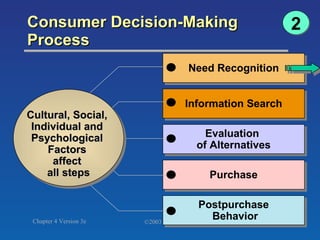
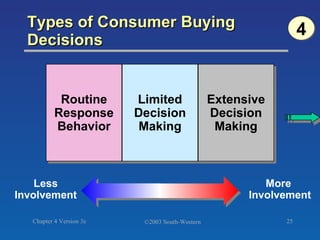
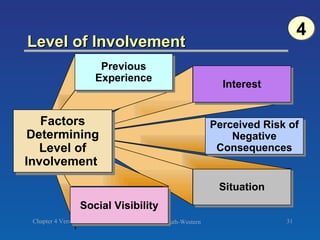
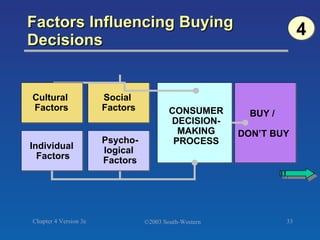
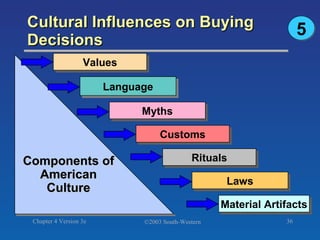
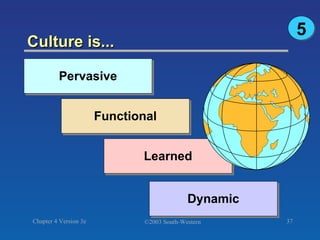
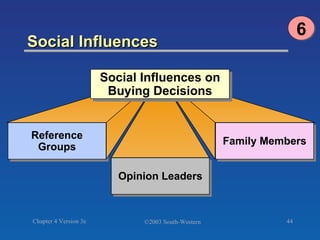
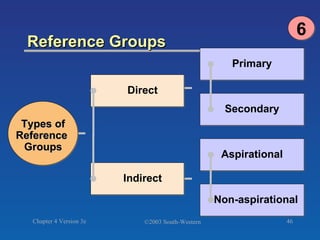
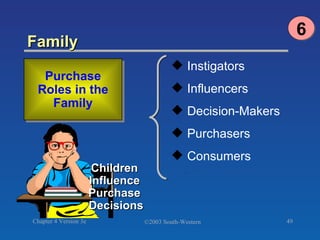
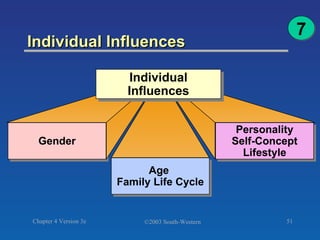
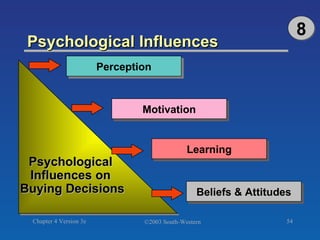
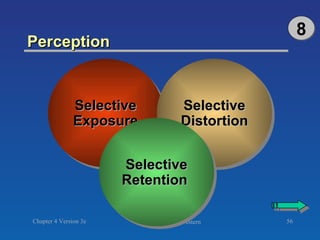
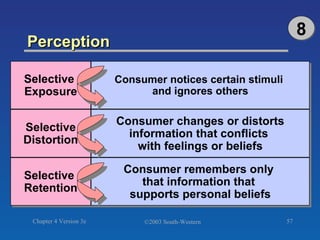
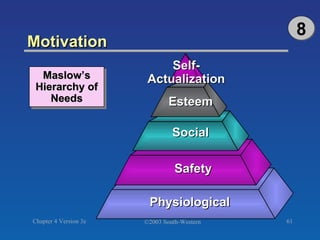
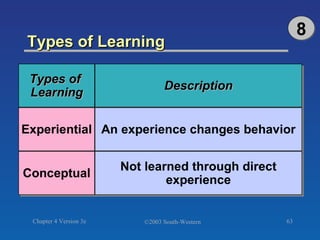
The document discusses key concepts related to consumer decision making and behavior. It covers the consumer decision making process, which includes need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. It also outlines various factors that influence consumer decisions, such as cultural, social, individual, and psychological factors. Finally, it provides learning objectives that explain why marketers should understand consumer behavior and identify the different types of consumer decisions and levels of involvement.