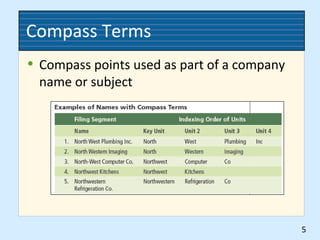
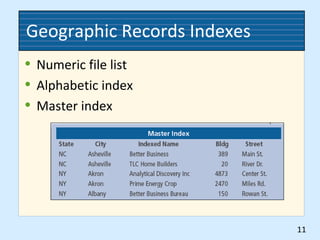
This document discusses different methods for organizing records geographically. It describes geographic records storage as a system for storing and retrieving records based on location. There are advantages like related records being filed together, but disadvantages like needing to know the location to find records. Arrangements depend on factors like the business type and how locations are referenced. Major methods include dictionary, encyclopedic, and compass term arrangements, which organize records alphabetically with guides and indexes. Effective storage and retrieval requires procedures like inspecting, indexing, cross-referencing, sorting, and different guide plans.