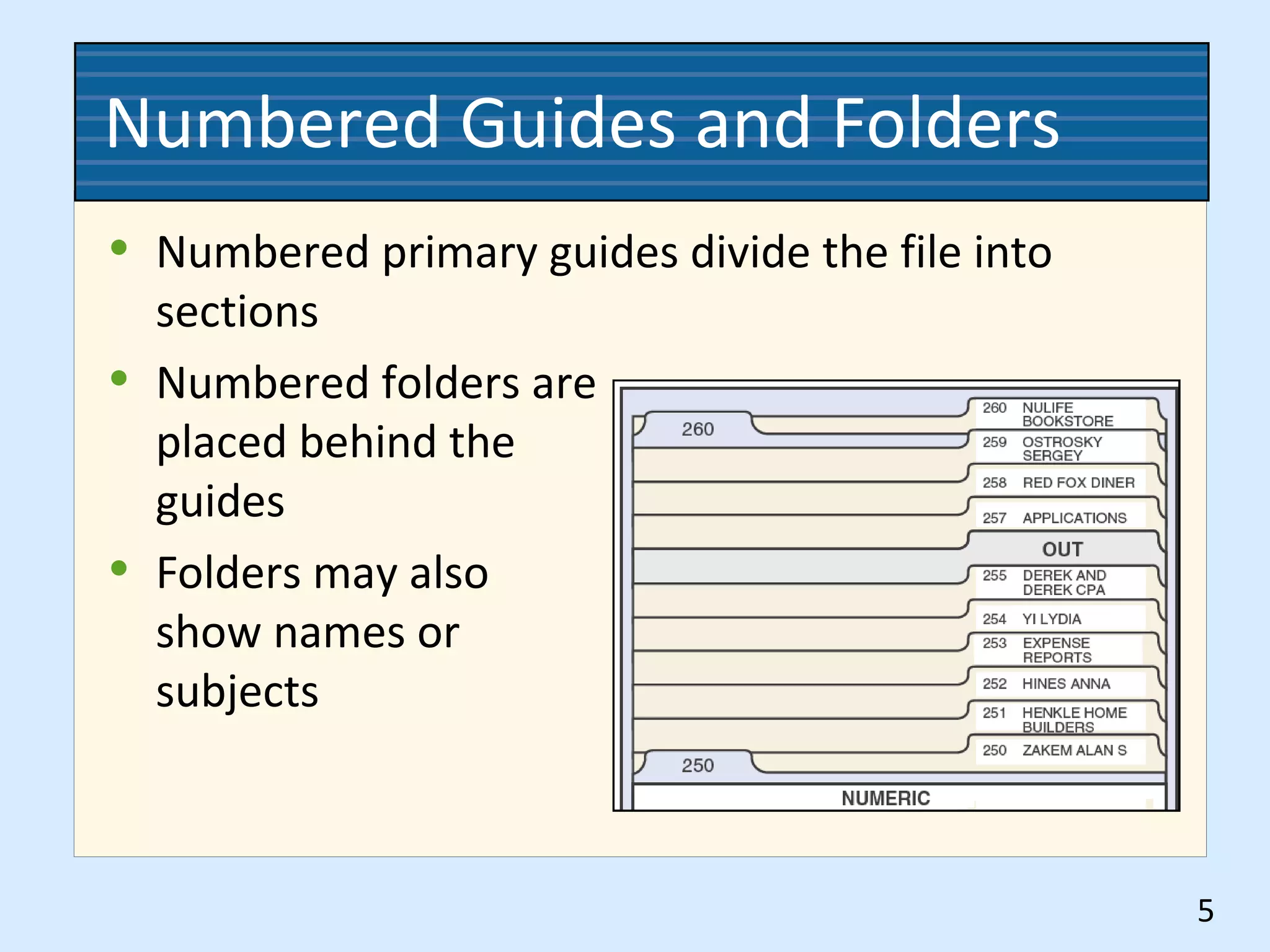
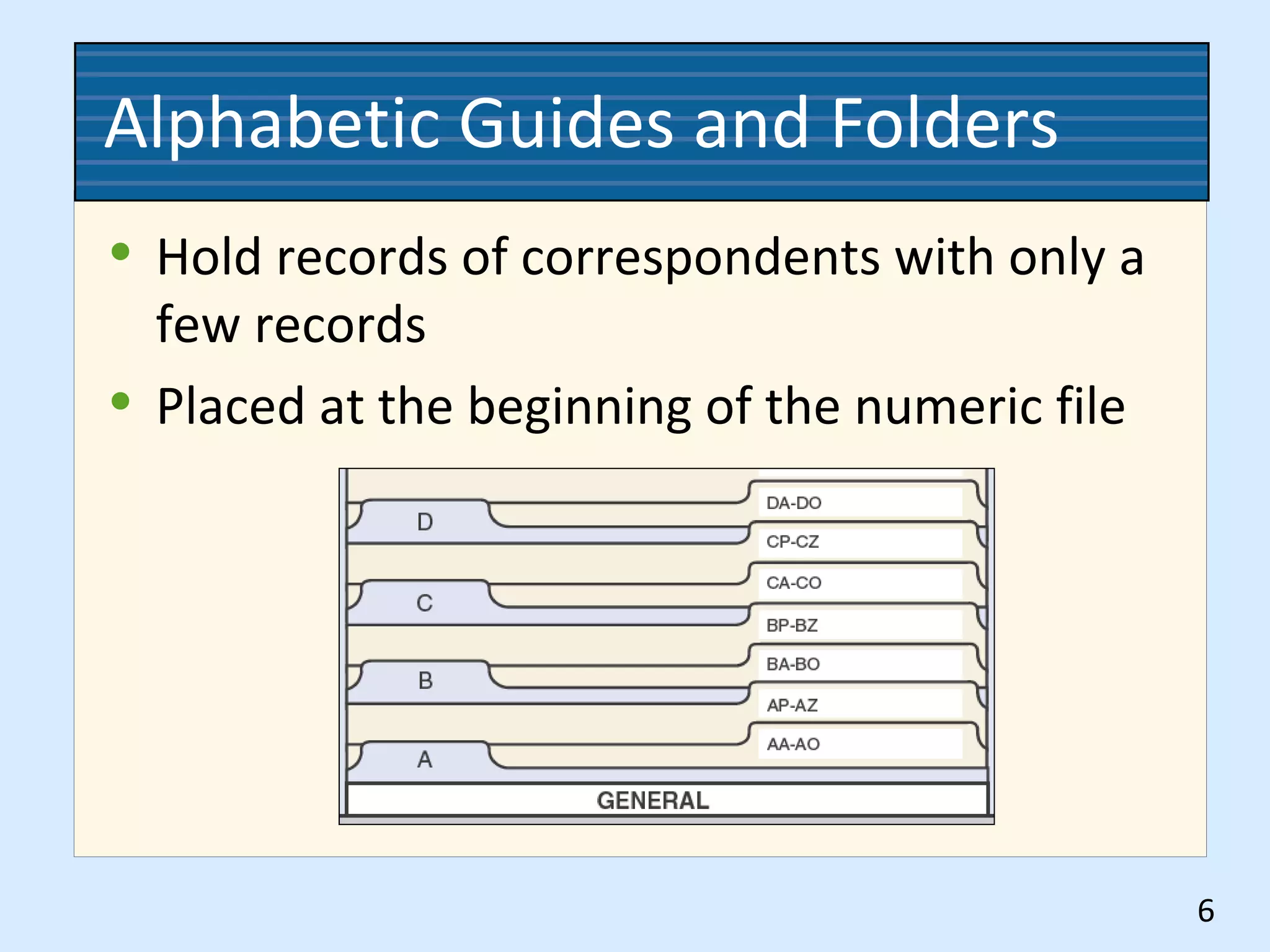
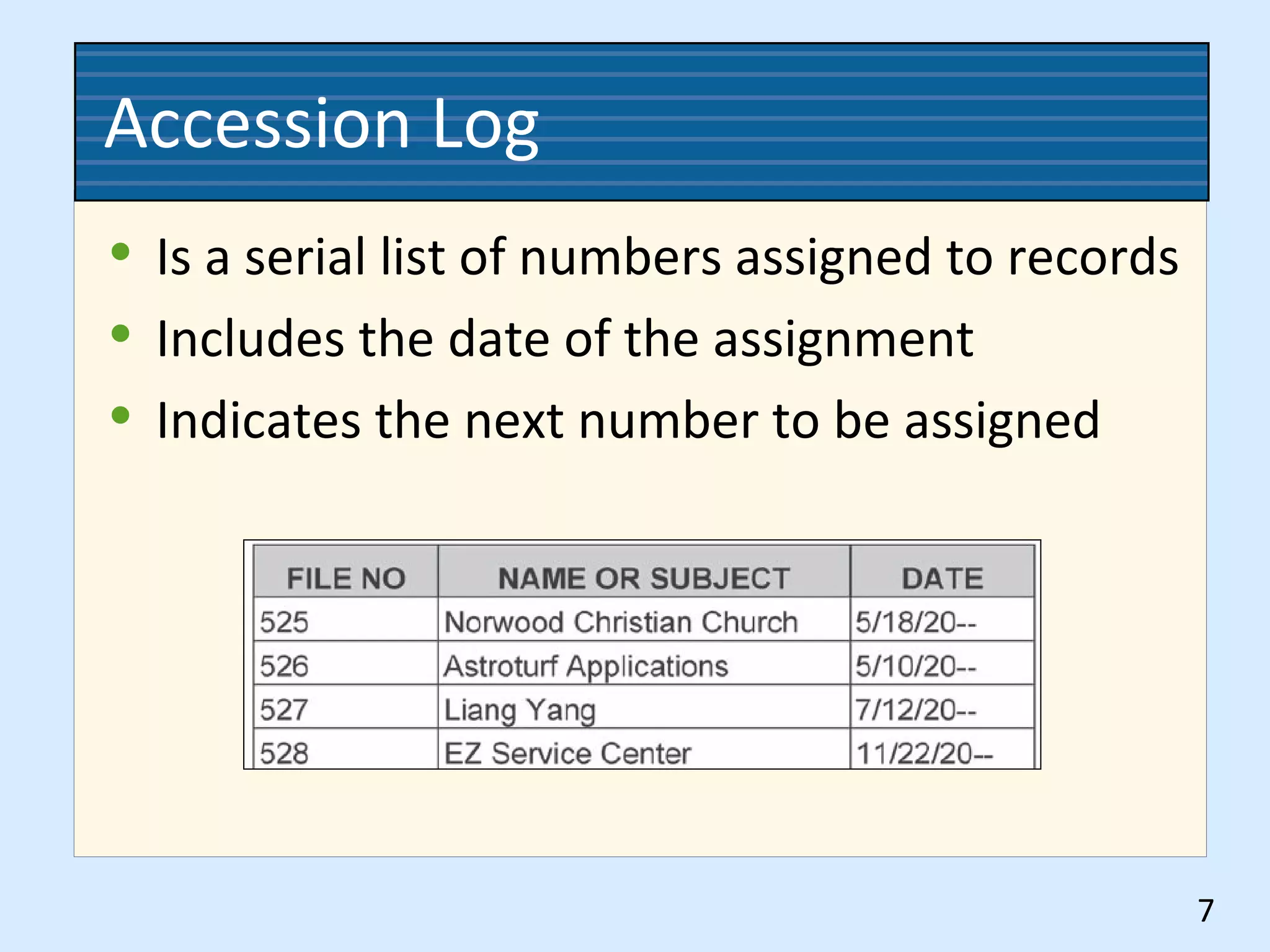
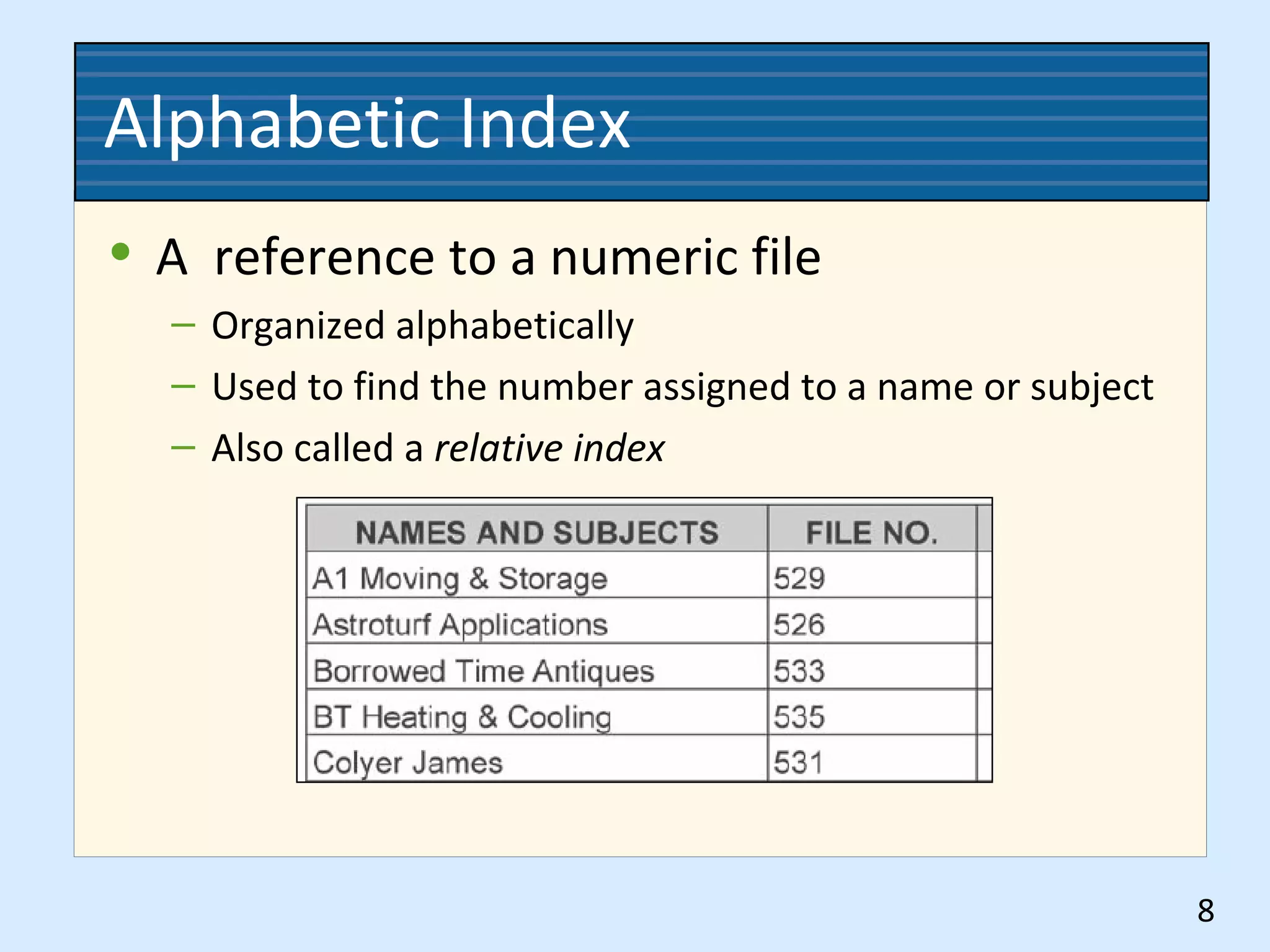
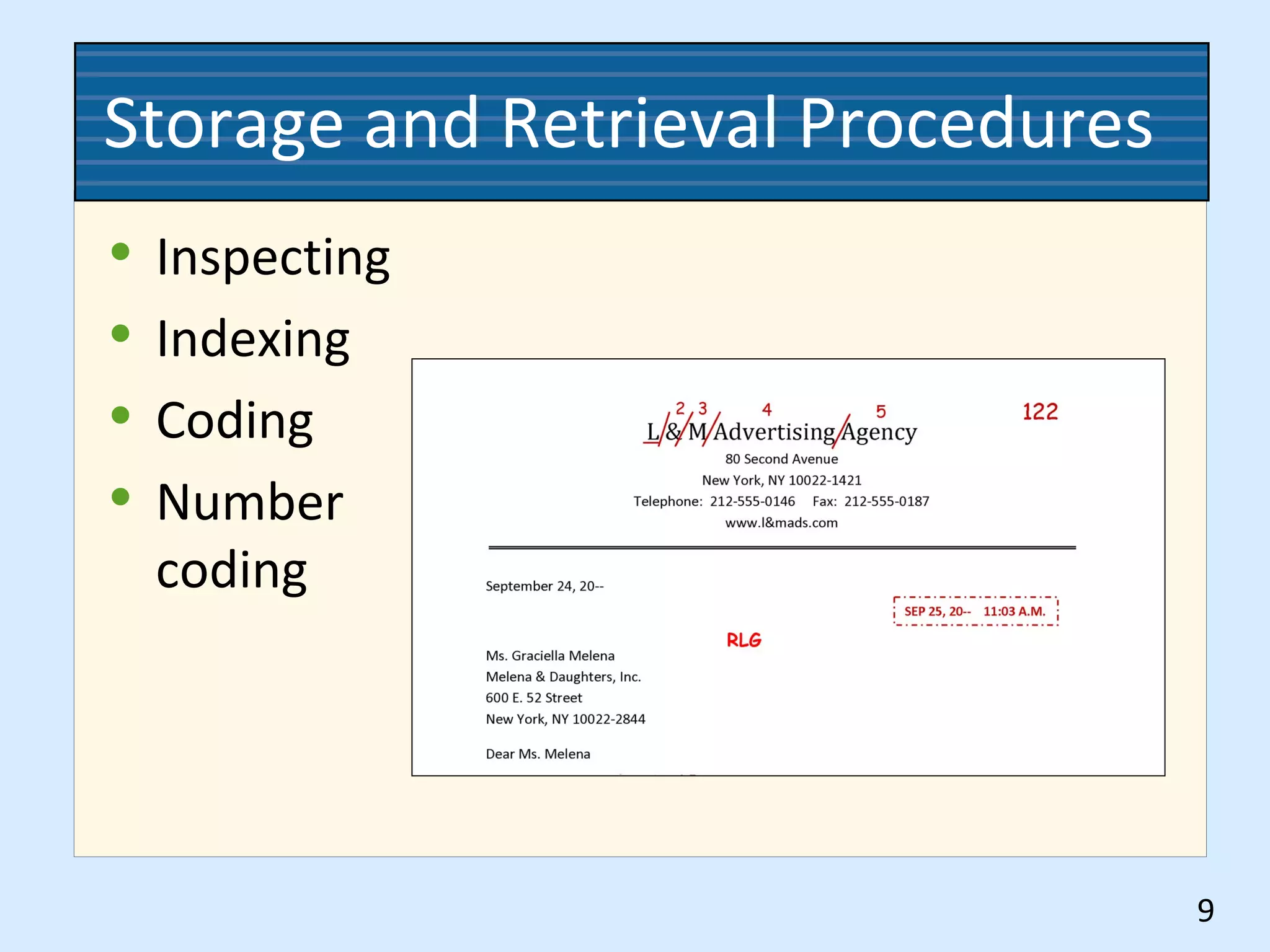
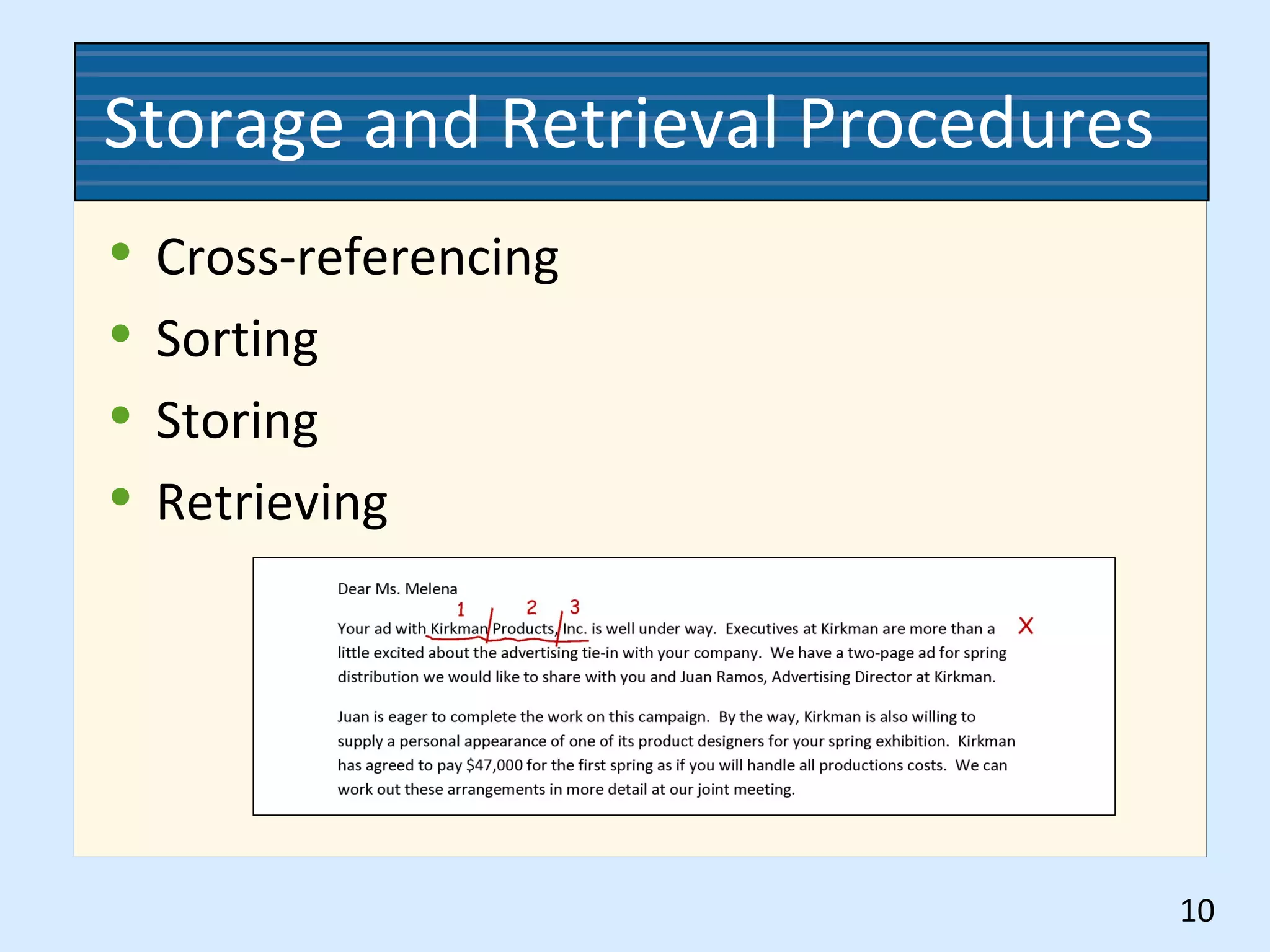
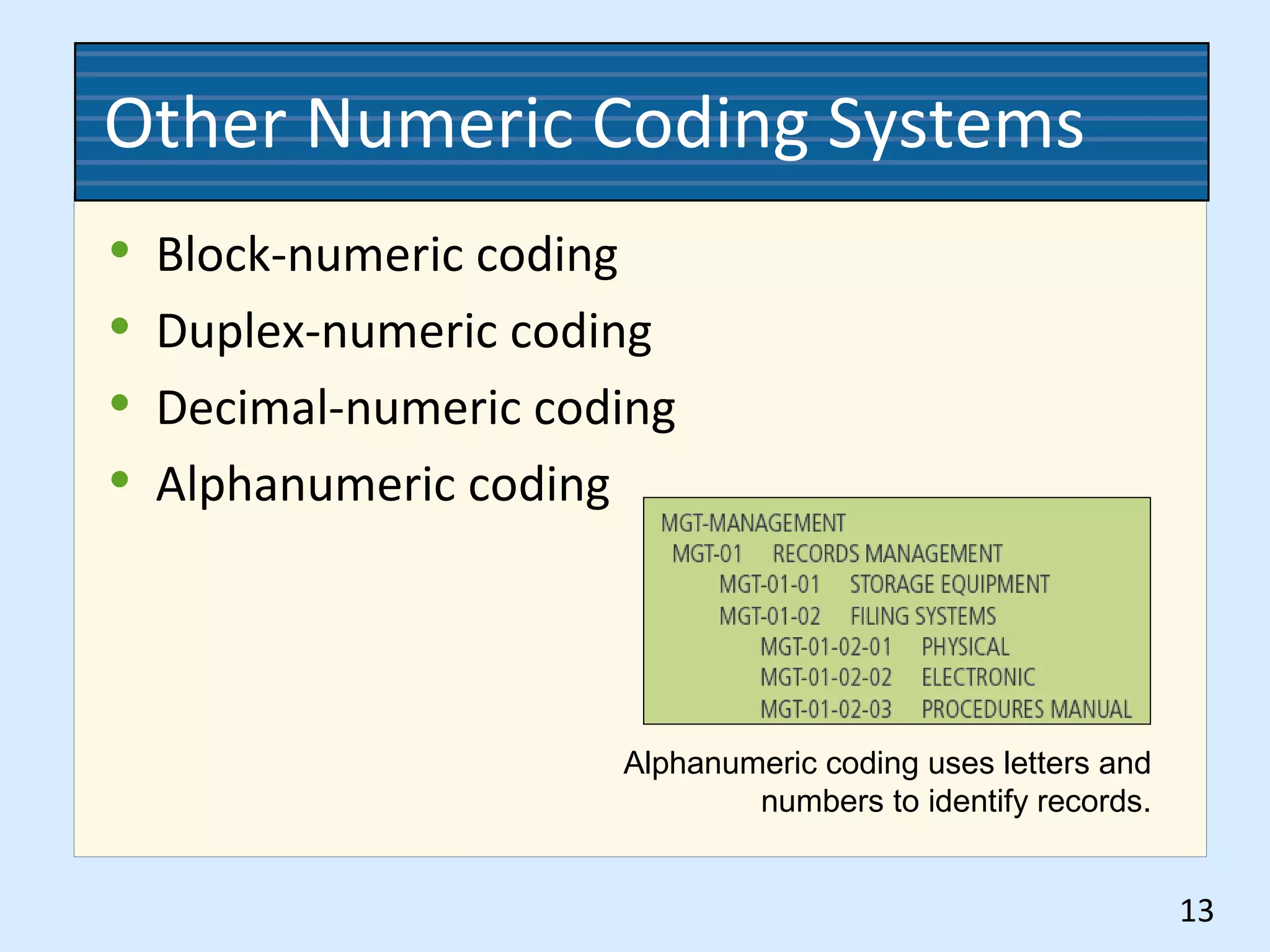
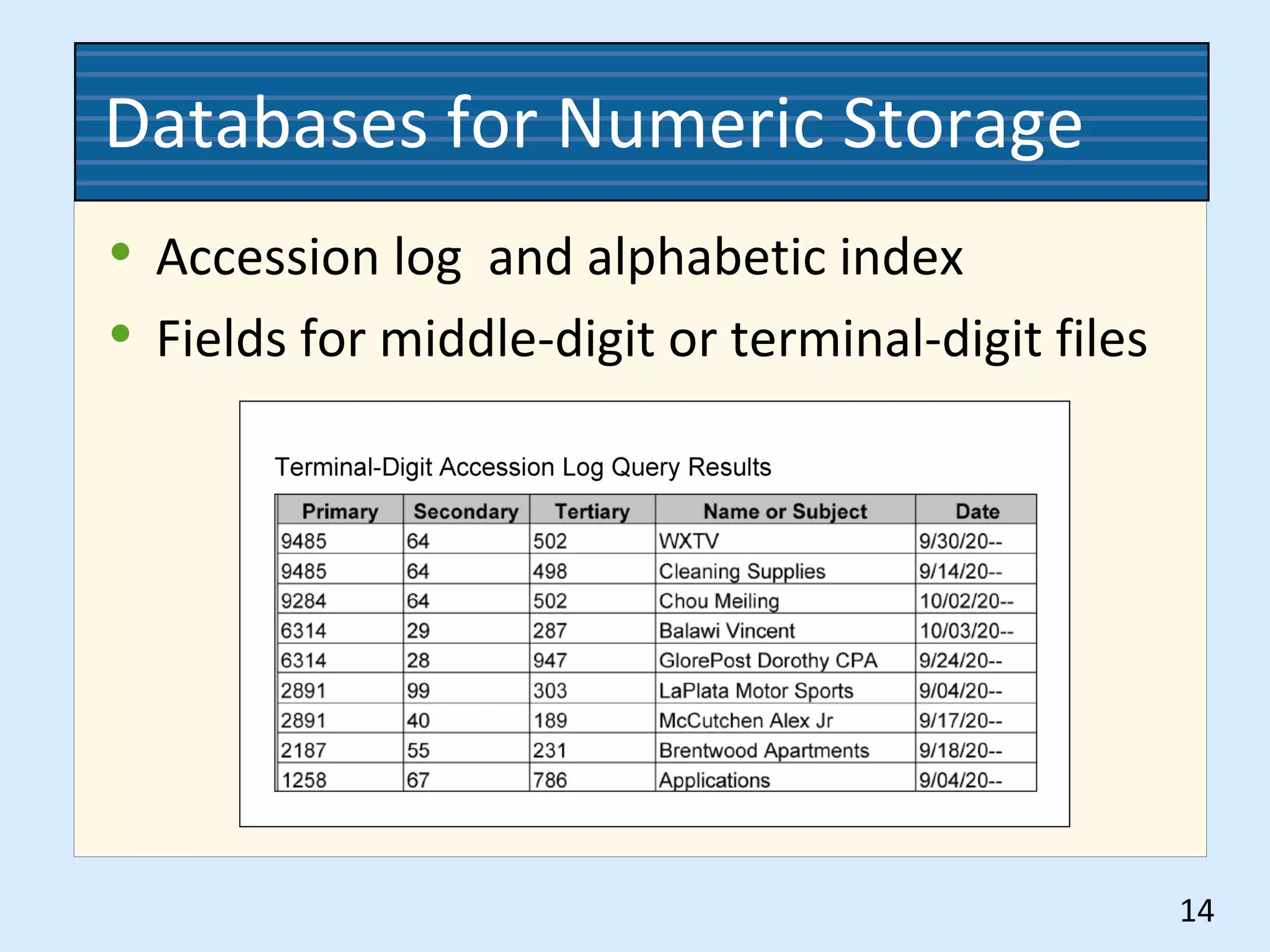
This document discusses numeric records management systems which arrange records based on assigned numbers. There are several key components of a numeric records management system: numbered guides and folders to organize the files, an accession log to track assigned numbers, and an alphabetic index to reference file numbers. Records can be stored consecutively by assigned number or using other methods like terminal-digit or middle-digit storage depending on the needs and size of the organization.