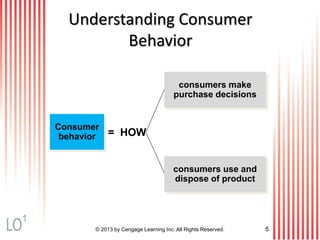
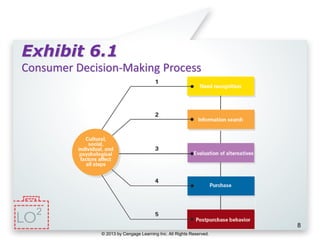
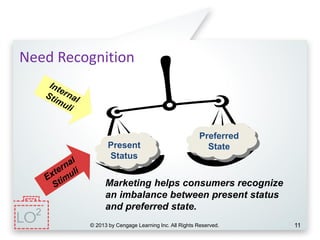
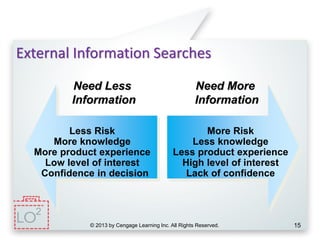
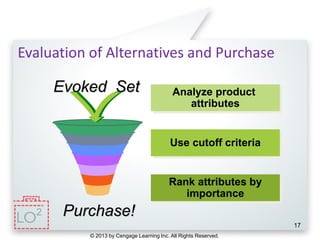
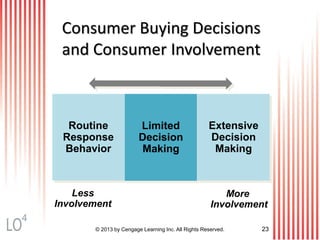
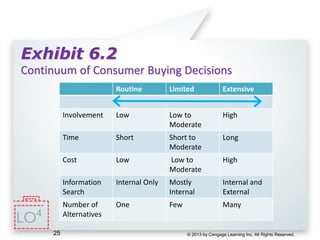
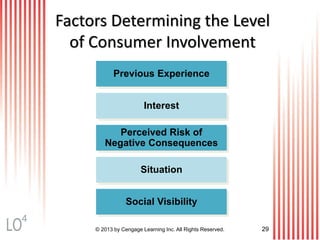
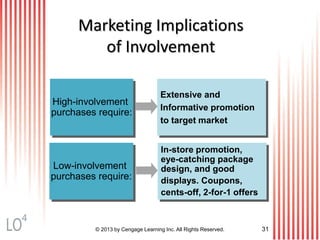
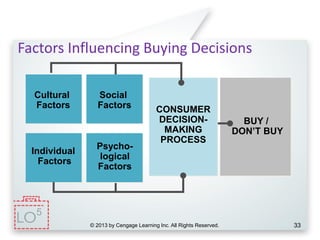
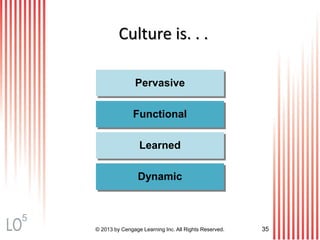
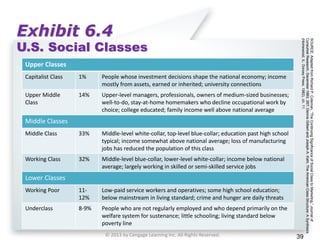
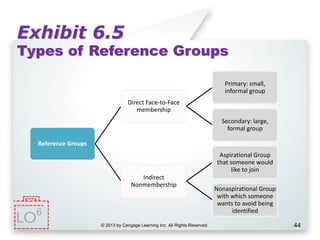
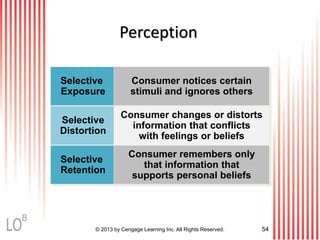
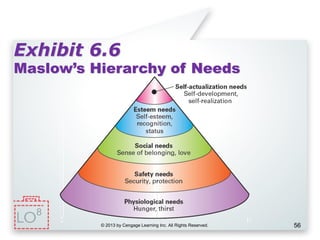
This document provides an overview of consumer decision making by outlining key concepts across 8 chapters. It examines why marketing managers should understand consumer behavior and analyzes the 5 stages of the consumer decision making process: need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. It also identifies the types of consumer buying decisions based on involvement and discusses cultural, social, psychological, and individual factors that influence purchasing.