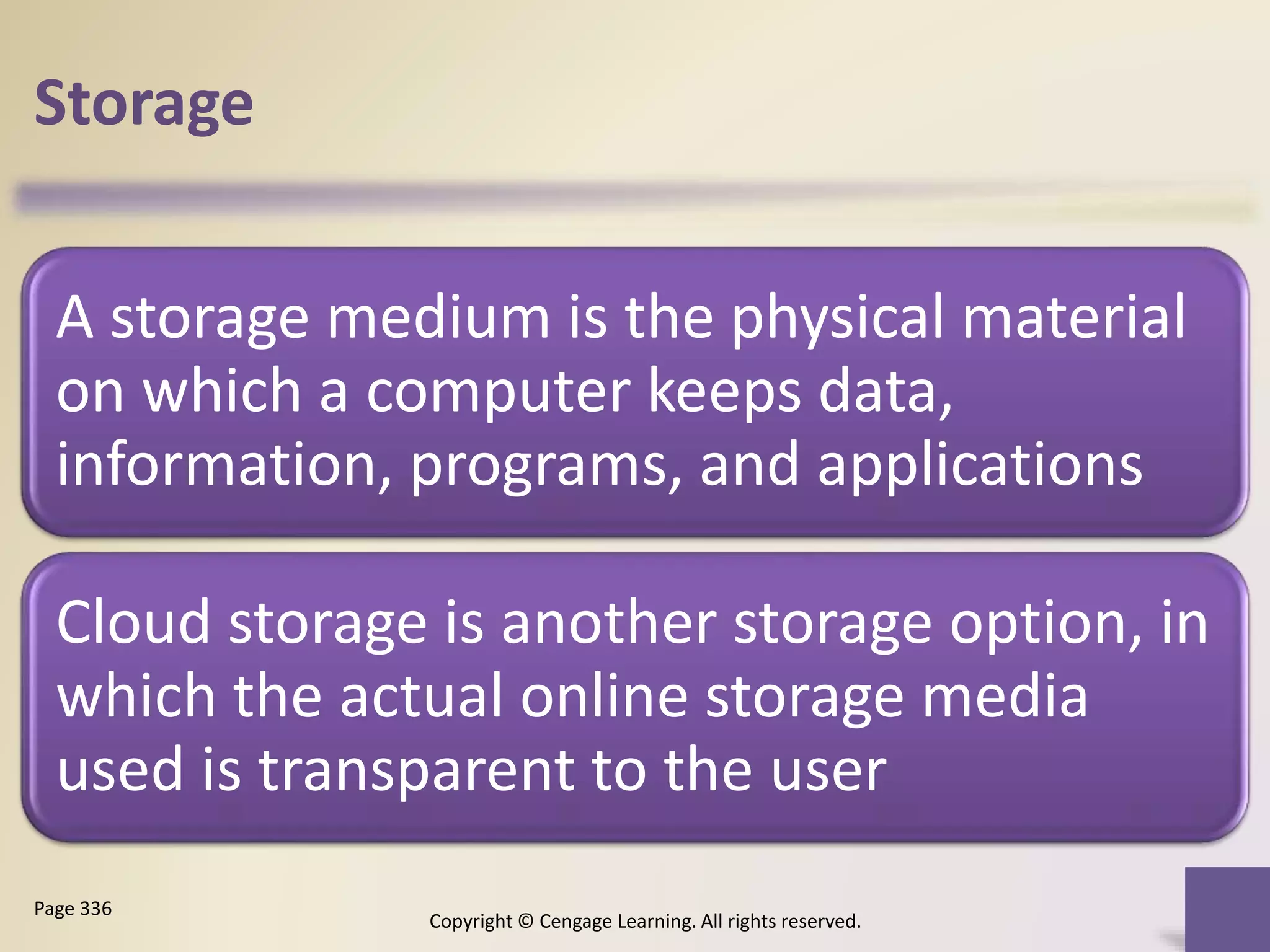
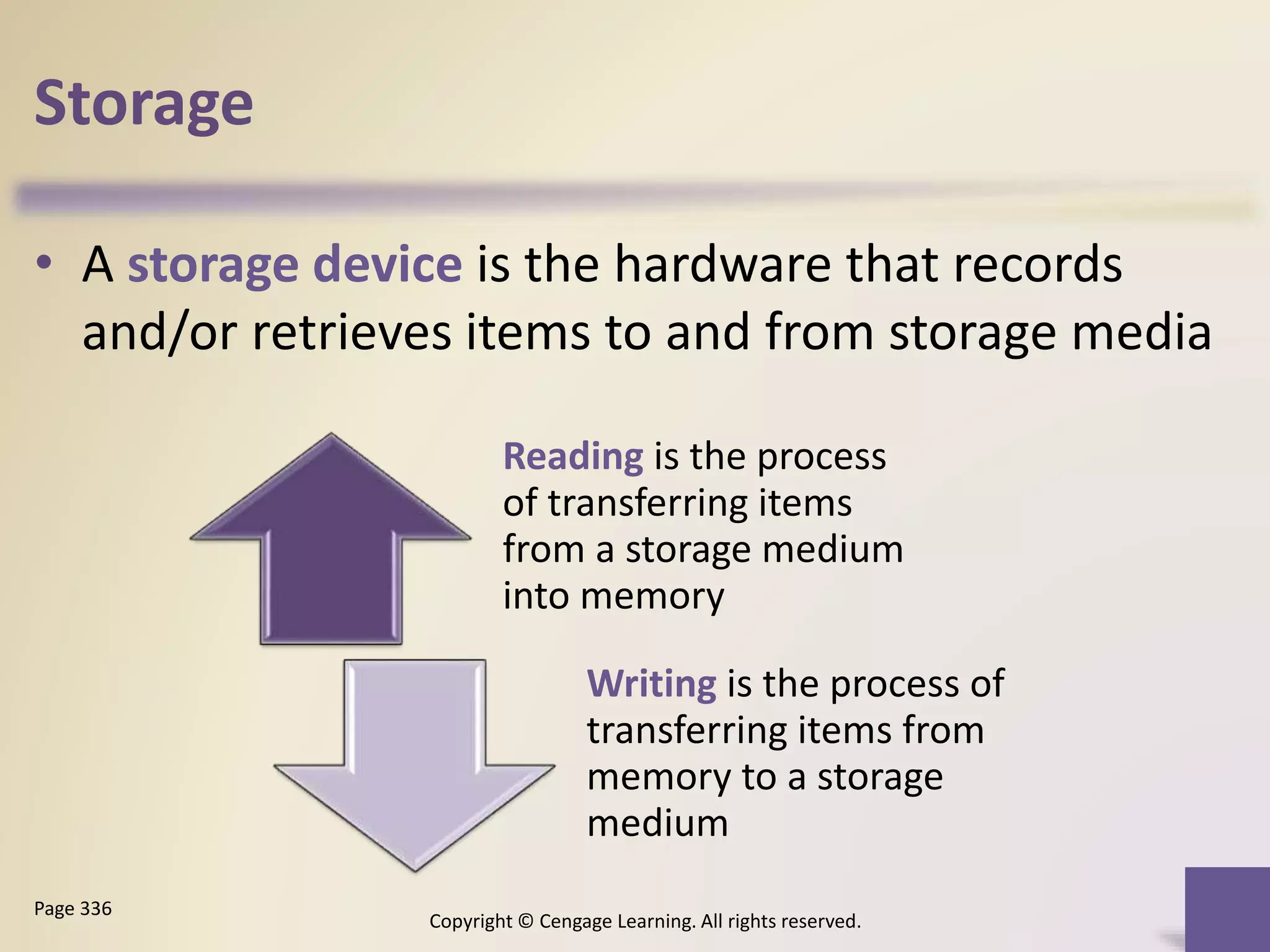
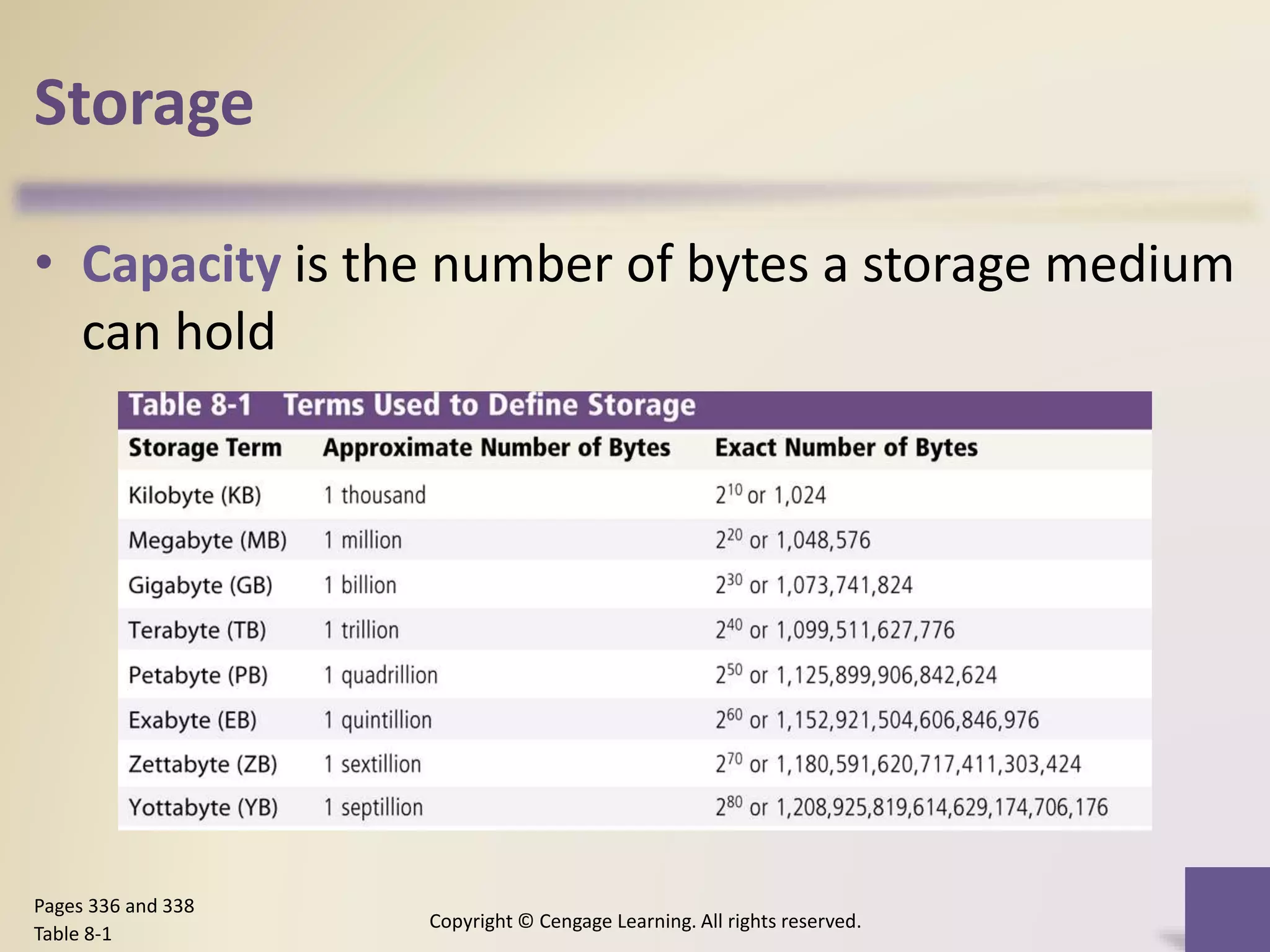
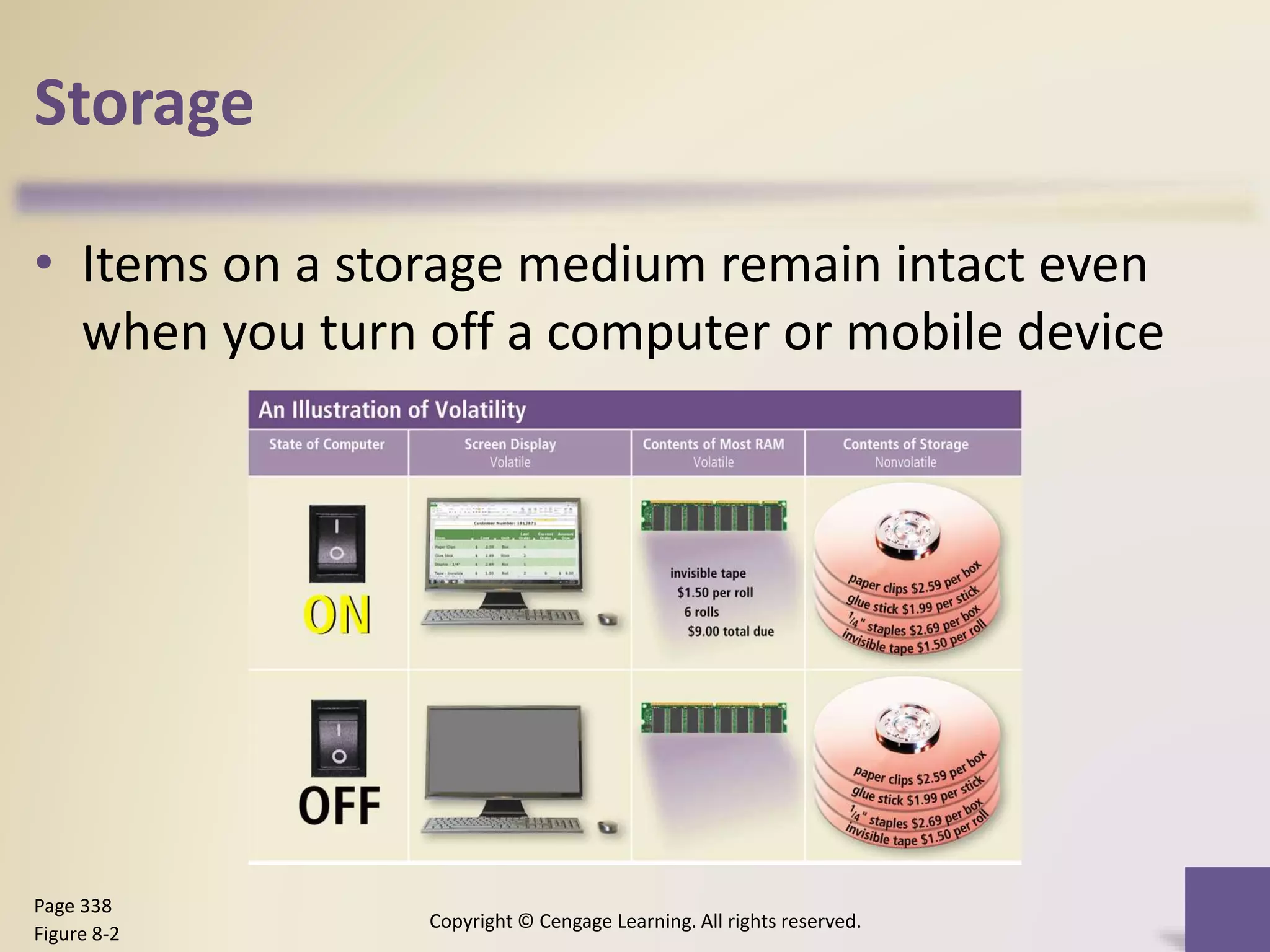
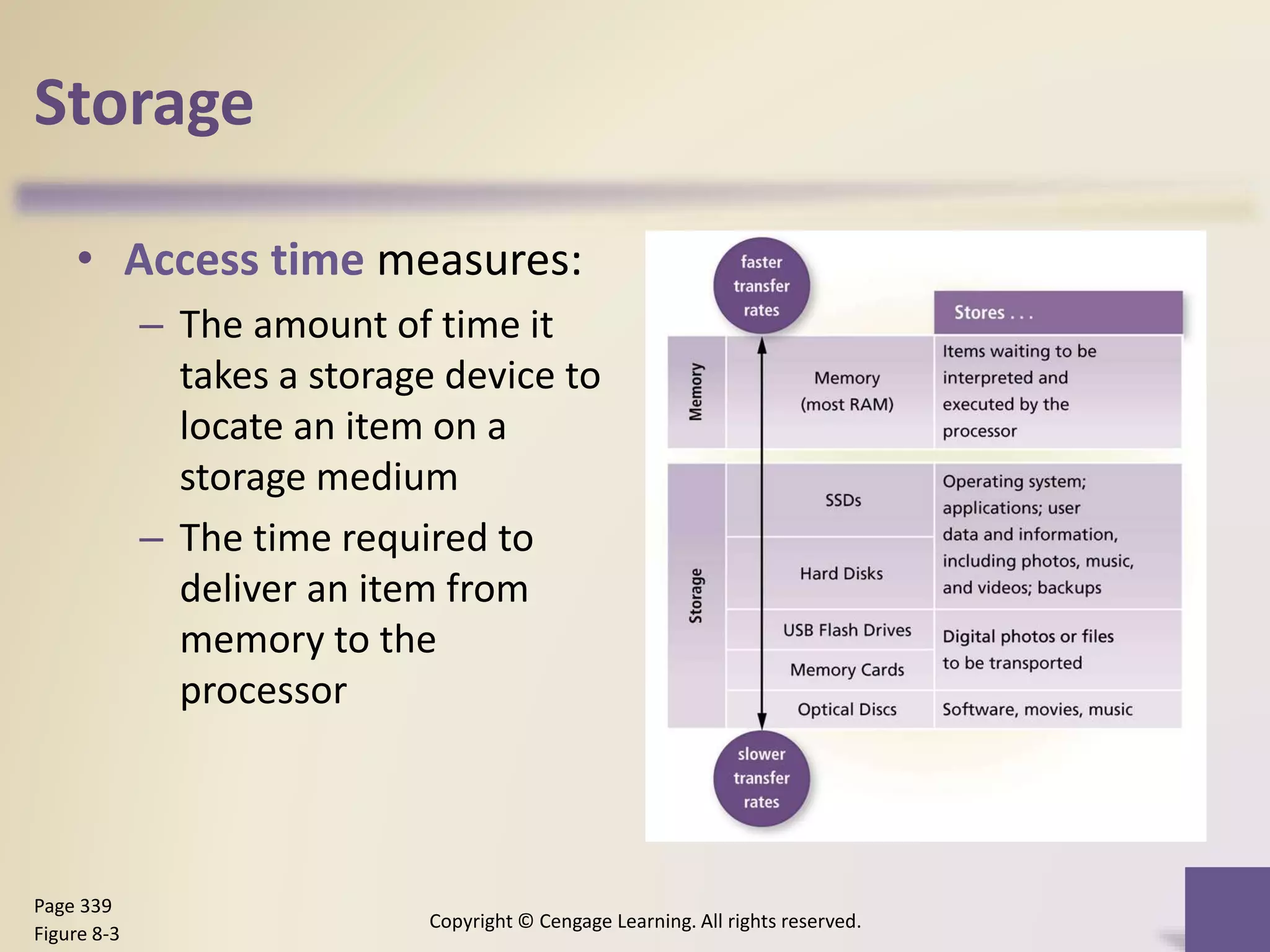
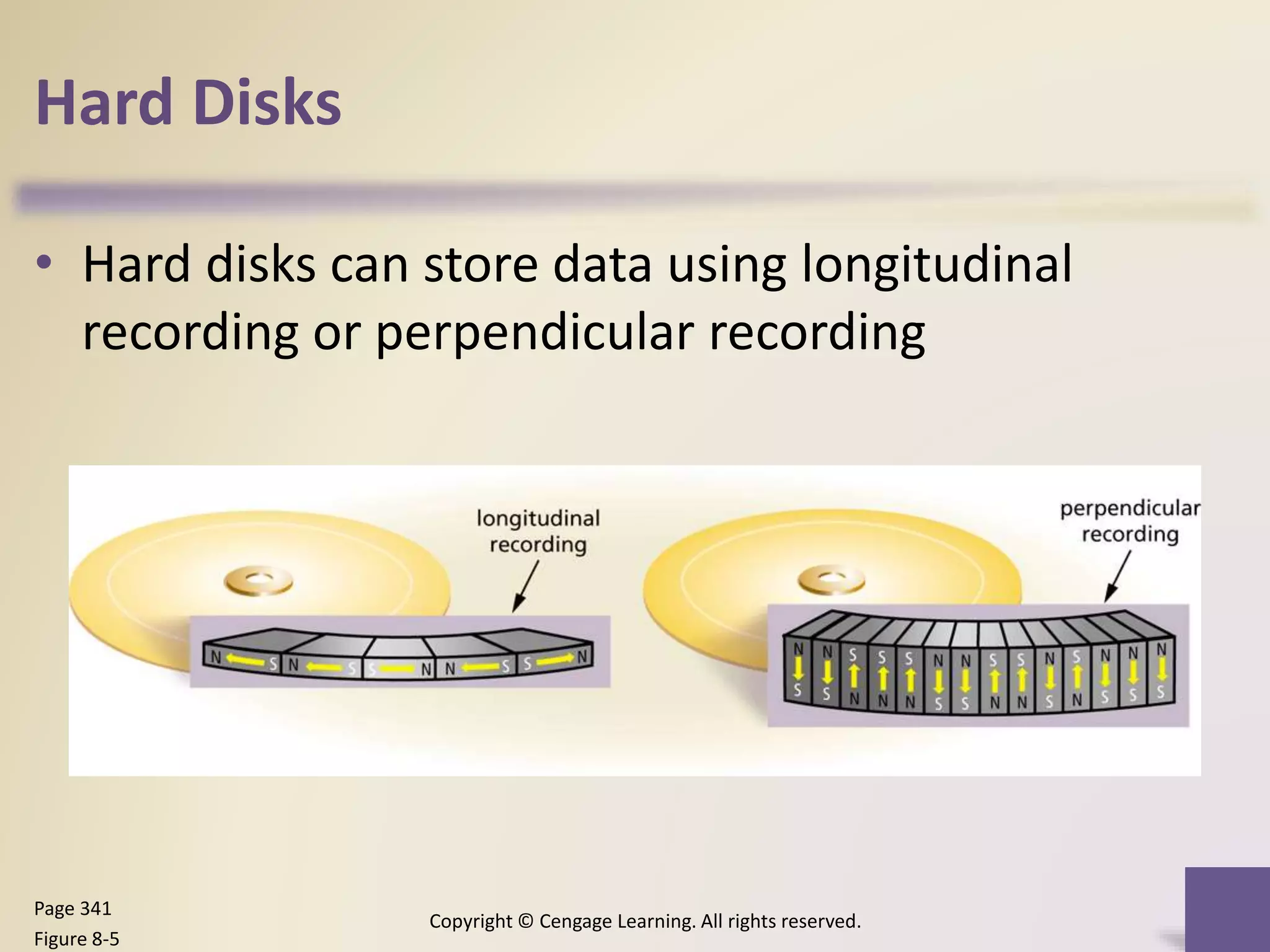
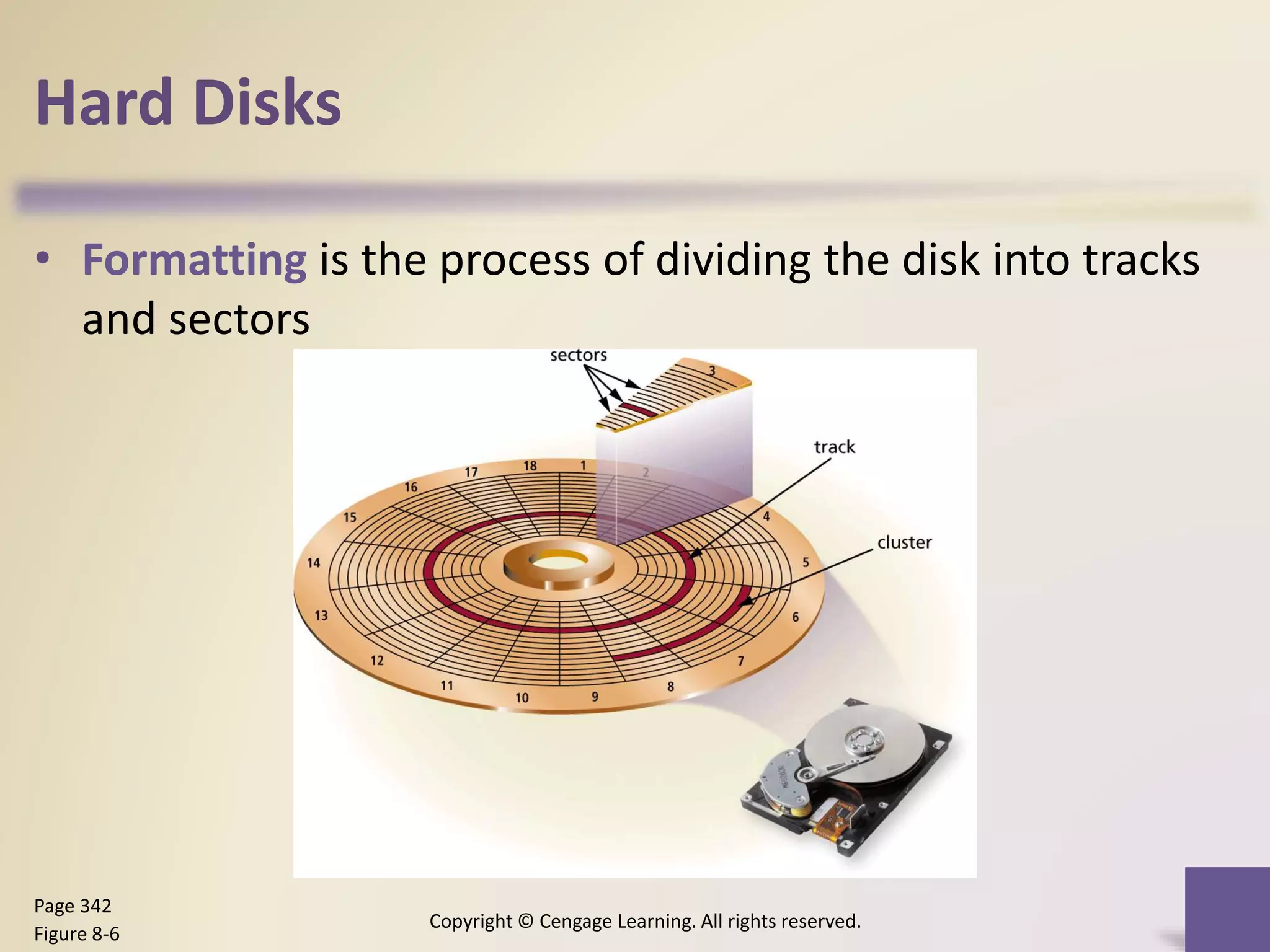
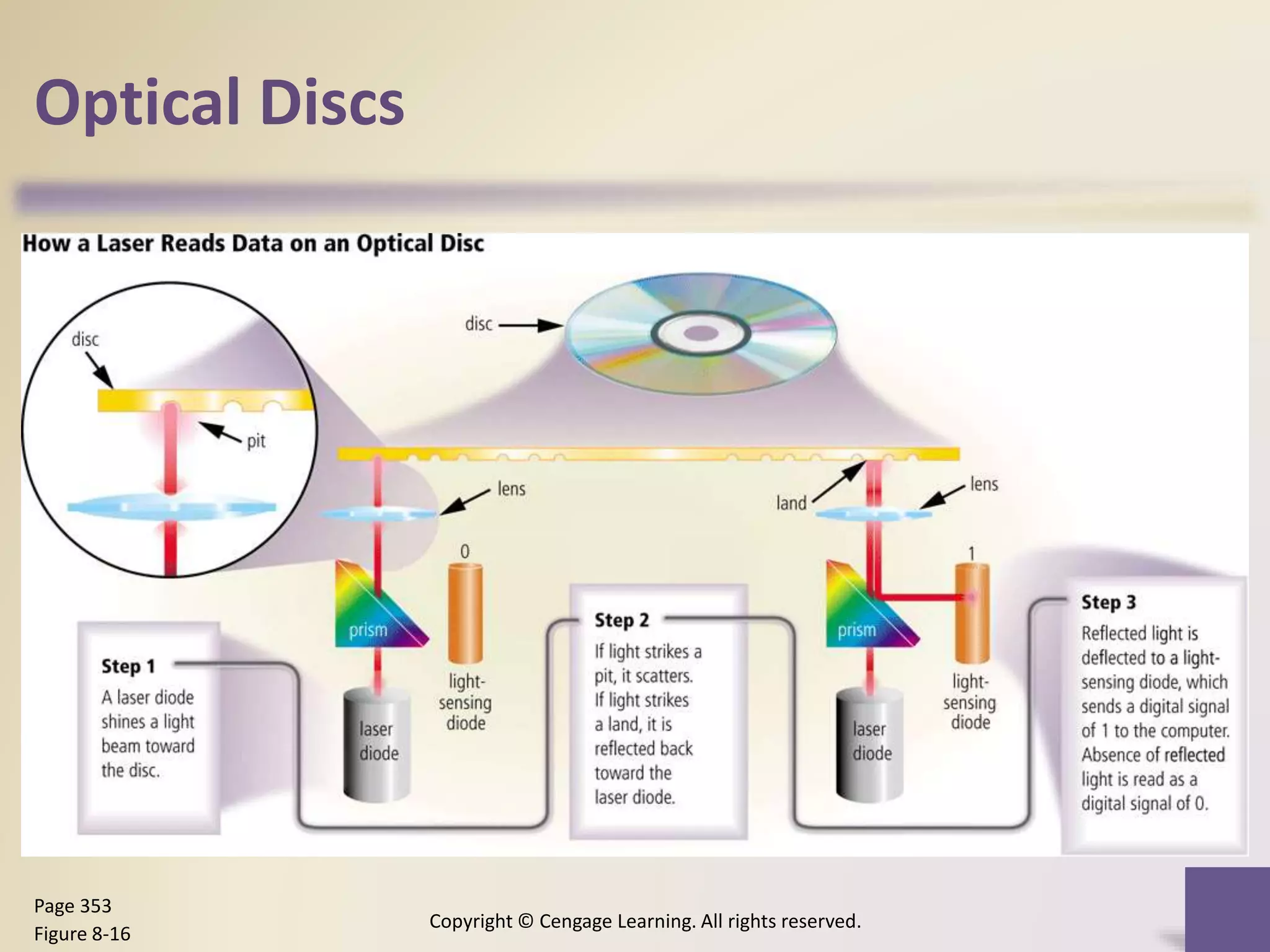
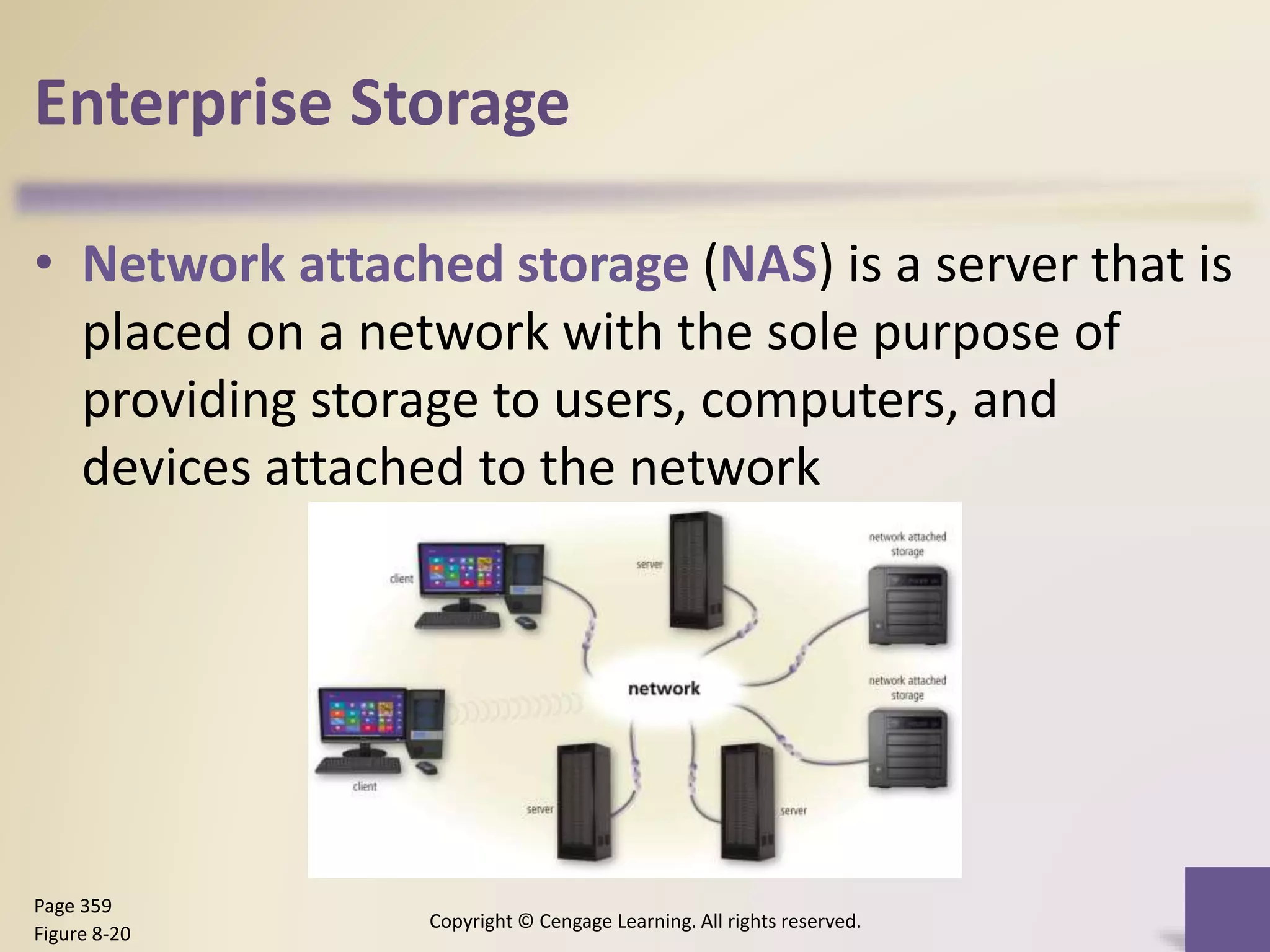
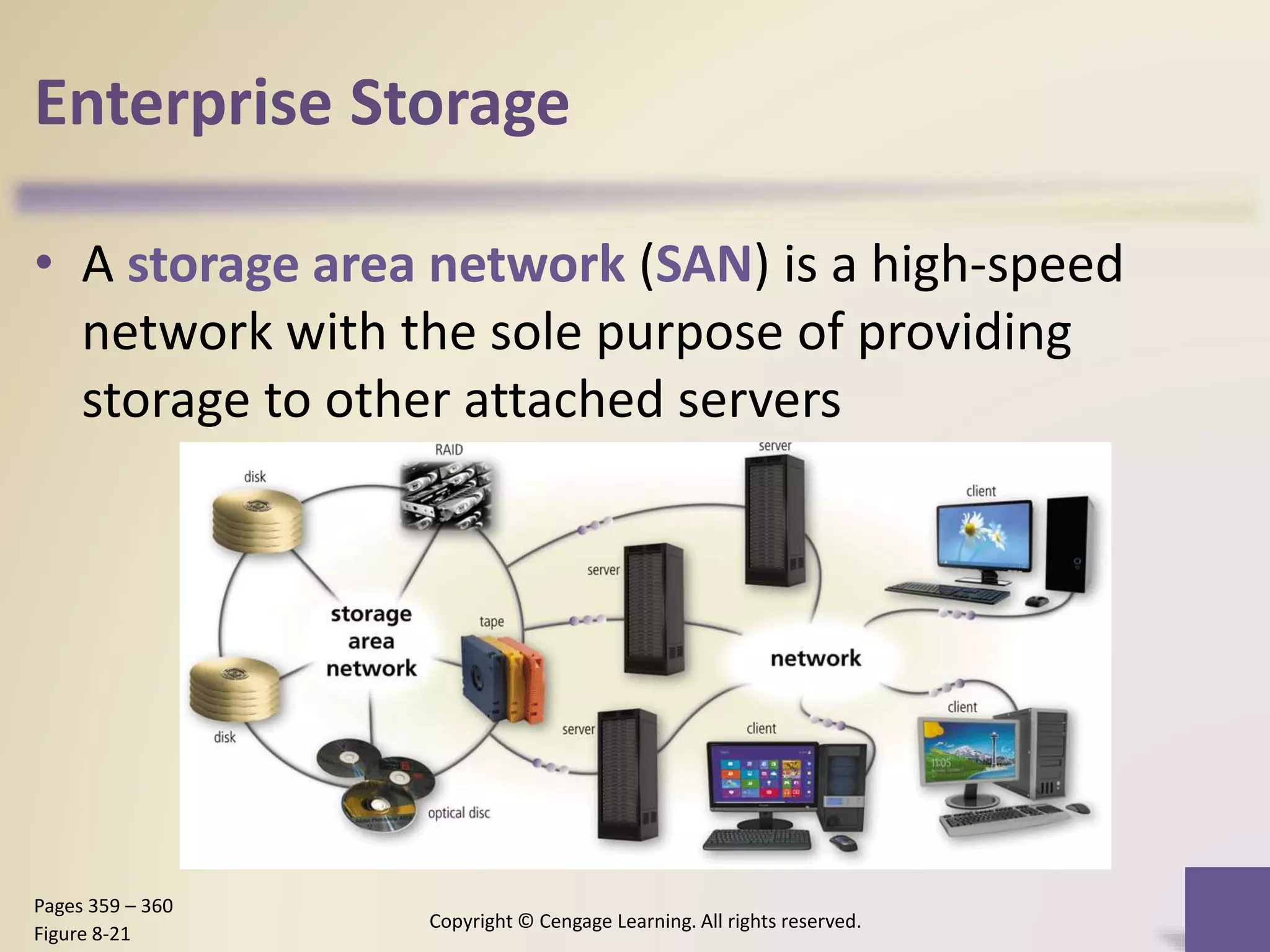
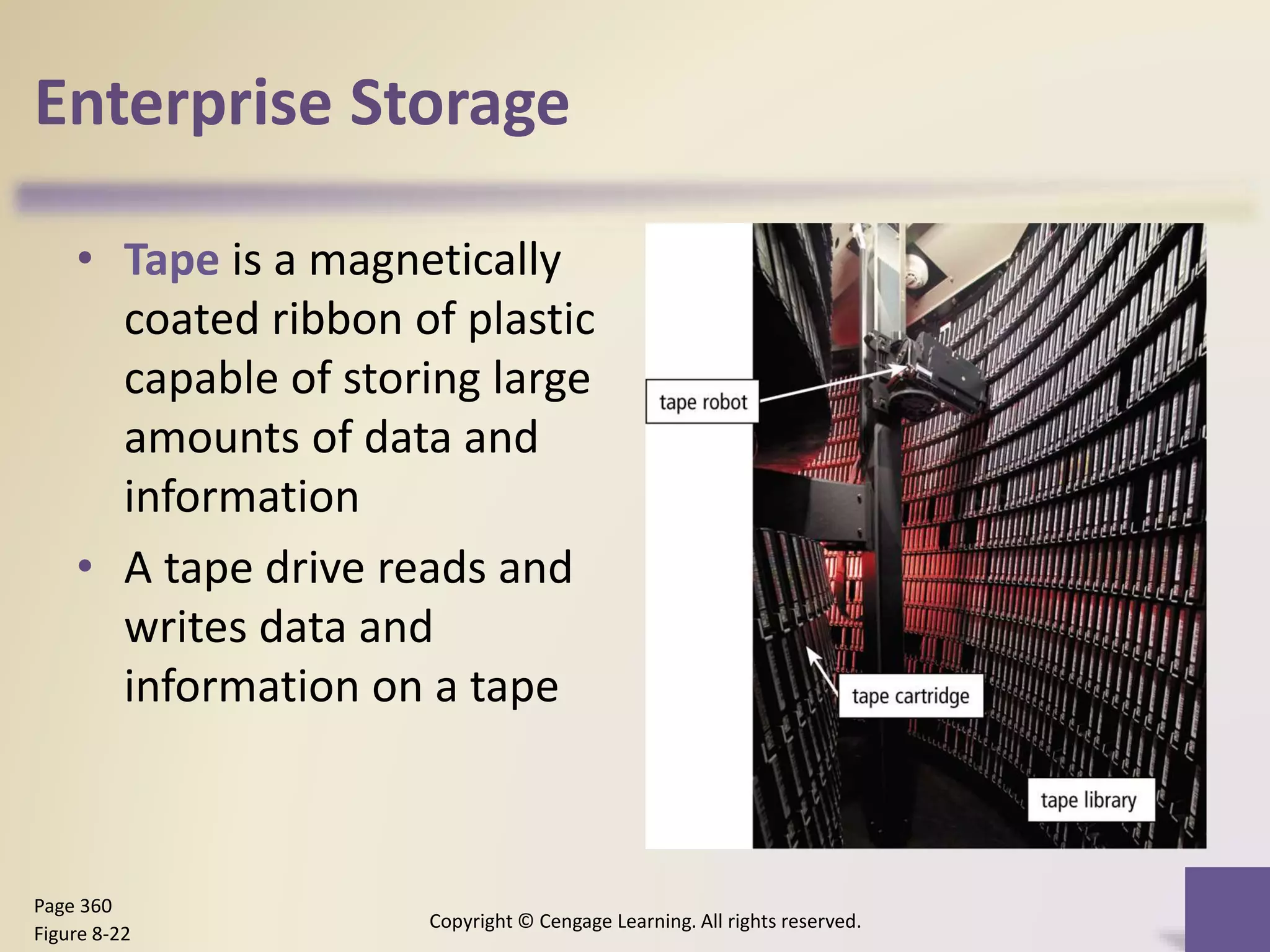
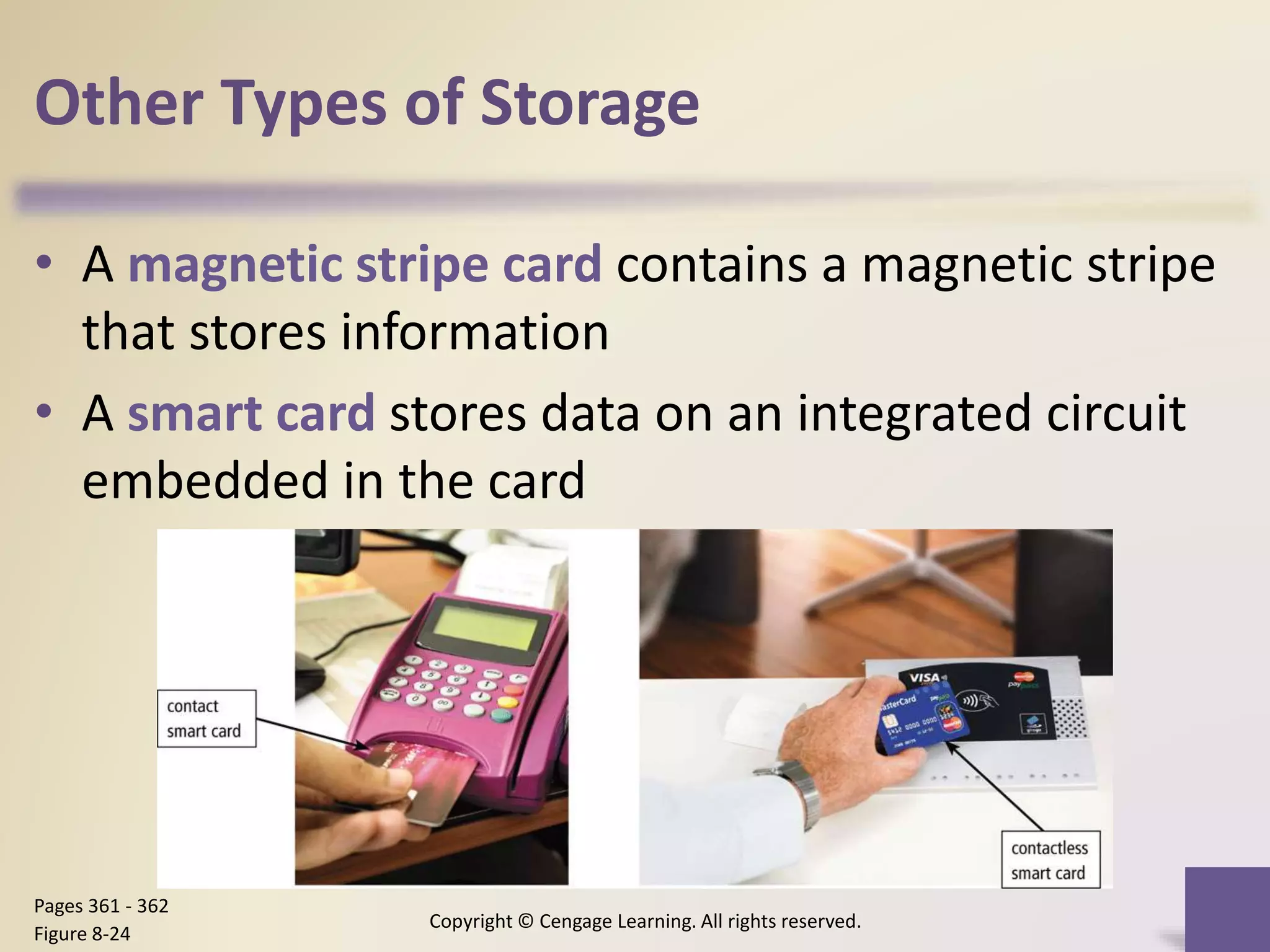
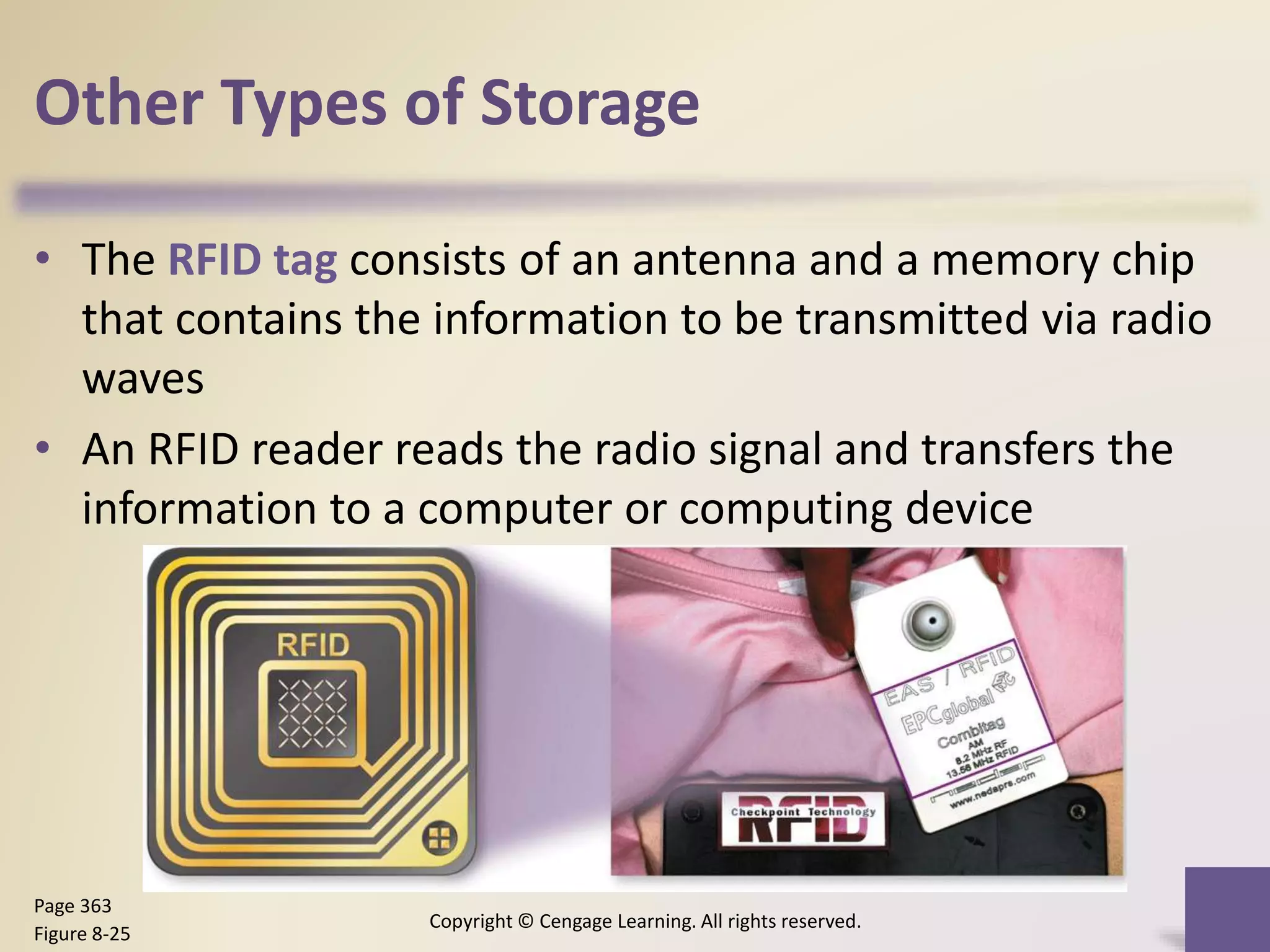
This chapter discusses different types of digital storage used in computing. It describes internal hard disks and their characteristics like tracks, sectors and platters. External hard disks and RAID configurations are used to improve storage capacity and reliability. Flash memory provides alternatives like solid state drives, memory cards and USB drives. Cloud storage holds data on internet servers. Optical discs include CDs, DVDs and their read/write capabilities. Larger organizations use enterprise storage such as RAID, NAS, SAN and tape drives to manage large volumes of data and information. A variety of other storage methods are also covered like magnetic stripe cards, smart cards, RFID and microfilm.