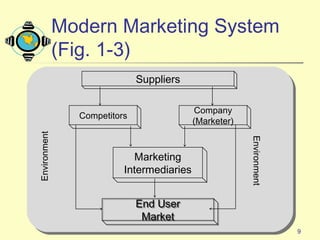
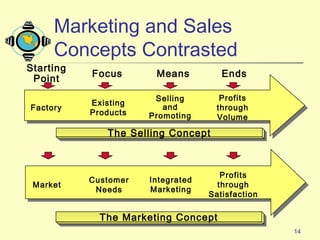
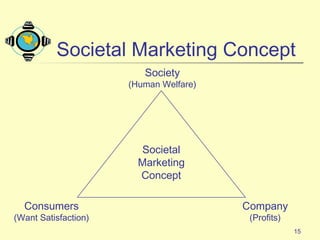
1) The document discusses the core concepts of marketing, including how marketers meet customer needs through products and services to achieve customer satisfaction and profit.
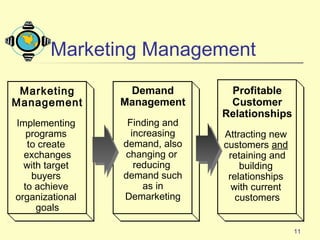
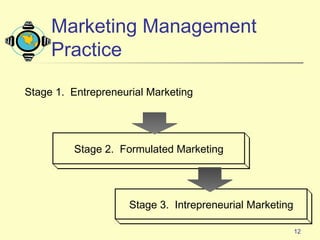
2) It defines marketing management and examines how marketers manage demand and build relationships to achieve organizational goals.
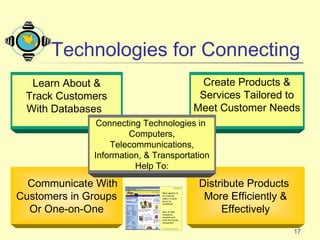
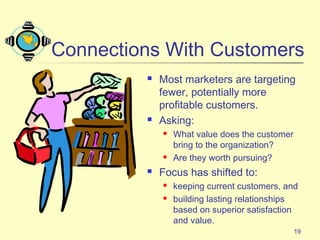
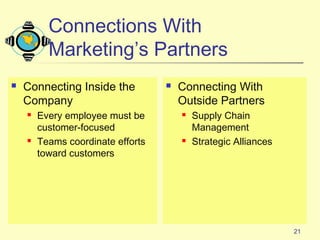
3) Emerging technologies are enabling new ways for companies to connect with customers and partners, including more direct and personalized connections through e-commerce and databases.