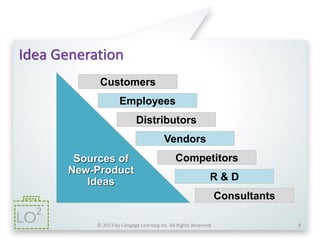
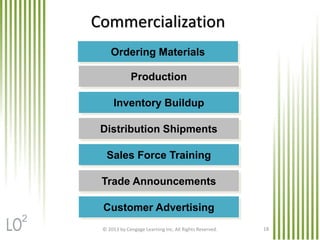
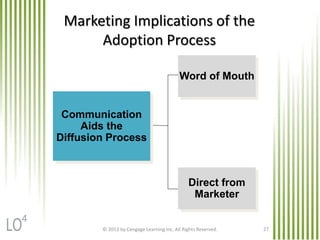
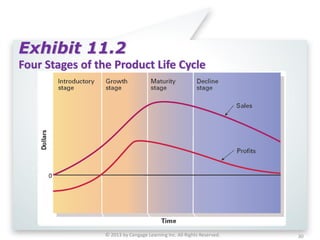
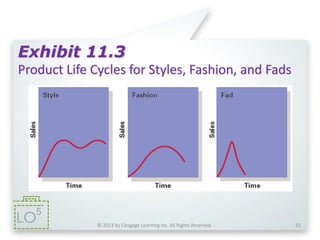
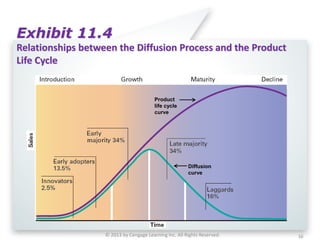
The document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 11 on developing and managing new products. It explains the six categories of new products, the steps in the new product development process, global issues to consider, how new products diffuse through different customer groups, and the concept of product life cycles moving from introduction to growth, maturity, and decline. Various exhibits and figures are referenced to further illustrate these important new product development topics.