This document discusses electronic records, image records, and records management. It covers:
1) The definitions of electronic records, which are digitized data stored on electronic media, and image records, which are digital or photographic representations of records.
2) Types of storage media like magnetic media (hard drives, tape) and optical media (CDs, DVDs).
3) Procedures for indexing, retrieving, storing, and ensuring security of electronic records.
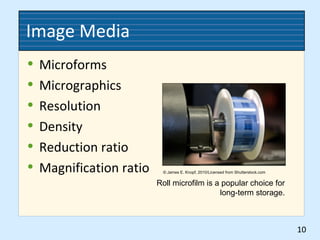
4) The use of imaging technologies like microfilming, digitization, and optical storage to create archival copies of records.